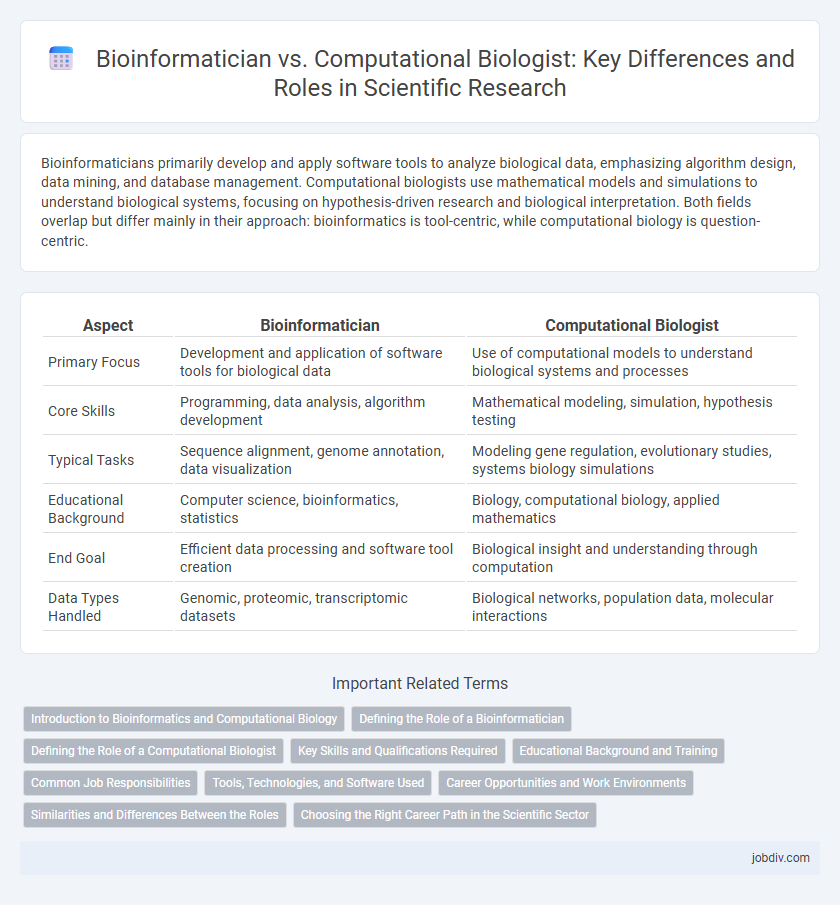
Bioinformaticians primarily develop and apply software tools to analyze biological data, emphasizing algorithm design, data mining, and database management. Computational biologists use mathematical models and simulations to understand biological systems, focusing on hypothesis-driven research and biological interpretation. Both fields overlap but differ mainly in their approach: bioinformatics is tool-centric, while computational biology is question-centric.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bioinformatician | Computational Biologist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Development and application of software tools for biological data | Use of computational models to understand biological systems and processes |
| Core Skills | Programming, data analysis, algorithm development | Mathematical modeling, simulation, hypothesis testing |
| Typical Tasks | Sequence alignment, genome annotation, data visualization | Modeling gene regulation, evolutionary studies, systems biology simulations |
| Educational Background | Computer science, bioinformatics, statistics | Biology, computational biology, applied mathematics |
| End Goal | Efficient data processing and software tool creation | Biological insight and understanding through computation |
| Data Types Handled | Genomic, proteomic, transcriptomic datasets | Biological networks, population data, molecular interactions |
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
Bioinformaticians primarily develop algorithms and software tools to manage and analyze biological data, emphasizing programming and data management skills. Computational biologists apply these tools and theoretical models to interpret biological systems, often integrating experimental data to address biological questions. Introduction to bioinformatics covers sequence analysis and database management, while computational biology involves modeling complex biological processes and systems biology simulations.
Defining the Role of a Bioinformatician
A bioinformatician specializes in developing algorithms and software tools to analyze complex biological data, bridging computer science and molecular biology. Their role involves managing large datasets, such as genomic sequences, and creating pipelines for data processing and interpretation. Unlike computational biologists, who often focus on modeling biological systems, bioinformaticians prioritize data integration and software development to support experimental research.
Defining the Role of a Computational Biologist
A Computational Biologist applies mathematical models, algorithms, and computational techniques to analyze biological data, emphasizing hypothesis-driven research in genomics, proteomics, and systems biology. Unlike bioinformaticians who primarily develop software tools and manage data pipelines, computational biologists integrate biological theory with computational methods to interpret complex biological processes. This role demands expertise in biology, computer science, and statistics to advance understanding in evolutionary biology, molecular biology, and personalized medicine.
Key Skills and Qualifications Required
Bioinformaticians require proficiency in programming languages such as Python, R, and Perl alongside expertise in database management and algorithm development to analyze large biological datasets. Computational biologists emphasize strong foundations in mathematics, statistics, and theoretical biology, enabling them to create and validate computational models of biological systems. Both roles demand advanced knowledge of molecular biology and experience with high-throughput sequencing data analysis, but computational biologists often need deeper skills in mathematical modeling and simulation techniques.
Educational Background and Training
Bioinformaticians typically have strong training in computer science, mathematics, and programming, often holding degrees in bioinformatics, computer science, or related fields. Computational biologists usually possess a deeper background in biological sciences combined with quantitative skills, often earning degrees in biology, computational biology, or biostatistics. Both fields require interdisciplinary education, but bioinformaticians prioritize algorithm development while computational biologists emphasize modeling and simulation of biological systems.
Common Job Responsibilities
Bioinformaticians primarily develop algorithms and software tools to analyze biological data, focusing on sequence alignment, data mining, and genome annotation. Computational biologists integrate mathematical modeling and statistical analysis to interpret biological systems and simulate complex biological processes. Both roles require proficiency in programming languages such as Python, R, and expertise in handling large-scale datasets and biological databases.
Tools, Technologies, and Software Used
Bioinformaticians primarily utilize software like BLAST, Bioconductor, and Python libraries such as Biopython to analyze genomic sequences and manage biological databases, focusing on data processing and algorithm development. Computational biologists employ simulation tools like GROMACS and MATLAB alongside machine learning frameworks such as TensorFlow to model biological systems and interpret complex biological interactions. Both fields rely heavily on high-performance computing environments and cloud platforms like AWS for scalable data analysis and computational efficiency.
Career Opportunities and Work Environments
Bioinformaticians often find career opportunities in pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare organizations, where they primarily develop algorithms and analyze biological data. Computational biologists generally engage in modeling biological systems and conducting hypothesis-driven research, frequently working within academia, government labs, or biotech firms. Both professions benefit from interdisciplinary collaboration, but bioinformaticians tend to have more roles focused on software development, while computational biologists emphasize theoretical and experimental integration.
Similarities and Differences Between the Roles
Bioinformaticians primarily develop algorithms and software tools to analyze biological data, while computational biologists apply mathematical models and simulations to understand biological systems. Both roles require expertise in biology, computer science, and statistics, but bioinformaticians focus more on data processing and tool creation, whereas computational biologists emphasize hypothesis-driven research and biological interpretation. Collaboration between these professionals enhances genomic analysis, systems biology, and personalized medicine advancements.
Choosing the Right Career Path in the Scientific Sector
Bioinformaticians primarily develop algorithms and software tools to analyze biological data, focusing on coding skills and database management. Computational biologists apply mathematical models and simulations to understand biological systems, emphasizing theoretical frameworks and hypothesis testing. Selecting between these careers depends on whether one prefers algorithm development and data handling or modeling and theoretical analysis within the scientific domain.
Bioinformatician vs Computational Biologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com