Botanists study the structure, function, and classification of plants, exploring their growth, reproduction, and ecology to understand plant life in various environments. Plant pathologists specialize in diagnosing and managing plant diseases caused by pathogens like fungi, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes, aiming to protect crops and natural vegetation. Both fields contribute to agriculture and environmental science, but botanists emphasize plant biology while plant pathologists focus on plant health and disease prevention.
Table of Comparison
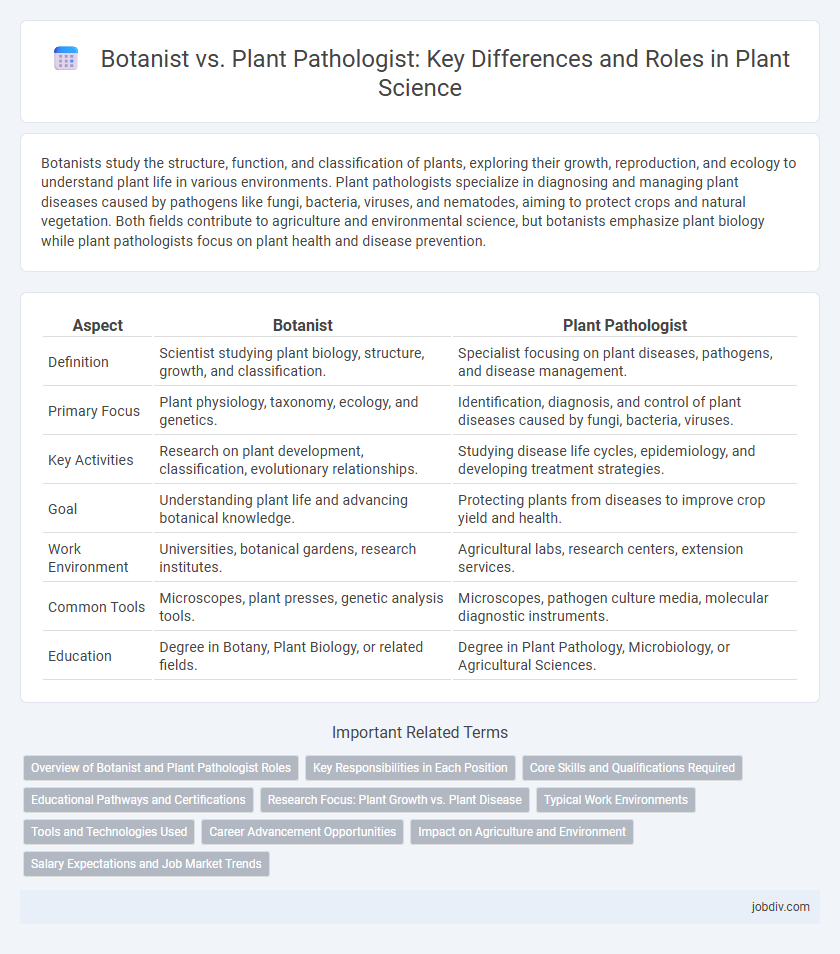
| Aspect | Botanist | Plant Pathologist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scientist studying plant biology, structure, growth, and classification. | Specialist focusing on plant diseases, pathogens, and disease management. |
| Primary Focus | Plant physiology, taxonomy, ecology, and genetics. | Identification, diagnosis, and control of plant diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, viruses. |
| Key Activities | Research on plant development, classification, evolutionary relationships. | Studying disease life cycles, epidemiology, and developing treatment strategies. |
| Goal | Understanding plant life and advancing botanical knowledge. | Protecting plants from diseases to improve crop yield and health. |
| Work Environment | Universities, botanical gardens, research institutes. | Agricultural labs, research centers, extension services. |
| Common Tools | Microscopes, plant presses, genetic analysis tools. | Microscopes, pathogen culture media, molecular diagnostic instruments. |
| Education | Degree in Botany, Plant Biology, or related fields. | Degree in Plant Pathology, Microbiology, or Agricultural Sciences. |
Overview of Botanist and Plant Pathologist Roles
Botanists primarily study plant biology, including anatomy, physiology, genetics, and ecology, to understand plant life and its interactions with the environment. Plant pathologists specialize in diagnosing, managing, and researching plant diseases caused by pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes. Both roles contribute to agriculture and ecosystem health, with botanists focusing on fundamental plant science and plant pathologists addressing disease prevention and crop protection.
Key Responsibilities in Each Position
Botanists primarily focus on studying plant physiology, genetics, and ecology to understand plant life cycles and environmental interactions, often conducting field research and laboratory experiments. Plant pathologists specialize in diagnosing, managing, and preventing plant diseases by identifying pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, and viruses, and developing disease-resistant crops or treatment strategies. Both roles require expertise in plant biology, but botanists emphasize fundamental plant science while plant pathologists concentrate on plant health and disease control.
Core Skills and Qualifications Required
Botanists require strong expertise in plant biology, taxonomy, and ecology, with skills in field research, laboratory analysis, and data interpretation using biostatistics. Plant pathologists specialize in diagnosing and managing plant diseases, necessitating proficiency in microbiology, pathology, and molecular techniques, alongside experience in disease control methods and resistant crop breeding. Both professions typically demand advanced degrees in biological sciences, with plant pathologists often needing additional training in plant disease management and diagnostic tools.
Educational Pathways and Certifications
Botanists typically pursue a bachelor's degree in botany or plant sciences, advancing to master's or doctoral programs for research or academic roles, while certifications such as Certified Professional Botanist (CPB) enhance professional credibility. Plant pathologists often follow a similar educational trajectory but specialize with degrees in plant pathology or microbiology, emphasizing disease diagnostics and management, with certifications like the American Society for Microbiology's plant pathologist credential validating their expertise. Both fields demand rigorous scientific training, but plant pathologists focus more on disease mechanisms, requiring additional laboratory skills and certifications tailored to plant disease control.
Research Focus: Plant Growth vs. Plant Disease
Botanists primarily research plant growth, physiology, and ecology, investigating processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and reproductive mechanisms to understand overall plant development. Plant pathologists concentrate on identifying, diagnosing, and managing plant diseases caused by pathogens like fungi, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes, with an emphasis on disease resistance and prevention strategies. Both fields employ molecular biology, genetics, and field studies but differ in their core research objectives--botanists focus on healthy plant functions while pathologists aim to mitigate biotic stress factors impacting plants.
Typical Work Environments
Botanists primarily conduct research in laboratories, greenhouses, botanical gardens, and natural habitats to study plant biology, ecology, and physiology. Plant pathologists typically work in similar settings but also spend significant time in agricultural fields, nurseries, and food production facilities to diagnose and manage plant diseases. Both professions collaborate with academic institutions, government agencies, and agricultural organizations to support plant health and sustainability initiatives.
Tools and Technologies Used
Botanists primarily utilize microscopy, genetic sequencing, and phenotyping software to study plant biology, structure, and development. Plant pathologists employ advanced diagnostic tools such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), and remote sensing technologies to detect and analyze plant diseases. Both professions leverage bioinformatics databases and geographic information systems (GIS) to support research and field data analysis.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Botanists often advance their careers through research roles in academia, government agencies, and environmental organizations, focusing on plant biology, ecology, and conservation. Plant pathologists have specialized opportunities in agricultural research, crop disease management, and biotechnology firms, where expertise in diagnosing and controlling plant diseases is critical. Both careers offer pathways to leadership positions, grant management, and interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing plant science and agricultural sustainability.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment
Botanists contribute to agriculture and environmental sustainability by studying plant biology, genetics, and ecology to improve crop yields and biodiversity conservation. Plant pathologists specialize in diagnosing and managing plant diseases, significantly reducing crop losses and enhancing food security. Both fields collaboratively influence sustainable farming practices and ecosystem health by advancing plant resilience and disease control.
Salary Expectations and Job Market Trends
Botanists earn an average annual salary of $70,000, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade, reflecting steady demand in environmental and agricultural research. Plant pathologists typically command higher salaries around $75,000 due to specialized expertise in diagnosing and managing plant diseases, with a job growth rate near 6% driven by increasing agricultural challenges. Both professions benefit from expanding opportunities in biotechnology and sustainable agriculture, but plant pathologists often have a competitive edge in funding and advanced research roles.
Botanist vs Plant Pathologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com