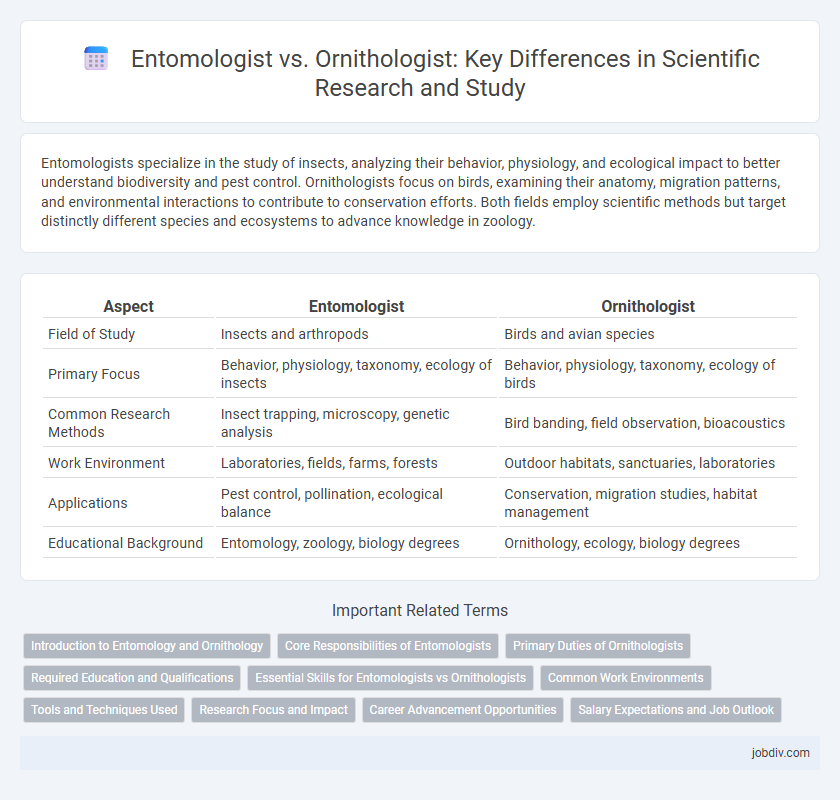
Entomologists specialize in the study of insects, analyzing their behavior, physiology, and ecological impact to better understand biodiversity and pest control. Ornithologists focus on birds, examining their anatomy, migration patterns, and environmental interactions to contribute to conservation efforts. Both fields employ scientific methods but target distinctly different species and ecosystems to advance knowledge in zoology.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Entomologist | Ornithologist |
|---|---|---|
| Field of Study | Insects and arthropods | Birds and avian species |
| Primary Focus | Behavior, physiology, taxonomy, ecology of insects | Behavior, physiology, taxonomy, ecology of birds |
| Common Research Methods | Insect trapping, microscopy, genetic analysis | Bird banding, field observation, bioacoustics |
| Work Environment | Laboratories, fields, farms, forests | Outdoor habitats, sanctuaries, laboratories |
| Applications | Pest control, pollination, ecological balance | Conservation, migration studies, habitat management |
| Educational Background | Entomology, zoology, biology degrees | Ornithology, ecology, biology degrees |
Introduction to Entomology and Ornithology
Entomologists specialize in the study of insects, focusing on their biology, behavior, ecology, and taxonomy, which plays a critical role in agriculture and biodiversity research. Ornithologists concentrate on birds, investigating avian physiology, migration patterns, and conservation efforts, contributing vital insights to ecosystems and environmental changes. Both fields employ advanced scientific methodologies such as field observations, genetic analysis, and ecological modeling to enhance understanding of species diversity and their environmental interactions.
Core Responsibilities of Entomologists
Entomologists specialize in the study of insects, focusing on their behavior, life cycle, ecology, and impact on the environment and human activities. Their core responsibilities include conducting field research to collect insect specimens, analyzing data to understand insect populations and their interactions with ecosystems, and developing pest control methods to mitigate agricultural damage or disease transmission. They frequently collaborate with agricultural experts, public health officials, and conservationists to apply their findings in practical and environmental management contexts.
Primary Duties of Ornithologists
Ornithologists primarily study bird species, focusing on their behavior, physiology, and habitats to understand avian ecology and conservation. They conduct field observations, collect data on migration patterns, and analyze vocalizations to monitor bird populations. Their research supports biodiversity preservation and informs environmental policies related to bird species protection.
Required Education and Qualifications
Entomologists typically require a bachelor's degree in entomology or biology, with advanced roles demanding a master's or Ph.D. specializing in insect science. Ornithologists pursue a similar educational path, often obtaining degrees in zoology or wildlife biology, with an emphasis on avian studies at the graduate level. Both professions necessitate strong research skills, internships, and fieldwork experience to excel in scientific investigation and environmental conservation.
Essential Skills for Entomologists vs Ornithologists
Entomologists require expertise in insect identification, taxonomy, and the analysis of arthropod behavior, often utilizing microscopy and field sampling techniques to study ecological interactions. Ornithologists focus on avian biology, necessitating skills in bird banding, vocalization analysis, and habitat assessment to monitor bird populations and migration patterns. Both professions demand proficiency in data collection, statistical analysis, and proficiency with geographic information systems (GIS) for environmental research.
Common Work Environments
Entomologists primarily conduct research in laboratories, forests, and agricultural fields to study insect behavior, physiology, and ecology, often collaborating with environmental agencies or agricultural companies. Ornithologists frequently work in natural habitats such as wetlands, forests, and grasslands, as well as research institutions and wildlife reserves, focusing on bird species identification, migration patterns, and conservation efforts. Both professions engage in fieldwork and data collection, but entomologists tend to have a broader range of microhabitats, while ornithologists specialize in avian ecosystems.
Tools and Techniques Used
Entomologists utilize tools such as sweep nets, aspirators, and microscopes to collect and study insects, employing techniques like pitfall trapping and malaise traps for sampling insect populations. Ornithologists rely on binoculars, mist nets, and bird banding equipment, using point counts and audio recordings to monitor bird behavior and populations. Both specialists integrate GPS technology and digital imaging for precise data collection and analysis in their respective fields.
Research Focus and Impact
Entomologists specialize in studying insects, exploring their behavior, physiology, and ecological roles to inform pest control, biodiversity conservation, and agricultural productivity. Ornithologists focus on bird species' anatomy, migration patterns, and communication, contributing to habitat preservation and climate change research. Both fields impact environmental science by advancing knowledge critical for ecosystem management and species protection.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Entomologists specializing in insect biology and pest control have diverse career advancement opportunities in agricultural research, environmental consulting, and pharmaceutical industries, often progressing to lead research projects or academic positions. Ornithologists focusing on bird behavior, conservation, and ecology frequently advance through roles in wildlife management, environmental policy, and academia, with potential to become senior researchers or conservation directors. Both fields offer progression through specialized expertise, grant acquisition, and publication impact, influencing career trajectories in scientific research and applied environmental science.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Entomologists, specializing in the study of insects, typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $50,000 to $80,000, with variations depending on experience and research funding. Ornithologists, experts in bird biology, often have salaries in a similar range but may experience higher demand due to growing conservation efforts, influencing job outlook positively. Both fields present steady job growth, projected at around 5% over the next decade, driven by environmental research and habitat preservation initiatives.
Entomologist vs Ornithologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com