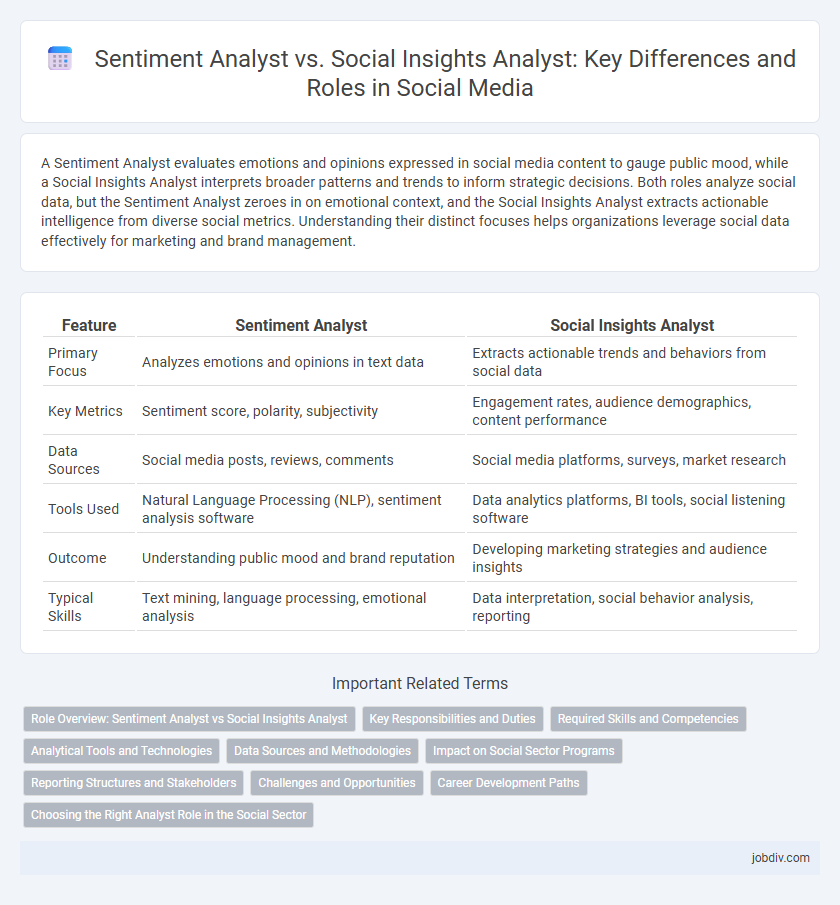
A Sentiment Analyst evaluates emotions and opinions expressed in social media content to gauge public mood, while a Social Insights Analyst interprets broader patterns and trends to inform strategic decisions. Both roles analyze social data, but the Sentiment Analyst zeroes in on emotional context, and the Social Insights Analyst extracts actionable intelligence from diverse social metrics. Understanding their distinct focuses helps organizations leverage social data effectively for marketing and brand management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sentiment Analyst | Social Insights Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Analyzes emotions and opinions in text data | Extracts actionable trends and behaviors from social data |
| Key Metrics | Sentiment score, polarity, subjectivity | Engagement rates, audience demographics, content performance |
| Data Sources | Social media posts, reviews, comments | Social media platforms, surveys, market research |
| Tools Used | Natural Language Processing (NLP), sentiment analysis software | Data analytics platforms, BI tools, social listening software |
| Outcome | Understanding public mood and brand reputation | Developing marketing strategies and audience insights |
| Typical Skills | Text mining, language processing, emotional analysis | Data interpretation, social behavior analysis, reporting |
Role Overview: Sentiment Analyst vs Social Insights Analyst
Sentiment Analysts specialize in interpreting emotional tones and opinions from social media data using natural language processing and machine learning techniques. Social Insights Analysts focus on broader social trends and consumer behavior by analyzing demographic data and engagement metrics across multiple platforms. Both roles leverage analytics to inform strategic decisions, but Sentiment Analysts emphasize emotional context while Social Insights Analysts prioritize behavioral patterns and market insights.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Sentiment Analysts primarily focus on interpreting emotions and opinions expressed in social media data to gauge public mood and brand perception. Social Insights Analysts analyze broader social trends and patterns by combining qualitative and quantitative data to provide strategic recommendations for marketing and product development. Both roles require expertise in data analysis and social media monitoring tools, but Sentiment Analysts emphasize emotional context while Social Insights Analysts prioritize actionable business intelligence.
Required Skills and Competencies
A Sentiment Analyst requires strong skills in natural language processing, text analytics, and emotion detection algorithms to accurately interpret customer opinions and emotions from social media data. A Social Insights Analyst must excel in data visualization, qualitative research, and trend analysis, focusing on extracting actionable business intelligence and consumer behavior patterns. Both roles demand proficiency in social media monitoring tools and a solid understanding of market research methodologies.
Analytical Tools and Technologies
Sentiment Analysts primarily utilize natural language processing (NLP) tools and machine learning algorithms to interpret emotions and opinions from social media data, leveraging platforms like IBM Watson and Lexalytics for real-time sentiment scoring. Social Insights Analysts integrate advanced analytics software such as Tableau, Power BI, and social listening tools like Brandwatch and Sprout Social to extract actionable trends and consumer behavior patterns from large datasets. Both roles depend heavily on data visualization and statistical analysis technologies to transform raw data into strategic social intelligence.
Data Sources and Methodologies
Sentiment Analysts primarily leverage natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze social media posts, customer reviews, and survey responses, extracting emotional tone from unstructured text data. Social Insights Analysts employ a broader range of methodologies, combining quantitative data from social media metrics, demographic information, and user engagement patterns with qualitative analysis to uncover underlying trends and audience behaviors. Data sources for Sentiment Analysts often center on textual inputs, while Social Insights Analysts integrate multiple data streams, including social listening tools and analytics platforms, to deliver comprehensive market intelligence.
Impact on Social Sector Programs
Sentiment Analysts enhance social sector programs by providing real-time emotional data that helps organizations tailor communication strategies to community needs. Social Insights Analysts deliver deeper contextual understanding through comprehensive data analysis, driving program improvements and policy development. Combining both roles leads to more effective interventions and increased community engagement in social initiatives.
Reporting Structures and Stakeholders
Sentiment Analysts typically report to marketing or customer experience teams, providing real-time emotional data for campaign adjustments. Social Insights Analysts often align with product management or strategic planning departments, delivering in-depth trend analysis to guide long-term decisions. Key stakeholders for both roles include brand managers, digital strategists, and executive leadership seeking actionable intelligence to enhance customer engagement and brand positioning.
Challenges and Opportunities
Sentiment Analysts face challenges in accurately interpreting nuanced emotions across diverse social media platforms, requiring sophisticated natural language processing tools to enhance sentiment detection. Social Insights Analysts encounter opportunities to leverage comprehensive data integration, enabling deeper understanding of consumer behaviors and trends beyond sentiment alone. Both roles can address challenges related to data volume and evolving language use, presenting opportunities for innovation in artificial intelligence and real-time analytics.
Career Development Paths
Sentiment Analysts specialize in interpreting emotional tone from social media data, honing skills in natural language processing and machine learning to enhance brand reputation management. Social Insights Analysts leverage quantitative and qualitative data to uncover consumer behavior trends, advancing to strategic roles in marketing analytics or consumer research. Career development for Sentiment Analysts often progresses towards data science, while Social Insights Analysts may evolve into roles focusing on business intelligence and strategic decision-making.
Choosing the Right Analyst Role in the Social Sector
Sentiment Analysts specialize in interpreting emotions and opinions expressed in social media data, enabling organizations to gauge public mood and customer satisfaction effectively. Social Insights Analysts focus on broader trends and behavioral patterns by analyzing diverse social metrics to inform strategic decision-making and campaign optimization. Selecting the right analyst role depends on whether the priority lies in emotional sentiment extraction or comprehensive social behavior analysis for targeted social sector initiatives.
Sentiment Analyst vs Social Insights Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com