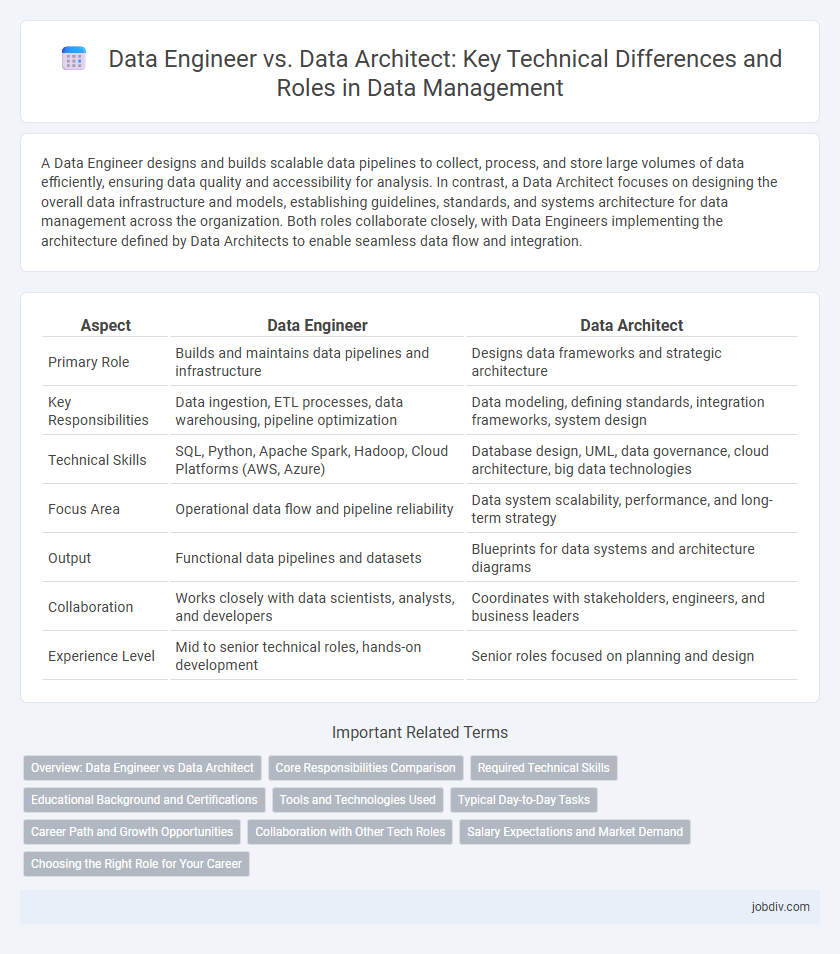
A Data Engineer designs and builds scalable data pipelines to collect, process, and store large volumes of data efficiently, ensuring data quality and accessibility for analysis. In contrast, a Data Architect focuses on designing the overall data infrastructure and models, establishing guidelines, standards, and systems architecture for data management across the organization. Both roles collaborate closely, with Data Engineers implementing the architecture defined by Data Architects to enable seamless data flow and integration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Data Engineer | Data Architect |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Builds and maintains data pipelines and infrastructure | Designs data frameworks and strategic architecture |
| Key Responsibilities | Data ingestion, ETL processes, data warehousing, pipeline optimization | Data modeling, defining standards, integration frameworks, system design |
| Technical Skills | SQL, Python, Apache Spark, Hadoop, Cloud Platforms (AWS, Azure) | Database design, UML, data governance, cloud architecture, big data technologies |
| Focus Area | Operational data flow and pipeline reliability | Data system scalability, performance, and long-term strategy |
| Output | Functional data pipelines and datasets | Blueprints for data systems and architecture diagrams |
| Collaboration | Works closely with data scientists, analysts, and developers | Coordinates with stakeholders, engineers, and business leaders |
| Experience Level | Mid to senior technical roles, hands-on development | Senior roles focused on planning and design |
Overview: Data Engineer vs Data Architect
Data Engineers specialize in designing, building, and maintaining data pipelines that ensure efficient data flow and storage across systems, focusing on the implementation of ETL processes and data warehousing solutions. Data Architects concentrate on creating the overall data strategy, architecture frameworks, and governance policies to structure and standardize data assets for effective use across the organization. Both roles collaborate closely to enable robust data infrastructure, with engineers executing technical solutions and architects defining high-level data models and integration patterns.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Data Engineers primarily focus on designing, building, and maintaining data pipelines to ensure reliable data flow and transformation, while Data Architects concentrate on creating the overall data strategy, modeling, and integration across systems. Data Engineers handle ETL processes, data warehousing, and optimizing database performance, whereas Data Architects develop blueprints for data management frameworks aligning with business objectives. Both roles collaborate closely, with Data Architects defining data standards and governance, and Data Engineers implementing scalable infrastructure to support analytics and reporting.
Required Technical Skills
Data Engineers require proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Java, and SQL, alongside expertise in data pipeline frameworks like Apache Spark and Kafka for efficient data processing. Data Architects demand strong skills in database design, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure), and data modeling tools to structure scalable and secure data systems. Both roles benefit from a solid understanding of ETL processes, big data technologies, and data warehousing solutions such as Snowflake or Redshift.
Educational Background and Certifications
Data engineers typically possess a background in computer science, software engineering, or information technology, with proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Java, and SQL, alongside certifications like Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer and Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Engineer Associate. Data architects often hold advanced degrees in computer science or data management and pursue certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect, TOGAF, and Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP) to demonstrate expertise in designing scalable data infrastructure. Both roles require continuous learning, but data architects emphasize strategic design and governance, while data engineers focus more on implementation and optimization skills.
Tools and Technologies Used
Data Engineers primarily work with ETL tools like Apache NiFi, Apache Airflow, and frameworks such as Apache Spark and Hadoop to build data pipelines and manage data ingestion. Data Architects focus on database design and modeling tools like ER/Studio and ERwin, employing technologies such as SQL Server, Oracle, and cloud platforms like AWS Redshift or Google BigQuery for data warehousing. Both roles utilize programming languages like Python and SQL, but Data Engineers emphasize automation and real-time processing, while Data Architects ensure scalable and optimized data infrastructure.
Typical Day-to-Day Tasks
Data Engineers focus on building, maintaining, and optimizing data pipelines, ensuring data is clean, accessible, and integrated from various sources. Data Architects design and implement complex data frameworks, create data models, and establish database standards to support scalable data management. Daily duties of Data Engineers involve coding, ETL process management, and monitoring data flows, while Data Architects concentrate on strategic planning, data schema design, and coordinating with stakeholders for system architecture alignment.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Data Engineers typically focus on building and maintaining data pipelines, ensuring data accessibility, and optimizing ETL processes, which provides a strong foundation in technical skills essential for data infrastructure. Data Architects design and manage complex data frameworks and strategies, emphasizing data modeling, governance, and integration to support enterprise-wide analytics. Career growth often moves from Data Engineer roles toward Data Architect positions as professionals expand their expertise in data strategy, scalability, and high-level system design.
Collaboration with Other Tech Roles
Data Engineers collaborate closely with software developers and data scientists to ensure efficient data pipeline creation and seamless data integration. Data Architects work alongside business analysts and IT managers to design robust data models and establish scalable data infrastructure. Their combined efforts facilitate effective data management and support strategic decision-making across the organization.
Salary Expectations and Market Demand
Data Engineers command competitive salaries averaging $110,000 to $140,000 annually, driven by strong demand for expertise in ETL processes and data pipeline development. Data Architects typically earn between $120,000 and $160,000, reflecting their strategic role in designing scalable data frameworks and ensuring data integrity across systems. Market trends indicate increasing demand for both roles, with Data Architects prioritized in enterprise environments for their ability to align data strategy with business goals.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career
Data Engineers focus on building, maintaining, and optimizing data pipelines and infrastructure to ensure efficient data flow, while Data Architects design and plan the overall data framework and strategy to support business goals. Choosing the right role depends on your strengths in hands-on engineering tasks versus strategic data modeling and architecture. Career growth in Data Engineering often leads to specialization in big data and cloud platforms, whereas Data Architecture offers paths towards enterprise data strategy and governance leadership.
Data Engineer vs Data Architect Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com