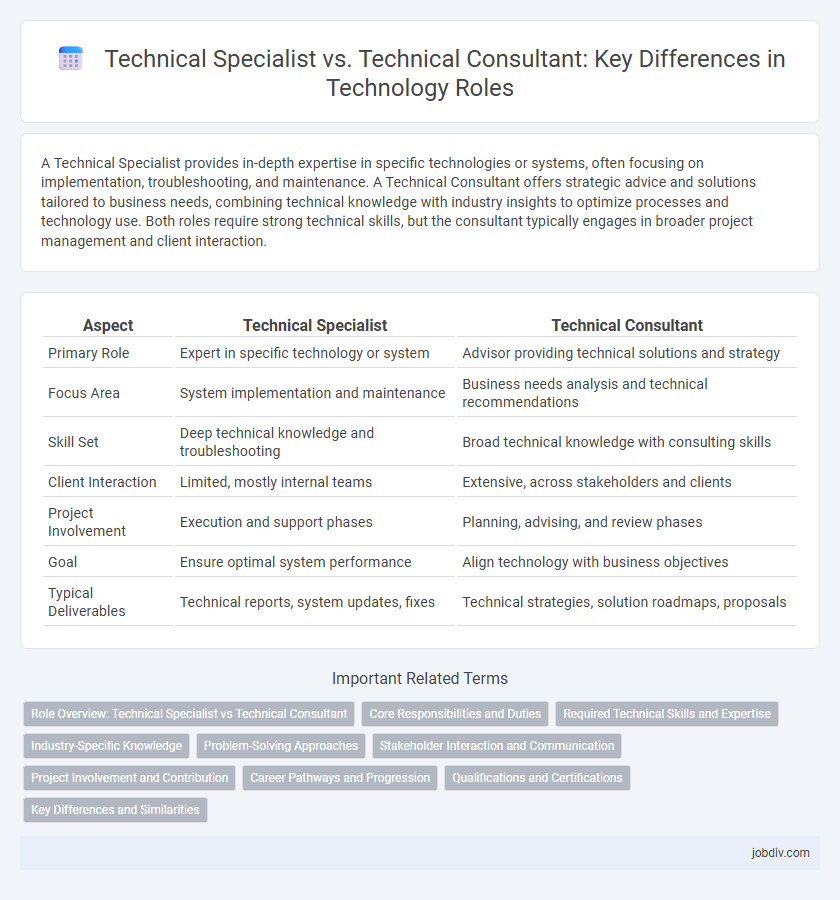
A Technical Specialist provides in-depth expertise in specific technologies or systems, often focusing on implementation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. A Technical Consultant offers strategic advice and solutions tailored to business needs, combining technical knowledge with industry insights to optimize processes and technology use. Both roles require strong technical skills, but the consultant typically engages in broader project management and client interaction.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Technical Specialist | Technical Consultant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Expert in specific technology or system | Advisor providing technical solutions and strategy |
| Focus Area | System implementation and maintenance | Business needs analysis and technical recommendations |
| Skill Set | Deep technical knowledge and troubleshooting | Broad technical knowledge with consulting skills |
| Client Interaction | Limited, mostly internal teams | Extensive, across stakeholders and clients |
| Project Involvement | Execution and support phases | Planning, advising, and review phases |
| Goal | Ensure optimal system performance | Align technology with business objectives |
| Typical Deliverables | Technical reports, system updates, fixes | Technical strategies, solution roadmaps, proposals |
Role Overview: Technical Specialist vs Technical Consultant
A Technical Specialist focuses on in-depth expertise in specific technologies, providing hands-on support, troubleshooting, and implementation within projects. A Technical Consultant offers broader strategic guidance, analyzing business needs to recommend and design technical solutions that align with organizational goals. Both roles require strong technical knowledge, but the Specialist emphasizes execution while the Consultant prioritizes advisory and planning functions.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Technical Specialists primarily focus on hands-on implementation, troubleshooting, and maintaining specific technologies or systems within an organization, ensuring optimal performance and adherence to technical standards. In contrast, Technical Consultants provide expert advice, strategic planning, and customized solutions to clients or businesses, leveraging broad industry knowledge to address complex challenges and improve technology adoption. Both roles require deep technical expertise, but Specialists emphasize operational tasks while Consultants drive strategic technology initiatives.
Required Technical Skills and Expertise
Technical Specialists possess in-depth expertise in specific technologies or systems, often requiring advanced proficiency in areas like network architecture, software development, or cybersecurity protocols. Technical Consultants combine broad industry knowledge with strong analytical skills to assess client needs, design solutions, and ensure integration across multiple platforms, emphasizing project management and communication abilities. Both roles demand continuous learning, but Specialists focus more on hands-on technical problem-solving, while Consultants prioritize strategic technical advisory and implementation planning.
Industry-Specific Knowledge
Technical Specialists possess deep, industry-specific expertise that enables them to solve complex technical problems within specialized sectors such as healthcare, finance, or manufacturing. Technical Consultants leverage broad industry knowledge to advise organizations on strategic technology implementations and best practices tailored to their unique business challenges. Both roles require a solid understanding of industry standards and regulations, but Specialists often focus more on hands-on technical execution, while Consultants emphasize advisory and integration services.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Technical Specialists apply deep expertise in specific technologies to identify and resolve complex system issues through hands-on troubleshooting and direct intervention. Technical Consultants leverage broad industry knowledge and strategic analysis to diagnose problems and recommend scalable solutions aligned with business objectives. Both roles emphasize problem-solving, but Specialists focus on technical execution while Consultants prioritize advisory and strategic guidance.
Stakeholder Interaction and Communication
Technical Specialists possess deep expertise in specific technologies, enabling precise communication with development teams and internal stakeholders to resolve complex technical issues. Technical Consultants prioritize clear and strategic communication with diverse external stakeholders, including clients and cross-functional teams, to align technical solutions with business objectives. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but consultants emphasize translating technical details into accessible language for varied audiences.
Project Involvement and Contribution
Technical Specialists deliver deep expertise in specific technologies, directly managing technical tasks within projects to ensure system functionality and performance. Technical Consultants provide strategic guidance by analyzing project requirements, recommending solutions, and overseeing implementation to align technology with business objectives. Both roles contribute to project success, but Specialists focus on hands-on execution, while Consultants emphasize planning and advisory functions.
Career Pathways and Progression
Technical Specialists typically advance by deepening expertise in specific technologies or systems, often moving towards senior specialist or technical architect roles. Technical Consultants progress by broadening their scope into client management, project leadership, and strategic advisory positions, frequently evolving into senior consultants or solution architects. Career pathways for Technical Specialists emphasize technical mastery, while Technical Consultants focus on combining technical knowledge with business acumen to drive organizational impact.
Qualifications and Certifications
Technical Specialists typically hold certifications such as CompTIA A+, Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE), or Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA), emphasizing hands-on expertise in specific technologies. Technical Consultants often possess advanced qualifications like Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Project Management Professional (PMP), reflecting a blend of technical knowledge and strategic advisory skills. Both roles may require industry-specific certifications, but Consultants generally have broader credentials aligned with problem-solving and client engagement.
Key Differences and Similarities
Technical Specialists possess deep expertise in specific technologies or systems, focusing on implementation, troubleshooting, and support to optimize performance. Technical Consultants offer broader strategic advice, assessing client needs and designing tailored solutions to enhance business processes and technology integration. Both roles require strong technical knowledge and problem-solving skills but differ in scope--Specialists emphasize hands-on technical execution, while Consultants prioritize strategic planning and client engagement.
Technical Specialist vs Technical Consultant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com