Technical trainers focus on skill development by delivering hands-on, practical sessions tailored to specific job roles, ensuring learners acquire competencies applicable to real-world scenarios. Technical instructors emphasize theoretical knowledge, providing foundational principles and detailed explanations of technical concepts that build a comprehensive understanding. Both roles complement each other by combining practical application with conceptual learning to enhance overall technical proficiency.
Table of Comparison
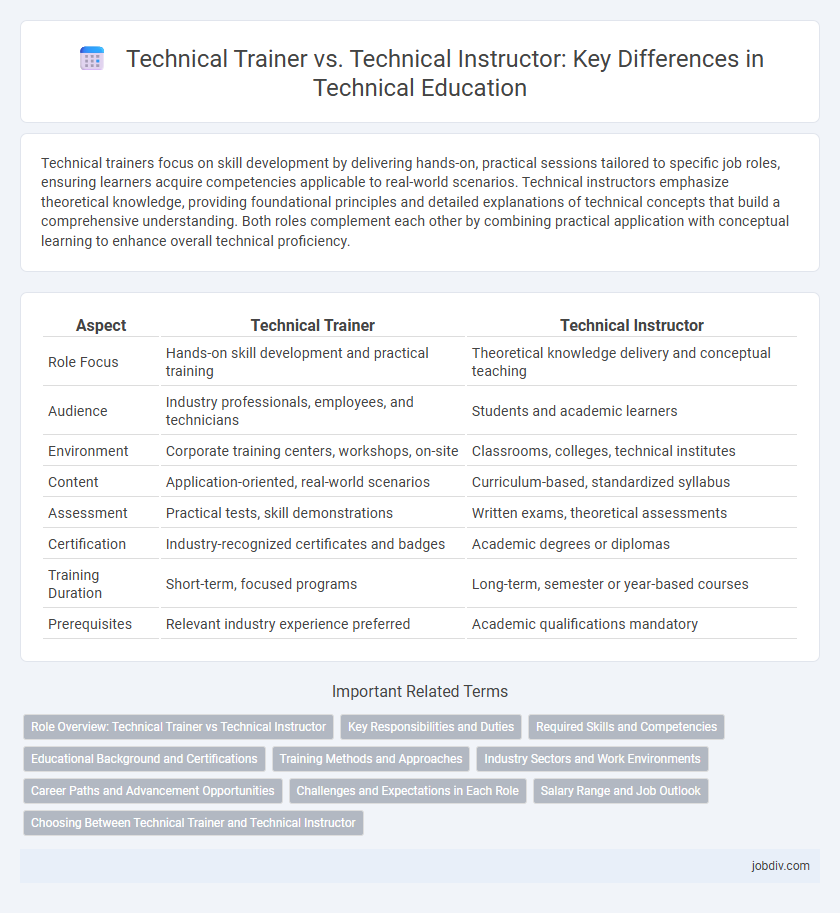
| Aspect | Technical Trainer | Technical Instructor |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Hands-on skill development and practical training | Theoretical knowledge delivery and conceptual teaching |
| Audience | Industry professionals, employees, and technicians | Students and academic learners |
| Environment | Corporate training centers, workshops, on-site | Classrooms, colleges, technical institutes |
| Content | Application-oriented, real-world scenarios | Curriculum-based, standardized syllabus |
| Assessment | Practical tests, skill demonstrations | Written exams, theoretical assessments |
| Certification | Industry-recognized certificates and badges | Academic degrees or diplomas |
| Training Duration | Short-term, focused programs | Long-term, semester or year-based courses |
| Prerequisites | Relevant industry experience preferred | Academic qualifications mandatory |
Role Overview: Technical Trainer vs Technical Instructor
A Technical Trainer specializes in developing and delivering hands-on training programs to enhance employees' practical skills and technical knowledge, often focusing on software, systems, or machinery. A Technical Instructor primarily concentrates on theoretical instruction, explaining complex technical concepts and principles within academic or institutional settings. Both roles aim to improve technical proficiency but differ in their instructional approaches and target audiences.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Technical Trainers design and deliver comprehensive training programs that enhance employees' technical skills, focusing on hands-on application and continuous learning. Technical Instructors primarily conduct structured lessons and workshops, emphasizing curriculum adherence and assessment of learner progress. Both roles require expertise in technical content, but Trainers engage more in skill development strategies, while Instructors focus on instruction and evaluation.
Required Skills and Competencies
Technical Trainers require strong communication skills, in-depth technical knowledge, and the ability to design curriculum tailored to adult learning principles. Technical Instructors must demonstrate subject matter expertise, hands-on proficiency with industry tools, and the capacity to assess learners' practical skills effectively. Both roles demand adaptability and continuous updating of technical competencies to keep pace with evolving technologies.
Educational Background and Certifications
Technical Trainers often hold advanced degrees in education or their technical field alongside industry certifications such as CompTIA, Cisco, or Microsoft Certified Professional, emphasizing instructional design and adult learning principles. Technical Instructors typically possess robust technical qualifications paired with specialized certifications relevant to the subject matter, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), focusing more on hands-on skill transmission. The educational background of trainers leans towards pedagogy and curriculum development, while instructors prioritize technical expertise and practical application.
Training Methods and Approaches
Technical trainers emphasize interactive learning techniques such as hands-on labs, simulations, and real-world problem solving to enhance skill acquisition and retention. Technical instructors primarily utilize structured lectures, standardized curricula, and demonstrations to deliver theoretical knowledge and foundational concepts. Training methods for trainers often adapt to individual learner needs and promote active participation, while instructors follow formalized teaching frameworks focused on content delivery and assessment.
Industry Sectors and Work Environments
Technical Trainers typically operate in corporate sectors such as IT, engineering, and manufacturing, focusing on upskilling employees through hands-on workshops and software simulations. Technical Instructors primarily work within academic institutions, vocational schools, and training centers, delivering structured curricula on technical subjects like electronics, automotive repair, and computer programming. Both roles require expertise in their technical disciplines but differ in their work environments and target audiences.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Technical trainers often focus on developing customized training programs and facilitating hands-on learning experiences, leading to roles in corporate training management or instructional design. Technical instructors typically emphasize delivering standardized curriculum in academic or vocational settings, with career advancement opportunities in educational administration or curriculum development. Both paths offer advancement into specialized consulting or leadership roles within technical education and workforce development sectors.
Challenges and Expectations in Each Role
Technical Trainers face the challenge of designing interactive training programs that accommodate diverse learning styles while ensuring mastery of complex technical concepts. Technical Instructors are expected to deliver precise, curriculum-based instruction and assess learner competence through standardized evaluations, often in classroom or workshop settings. Both roles demand up-to-date expertise in technology trends, effective communication skills, and the ability to adapt instructional methods to evolving industry standards.
Salary Range and Job Outlook
Technical trainers typically earn between $50,000 and $80,000 annually, reflecting demand in industries such as IT, engineering, and manufacturing. Technical instructors' salaries often range from $45,000 to $75,000, with job outlook influenced by educational institutions and certification programs. Both roles show positive growth projections due to ongoing technological advancements and the need for workforce upskilling.
Choosing Between Technical Trainer and Technical Instructor
Choosing between a Technical Trainer and a Technical Instructor depends on the learning objectives and audience expertise; Technical Trainers focus on practical skills and hands-on application, while Technical Instructors emphasize theoretical knowledge and foundational concepts. Organizations aiming to enhance employee performance in specific technologies prefer Technical Trainers, whereas those requiring comprehensive understanding and certification preparation rely on Technical Instructors. Evaluating the training goals, experience level of participants, and desired outcomes ensures the optimal selection for effective technical education.
Technical Trainer vs Technical Instructor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com