Full-stack developers possess expertise in both front-end and back-end technologies, enabling them to build complete web applications efficiently. Software engineers apply engineering principles to design, develop, and maintain software systems, often specializing in specific areas such as system architecture or algorithms. The key difference lies in the scope: full-stack developers focus on creating user-facing and server-side components, while software engineers handle broader technical challenges and software lifecycle management.
Table of Comparison
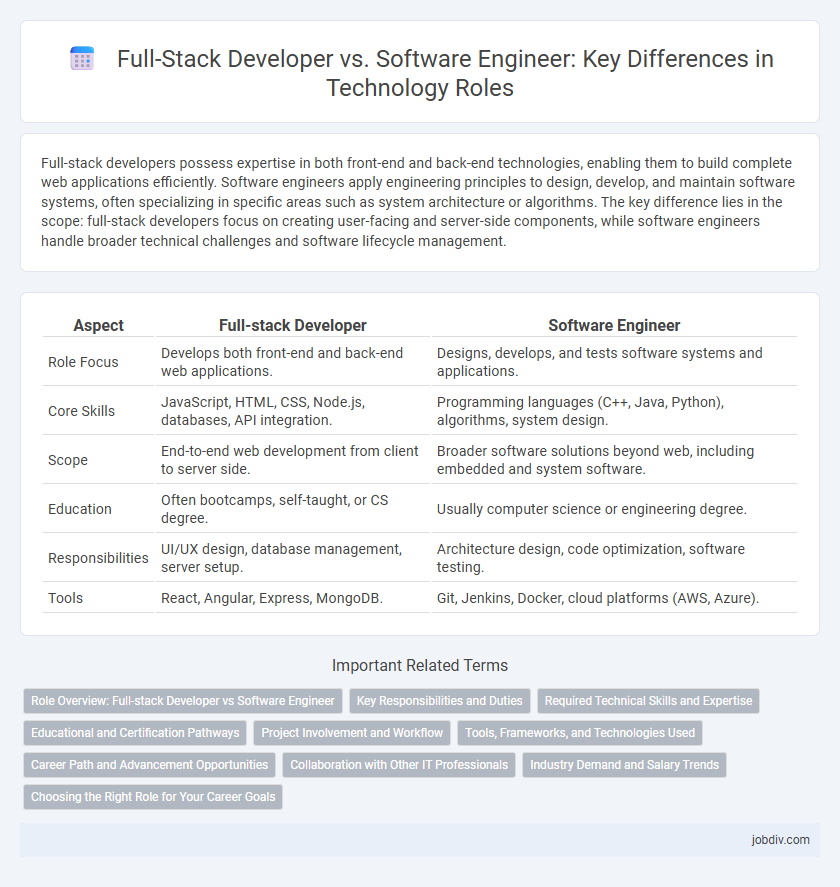
| Aspect | Full-stack Developer | Software Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Develops both front-end and back-end web applications. | Designs, develops, and tests software systems and applications. |
| Core Skills | JavaScript, HTML, CSS, Node.js, databases, API integration. | Programming languages (C++, Java, Python), algorithms, system design. |
| Scope | End-to-end web development from client to server side. | Broader software solutions beyond web, including embedded and system software. |
| Education | Often bootcamps, self-taught, or CS degree. | Usually computer science or engineering degree. |
| Responsibilities | UI/UX design, database management, server setup. | Architecture design, code optimization, software testing. |
| Tools | React, Angular, Express, MongoDB. | Git, Jenkins, Docker, cloud platforms (AWS, Azure). |
Role Overview: Full-stack Developer vs Software Engineer
Full-stack developers specialize in both front-end and back-end web development, managing databases, servers, and user interfaces to deliver complete web applications. Software engineers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining software systems through coding, testing, and system architecture, often working on large-scale projects beyond web-specific technologies. While full-stack developers require proficiency in multiple programming languages and frameworks, software engineers prioritize software development methodologies, algorithms, and system optimization.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Full-stack developers manage both client-side and server-side coding, ensuring seamless integration between front-end interfaces and back-end logic. Software engineers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining software systems, emphasizing scalable architecture and efficient algorithm implementation. While full-stack developers excel in versatile coding across the stack, software engineers prioritize software design principles and system optimization.
Required Technical Skills and Expertise
Full-stack developers require proficiency in both front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, and back-end languages including Node.js, Python, or Ruby, alongside database management skills using SQL or NoSQL. Software engineers emphasize a deeper understanding of software design principles, algorithms, data structures, and system architecture, often specializing in languages like Java, C++, or Python and focusing on scalable, maintainable code. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and familiarity with version control systems like Git, but full-stack developers lean towards versatile, end-to-end web application development, whereas software engineers prioritize robust software systems and infrastructure.
Educational and Certification Pathways
Full-stack developers often pursue certifications in front-end and back-end technologies such as JavaScript frameworks, databases, and cloud platforms to build practical skills, whereas software engineers typically follow a formal education path with degrees in computer science or software engineering emphasizing theoretical foundations and algorithmic problem-solving. Certifications like Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate or AWS Certified Developer help full-stack developers demonstrate specialized expertise, while software engineers may obtain certifications like Certified Software Development Professional (CSDP) to validate their knowledge of software design principles and engineering best practices. Both career paths benefit from continuous learning through online courses, coding bootcamps, and professional workshops to stay updated with evolving technologies and industry standards.
Project Involvement and Workflow
Full-stack developers engage in both front-end and back-end development, managing the entire project lifecycle from design to deployment, which enables a seamless integration of user interface and server-side logic. Software engineers often specialize in specific parts of the development process, focusing on system architecture, algorithms, or middleware to optimize performance and scalability within a team-based workflow. Project involvement for full-stack developers includes rapid prototyping and iterative testing, while software engineers typically handle complex problem-solving and code optimization within collaborative development cycles.
Tools, Frameworks, and Technologies Used
Full-stack developers commonly work with a combination of front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript frameworks such as React or Angular, and back-end tools including Node.js, Express.js, and databases like MongoDB or SQL. Software engineers often engage with a broader range of technologies including programming languages like Java, C++, Python, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure, and DevOps tools such as Docker and Kubernetes to design scalable systems. Both roles utilize integrated development environments (IDEs) such as Visual Studio Code and version control systems like Git to streamline development workflows.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Full-stack developers often advance by deepening expertise in both front-end and back-end technologies, enabling them to manage entire projects and transition into roles like technical lead or product manager. Software engineers typically follow a path toward specialization in areas such as algorithms, systems design, or DevOps, leading to senior engineer, architect, or engineering management positions. Both roles offer robust career growth, but full-stack developers benefit from versatile skill sets while software engineers gain depth in specific technical domains.
Collaboration with Other IT Professionals
Full-stack developers and software engineers both collaborate extensively with IT professionals such as designers, system administrators, and QA testers to ensure seamless application development and deployment. Full-stack developers often bridge the gap between front-end and back-end teams, facilitating communication and integration across project phases. Software engineers focus on designing scalable architectures and optimizing system performance, working closely with database administrators and DevOps engineers to maintain robust infrastructure.
Industry Demand and Salary Trends
Industry demand for full-stack developers continues to rise sharply due to their ability to manage both front-end and back-end development, making them highly valuable for startups and agile teams. Software engineers, with their broader expertise in system architecture and software design, maintain strong demand across large enterprises and specialized tech roles. Salary trends indicate full-stack developers earn competitive wages averaging $110,000 annually, while software engineers, depending on experience and specialization, can command salaries ranging from $95,000 to $140,000 or more in leading tech hubs.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career Goals
Full-stack developers specialize in both front-end and back-end web development, mastering languages like JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and frameworks such as React and Node.js, making them ideal for roles requiring versatile coding skills and rapid project deployment. Software engineers have a broader focus on software architecture, algorithm design, and system-level programming, often working with languages like Java, C++, and Python to build scalable, maintainable software solutions across various platforms. Choosing between these roles depends on career goals: full-stack development suits professionals aiming to build complete applications with a focus on web technologies, while software engineering appeals to those interested in deep technical problem-solving and software infrastructure design.
Full-stack Developer vs Software Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com