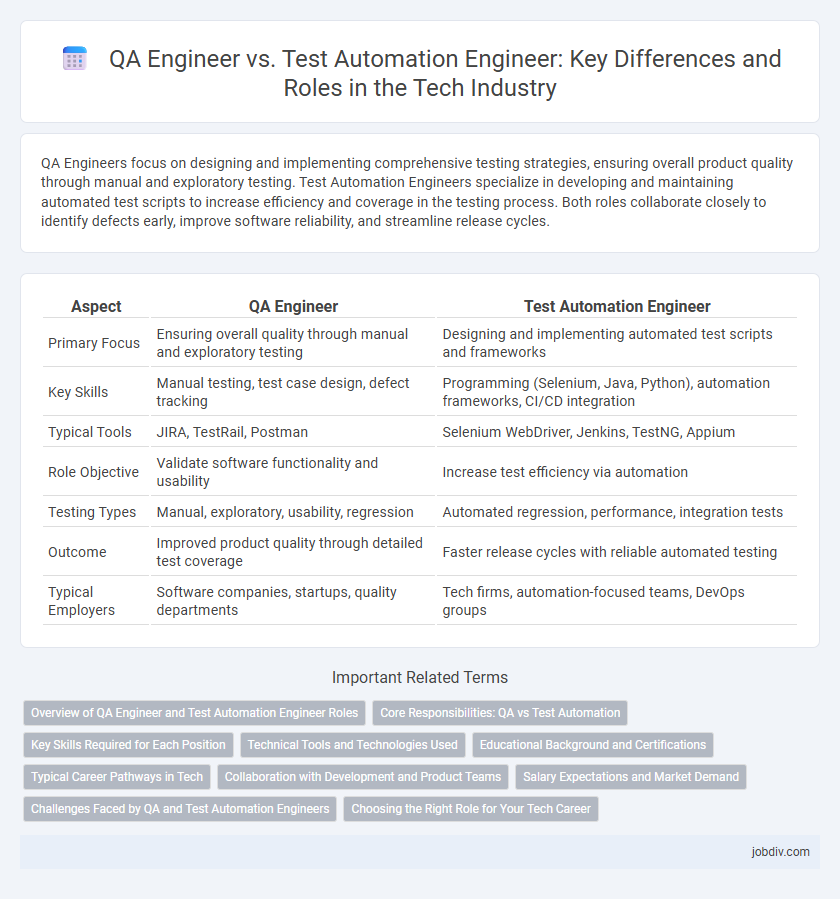
QA Engineers focus on designing and implementing comprehensive testing strategies, ensuring overall product quality through manual and exploratory testing. Test Automation Engineers specialize in developing and maintaining automated test scripts to increase efficiency and coverage in the testing process. Both roles collaborate closely to identify defects early, improve software reliability, and streamline release cycles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | QA Engineer | Test Automation Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ensuring overall quality through manual and exploratory testing | Designing and implementing automated test scripts and frameworks |
| Key Skills | Manual testing, test case design, defect tracking | Programming (Selenium, Java, Python), automation frameworks, CI/CD integration |
| Typical Tools | JIRA, TestRail, Postman | Selenium WebDriver, Jenkins, TestNG, Appium |
| Role Objective | Validate software functionality and usability | Increase test efficiency via automation |
| Testing Types | Manual, exploratory, usability, regression | Automated regression, performance, integration tests |
| Outcome | Improved product quality through detailed test coverage | Faster release cycles with reliable automated testing |
| Typical Employers | Software companies, startups, quality departments | Tech firms, automation-focused teams, DevOps groups |
Overview of QA Engineer and Test Automation Engineer Roles
QA Engineers focus on designing and executing manual test cases to ensure software quality and identify defects early in the development cycle. Test Automation Engineers develop and maintain automated testing scripts using frameworks like Selenium or Appium to increase test efficiency and coverage. Both roles collaborate closely with development teams to deliver reliable, high-quality software products.
Core Responsibilities: QA vs Test Automation
QA Engineers focus on ensuring the overall quality of software by designing test plans, executing manual tests, and identifying bugs through exploratory testing techniques. Test Automation Engineers specialize in developing, maintaining, and optimizing automated test scripts using frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, or Appium to accelerate regression and functional testing. Both roles collaborate to enhance software reliability, but QA Engineers emphasize quality assurance processes while Test Automation Engineers prioritize automation efficiency.
Key Skills Required for Each Position
QA Engineers require strong analytical skills, proficiency in manual testing techniques, and expertise in test case design to identify defects and ensure software quality. Test Automation Engineers need advanced programming knowledge in languages like Java or Python, experience with automation frameworks such as Selenium or Appium, and skills in continuous integration tools to develop and maintain automated test scripts. Both roles demand a deep understanding of software development life cycle (SDLC) and bug tracking systems like JIRA.
Technical Tools and Technologies Used
QA Engineers primarily utilize manual testing tools such as JIRA, TestRail, and Selenium IDE to design and execute test cases, ensuring software quality through exploratory and regression testing. Test Automation Engineers focus on programming languages like Java, Python, or C# combined with automation frameworks such as Selenium WebDriver, Appium, and TestNG to develop and maintain automated test scripts that enhance testing efficiency and coverage. Both roles leverage continuous integration tools like Jenkins and version control systems like Git to streamline testing workflows and collaborate effectively in Agile development environments.
Educational Background and Certifications
QA Engineers typically hold degrees in Computer Science, Software Engineering, or Information Technology, often complemented by certifications like ISTQB Foundation or Certified Software Tester (CST). Test Automation Engineers usually possess similar educational backgrounds but prioritize specialized certifications such as Certified Selenium Professional or Test Automation Engineer by ASTQB, which emphasize scripting and automation tools proficiency. Both roles benefit from continuous learning in programming languages, software testing frameworks, and quality standards to enhance their technical expertise.
Typical Career Pathways in Tech
QA Engineers typically begin their careers by mastering manual testing techniques and gradually acquire skills in test case design, defect tracking, and basic scripting. Test Automation Engineers often progress from software development roles or QA positions, emphasizing proficiency in programming languages, automation frameworks, and continuous integration tools. Career pathways for both roles may converge into advanced positions such as QA Lead, Automation Architect, or roles in DevOps, reflecting the increasing integration of testing and development processes.
Collaboration with Development and Product Teams
QA Engineers collaborate closely with development and product teams to identify, document, and prioritize bugs and improvements, ensuring product quality through manual and exploratory testing. Test Automation Engineers work alongside these teams to develop and maintain automated test scripts that accelerate feedback cycles and improve release efficiency. Both roles rely on continuous communication and integration with development pipelines to align quality goals with product requirements.
Salary Expectations and Market Demand
QA Engineers typically earn between $70,000 and $95,000 annually, while Test Automation Engineers command higher salaries, averaging $90,000 to $120,000 due to specialized skills in scripting and tool development. Market demand for Test Automation Engineers is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing adoption of DevOps and continuous integration pipelines. Companies prioritize automation expertise to enhance testing efficiency, making test automation roles more competitive and financially rewarding than traditional QA positions.
Challenges Faced by QA and Test Automation Engineers
QA Engineers often encounter challenges such as managing extensive test coverage, handling ambiguous requirements, and ensuring consistency across manual and exploratory testing processes. Test Automation Engineers face difficulties in selecting appropriate automation frameworks, maintaining automated test scripts amid frequent application updates, and integrating tests into continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Both roles require balancing speed and accuracy while addressing evolving software complexities and tight delivery schedules.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Tech Career
QA Engineers focus on ensuring software quality through manual testing, exploratory analysis, and client requirement validation, making them ideal for professionals who excel in detail-oriented, human-centric evaluation. Test Automation Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and maintaining automated test scripts using frameworks like Selenium and Appium, suited for those with strong coding skills and a passion for efficiency in testing processes. Selecting the right role depends on your proficiency with programming languages, interest in automation tools, and career goals in software quality assurance versus automated testing innovation.
QA Engineer vs Test Automation Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com