Customs brokers facilitate the import and export process by preparing and submitting necessary documentation, ensuring compliance with trade regulations, and managing duties and taxes on behalf of importers and exporters. Border agents, on the other hand, are government officials responsible for enforcing customs laws, inspecting goods, and preventing illegal activities at borders. Understanding the distinct roles of customs brokers and border agents is essential for efficient cross-border transportation and logistics management.
Table of Comparison
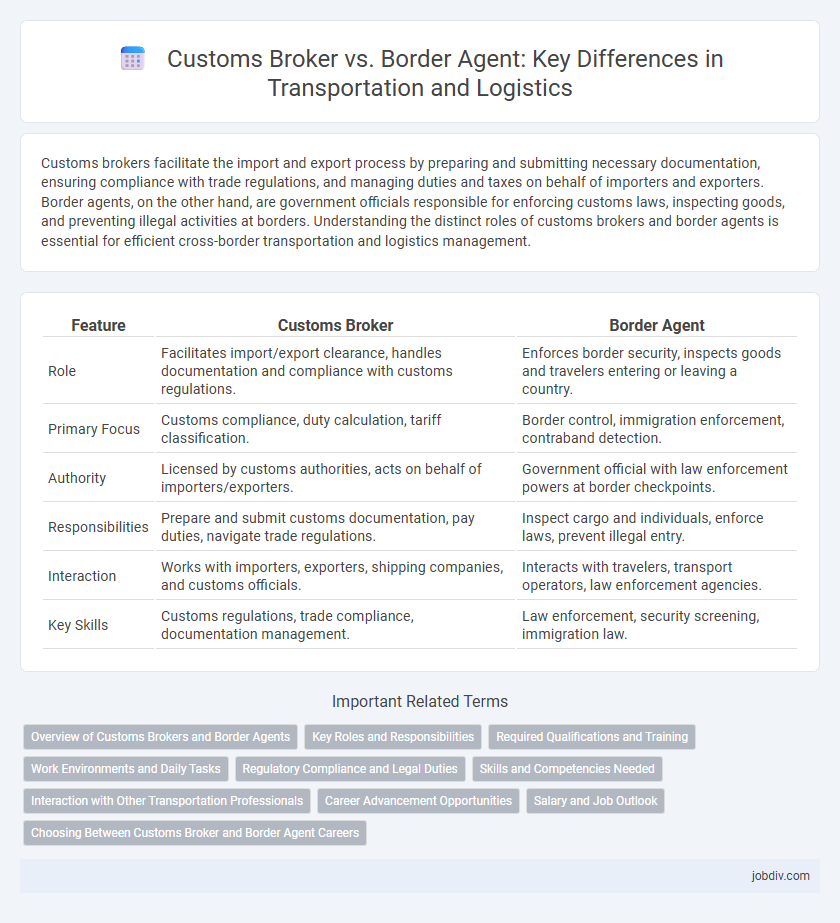
| Feature | Customs Broker | Border Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Facilitates import/export clearance, handles documentation and compliance with customs regulations. | Enforces border security, inspects goods and travelers entering or leaving a country. |
| Primary Focus | Customs compliance, duty calculation, tariff classification. | Border control, immigration enforcement, contraband detection. |
| Authority | Licensed by customs authorities, acts on behalf of importers/exporters. | Government official with law enforcement powers at border checkpoints. |
| Responsibilities | Prepare and submit customs documentation, pay duties, navigate trade regulations. | Inspect cargo and individuals, enforce laws, prevent illegal entry. |
| Interaction | Works with importers, exporters, shipping companies, and customs officials. | Interacts with travelers, transport operators, law enforcement agencies. |
| Key Skills | Customs regulations, trade compliance, documentation management. | Law enforcement, security screening, immigration law. |
Overview of Customs Brokers and Border Agents
Customs brokers are licensed professionals who assist importers and exporters in complying with customs regulations, facilitating the clearance of goods through customs by preparing and submitting necessary documentation. Border agents are government officials responsible for enforcing customs, immigration, and security laws at national borders, inspecting cargo and travelers to prevent illegal activities. Both play crucial roles in international trade, with customs brokers focusing on regulatory compliance and border agents ensuring border security and legal enforcement.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Customs brokers facilitate the clearance of goods by preparing and submitting necessary documentation, ensuring compliance with import/export regulations, and calculating duties and taxes. Border agents enforce laws at entry points, conduct inspections, and prevent illegal activities such as smuggling or unauthorized entry. Both roles are crucial for smooth international trade and security, but customs brokers operate mostly in paperwork and regulatory compliance, while border agents focus on enforcement and inspection.
Required Qualifications and Training
Customs brokers must complete rigorous training and pass the U.S. Customs Broker License Examination, demonstrating expertise in customs regulations, tariff schedules, and trade compliance. Border agents, employed by agencies such as U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), undergo extensive federal law enforcement training at the CBP Academy, focusing on immigration laws, drug interdiction, and security protocols. Both roles require in-depth knowledge of import-export processes, but customs brokers emphasize regulatory compliance while border agents prioritize enforcement and security.
Work Environments and Daily Tasks
Customs brokers typically work in office settings or freight terminals, managing paperwork, tariffs, and compliance with trade regulations to facilitate smooth import and export processes. Border agents operate primarily at ports of entry, such as airports and land borders, conducting inspections, enforcing customs laws, and ensuring security by examining cargo and travelers. While customs brokers handle administrative and regulatory tasks related to shipments, border agents focus on enforcement, inspections, and maintaining national security.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Duties
Customs brokers facilitate regulatory compliance by preparing and submitting documentation required for importing and exporting goods, ensuring adherence to tariff classifications and duty payments. Border agents enforce legal duties by inspecting shipments, verifying cargo against declarations, and preventing illegal goods from crossing borders. Both roles are essential for maintaining secure and lawful international trade operations.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Customs brokers require in-depth knowledge of import and export regulations, tariff classifications, and clearance procedures to ensure compliance and expedite shipments. Border agents need strong skills in risk assessment, inspection techniques, and enforcement of customs laws to prevent illegal activities and protect national security. Both roles demand proficiency in communication, attention to detail, and the ability to work under pressure in dynamic transportation environments.
Interaction with Other Transportation Professionals
Customs brokers facilitate communication between importers, exporters, and border agents to ensure accurate documentation and compliance with trade regulations. Border agents work closely with customs brokers, shipping companies, and freight forwarders to inspect goods and enforce security protocols at entry points. Their collaboration streamlines cargo clearance, reduces delays, and maintains the integrity of international supply chains.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Customs brokers offer extensive career advancement opportunities by specializing in import/export regulations, compliance consulting, and supply chain management, often leading to roles in logistics firms or international trade compliance departments. Border agents, working primarily with government agencies, can advance into supervisory positions, specialize in immigration enforcement, or transition into federal law enforcement roles with increased responsibility. Both careers require continuous knowledge of trade laws and policies, but customs brokers typically experience broader growth in the private sector while border agents progress within public service hierarchies.
Salary and Job Outlook
Customs brokers earn a median annual salary of approximately $56,000, with job growth projected at 4% through 2031 due to increasing international trade. Border agents typically receive higher pay, averaging around $65,000 per year, supported by strong government demand and a projected growth rate of 5% over the next decade. Employment prospects favor border agents given expanded security measures and border control enforcement priorities.
Choosing Between Customs Broker and Border Agent Careers
Choosing between customs broker and border agent careers involves evaluating job functions, regulatory knowledge, and work environment preferences. Customs brokers specialize in facilitating the import and export process by ensuring compliance with trade regulations, handling documentation, and liaising with customs authorities. Border agents enforce laws at ports of entry, focusing on security, immigration control, and preventing contraband, requiring strong law enforcement skills and the ability to work in dynamic, high-pressure scenarios.
Customs Broker vs Border Agent Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com