Shippers are responsible for preparing goods for shipment, including packaging, labeling, and documentation, while carriers handle the physical transportation of those goods from origin to destination. The shipper selects the carrier based on factors such as cost, reliability, and transit times, ensuring efficient delivery. Effective communication and coordination between shipper and carrier are essential for minimizing delays and ensuring cargo safety throughout the supply chain.
Table of Comparison
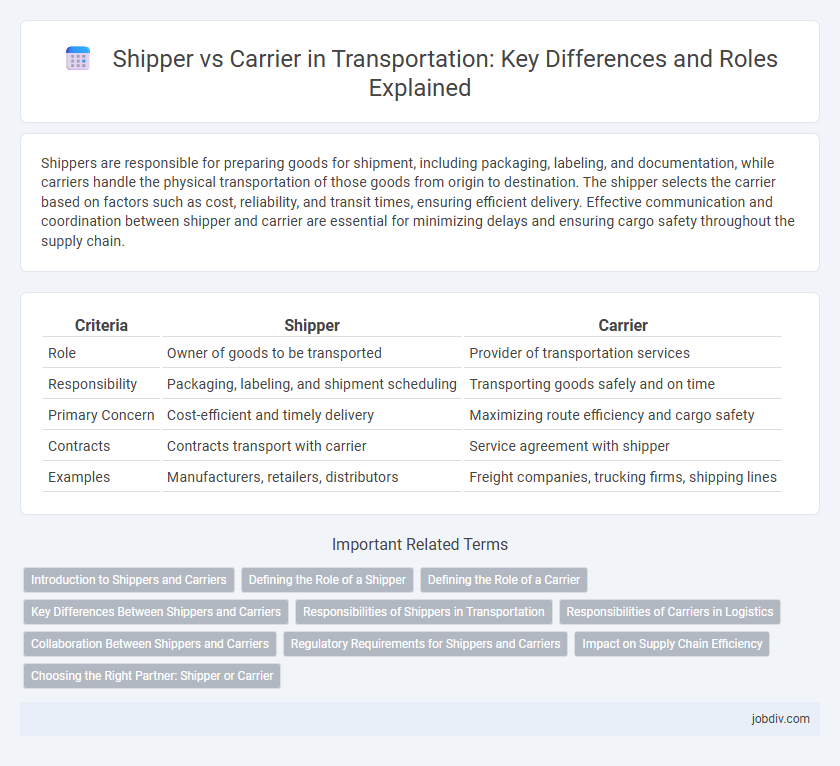
| Criteria | Shipper | Carrier |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Owner of goods to be transported | Provider of transportation services |
| Responsibility | Packaging, labeling, and shipment scheduling | Transporting goods safely and on time |
| Primary Concern | Cost-efficient and timely delivery | Maximizing route efficiency and cargo safety |
| Contracts | Contracts transport with carrier | Service agreement with shipper |
| Examples | Manufacturers, retailers, distributors | Freight companies, trucking firms, shipping lines |
Introduction to Shippers and Carriers
Shippers are entities responsible for initiating the transportation of goods by arranging shipment details and preparing cargo for transit. Carriers operate the vehicles or transportation modes, ensuring the physical movement and delivery of goods from origin to destination. Understanding the distinct roles of shippers and carriers is essential for optimizing logistics and supply chain efficiency.
Defining the Role of a Shipper
A shipper is an individual or company responsible for initiating the transportation process by preparing and sending goods to a specified destination. This role includes packaging, labeling, and ensuring compliance with shipping regulations to facilitate smooth transit. Shippers coordinate with carriers who physically transport the goods, emphasizing logistical planning and documentation accuracy.
Defining the Role of a Carrier
A carrier is a company or individual responsible for the physical transportation of goods from the shipper's location to the designated destination, managing logistics, and ensuring timely delivery. Carriers operate using various modes of transport, including trucking, rail, air, and maritime shipping, and must comply with regulatory requirements for safety and documentation. The carrier assumes liability for the cargo during transit, implementing tracking systems and handling any required transfers or storage along the route.
Key Differences Between Shippers and Carriers
Shippers are responsible for preparing and sending goods, managing packaging, labeling, and documentation to ensure proper handling and timely delivery, while carriers provide the physical transportation of these goods using various modes such as trucks, ships, or airplanes. The primary difference lies in the role where shippers initiate the logistics process and select carriers, whereas carriers execute the transportation contract and ensure the safe movement of freight. Contractual responsibilities also differ; shippers focus on compliance with regulations and shipment details, while carriers handle route planning, cargo safety, and adherence to delivery schedules.
Responsibilities of Shippers in Transportation
Shippers are responsible for accurately packaging and labeling goods to ensure safe and compliant transportation, adhering to legal regulations and carrier requirements. They must provide precise shipping documentation, including bills of lading and customs paperwork, to facilitate smooth cargo handling and delivery. Additionally, shippers are accountable for timely scheduling and communication with carriers to optimize shipment efficiency and reduce delays.
Responsibilities of Carriers in Logistics
Carriers in logistics are responsible for the safe and timely transportation of goods from the shipper to the consignee, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining proper documentation. They manage vehicle operations, route planning, and cargo handling to prevent damage and delays while optimizing delivery efficiency. Carriers also coordinate with customs, track shipments in real-time, and provide insurance coverage to mitigate risks during transit.
Collaboration Between Shippers and Carriers
Effective collaboration between shippers and carriers enhances supply chain efficiency by optimizing route planning, reducing transit times, and minimizing costs. Transparent communication channels and data sharing platforms enable real-time tracking and proactive problem resolution, improving delivery reliability. Integrating technology such as Transportation Management Systems (TMS) fosters seamless coordination and performance monitoring across both parties.
Regulatory Requirements for Shippers and Carriers
Shippers must comply with hazardous materials regulations, including proper classification, packaging, and documentation under the Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) enforced by the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA). Carriers are responsible for adhering to safety standards such as vehicle inspections, driver qualifications, and hours-of-service rules as mandated by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). Both parties must ensure compliance with the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC) and Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations when transporting goods via sea or air, respectively.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Shippers manage the shipment of goods, selecting carriers to transport cargo effectively, which directly influences supply chain efficiency through timely deliveries and optimized routing. Carriers provide transportation services by executing the movement of freight, impacting the supply chain with reliability, capacity, and real-time tracking capabilities. Efficient collaboration between shippers and carriers reduces delays, minimizes costs, and enhances inventory management across the supply chain network.
Choosing the Right Partner: Shipper or Carrier
Selecting the right partner between a shipper and a carrier hinges on the specific needs of your supply chain, including cargo type, delivery timelines, and budget constraints. Shippers manage the origin and coordination of goods, ensuring packaging and documentation meet regulatory standards, while carriers specialize in the physical transportation and timely delivery of freight. Evaluating factors such as service reliability, network coverage, and cost-efficiency is critical for optimizing logistics and maintaining seamless supply chain operations.
Shipper vs Carrier Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com