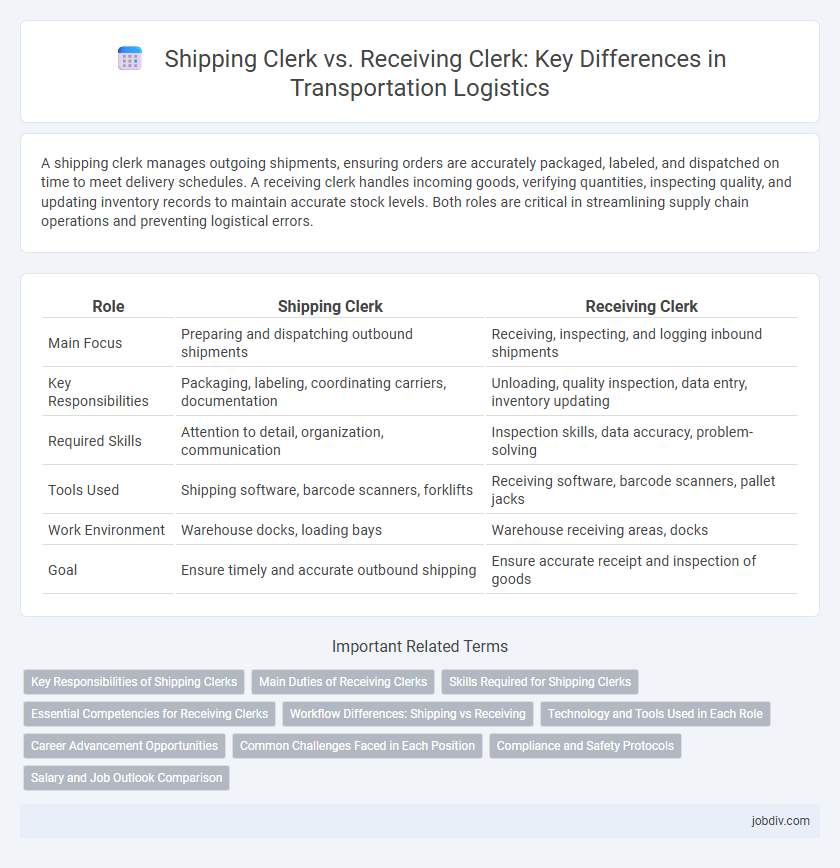
A shipping clerk manages outgoing shipments, ensuring orders are accurately packaged, labeled, and dispatched on time to meet delivery schedules. A receiving clerk handles incoming goods, verifying quantities, inspecting quality, and updating inventory records to maintain accurate stock levels. Both roles are critical in streamlining supply chain operations and preventing logistical errors.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Shipping Clerk | Receiving Clerk |
|---|---|---|
| Main Focus | Preparing and dispatching outbound shipments | Receiving, inspecting, and logging inbound shipments |
| Key Responsibilities | Packaging, labeling, coordinating carriers, documentation | Unloading, quality inspection, data entry, inventory updating |
| Required Skills | Attention to detail, organization, communication | Inspection skills, data accuracy, problem-solving |
| Tools Used | Shipping software, barcode scanners, forklifts | Receiving software, barcode scanners, pallet jacks |
| Work Environment | Warehouse docks, loading bays | Warehouse receiving areas, docks |
| Goal | Ensure timely and accurate outbound shipping | Ensure accurate receipt and inspection of goods |
Key Responsibilities of Shipping Clerks
Shipping clerks manage the accurate preparation and dispatch of outgoing shipments, ensuring all paperwork, labels, and shipping documentation comply with carrier requirements and company policies. They coordinate with warehouse personnel to verify product quantities and packaging quality before shipment, optimizing delivery schedules and reducing errors. Efficient communication with carriers and maintaining detailed records of shipped goods enhance overall supply chain reliability and customer satisfaction.
Main Duties of Receiving Clerks
Receiving Clerks primarily manage incoming shipments, verifying and inspecting goods against purchase orders to ensure accuracy and quality. They document and report discrepancies, maintain detailed records of received products, and coordinate with inventory control to update stock levels. Their role is critical in preventing errors and facilitating smooth warehouse operations by promptly addressing damaged or missing items.
Skills Required for Shipping Clerks
Shipping clerks require strong organizational skills to efficiently manage inventory, prepare shipping documents, and coordinate carrier schedules. Proficiency in warehouse management systems (WMS) and knowledge of federal shipping regulations ensure accurate labeling and compliance. Attention to detail and effective communication skills facilitate timely shipments and proper handling of goods during the logistics process.
Essential Competencies for Receiving Clerks
Receiving clerks must possess strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and the ability to accurately verify shipment contents against purchase orders and invoices. Proficiency in inventory management software and knowledge of safety regulations for handling goods are essential for ensuring efficient warehouse operations. Effective communication skills facilitate coordination with shipping clerks and warehouse personnel to resolve discrepancies and maintain accurate records.
Workflow Differences: Shipping vs Receiving
Shipping clerks manage outbound logistics by preparing orders, processing shipping documentation, and coordinating carrier pickups to ensure timely delivery. Receiving clerks handle inbound shipments, inspecting goods for accuracy, documenting received items, and updating inventory records to maintain stock integrity. Both roles require meticulous coordination but differ in focus: shipping clerks emphasize order fulfillment efficiency, while receiving clerks prioritize quality control and inventory accuracy.
Technology and Tools Used in Each Role
Shipping clerks utilize advanced shipping software, barcode scanners, and automated labeling systems to track outgoing shipments and ensure accurate order fulfillment. Receiving clerks rely on inventory management systems, handheld devices, and quality control technologies to verify and document incoming goods efficiently. Both roles increasingly integrate warehouse management systems (WMS) and RFID technology to streamline operations and enhance supply chain visibility.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Shipping clerks gain expertise in logistics coordination and inventory management, positioning themselves for advancement into roles such as logistics supervisor or supply chain analyst. Receiving clerks develop skills in quality control and verification processes, often progressing to inventory control manager or warehouse supervisor positions. Both roles serve as foundational steps within transportation operations, offering distinct pathways for career growth based on specialization in outbound or inbound freight management.
Common Challenges Faced in Each Position
Shipping clerks often face challenges such as managing tight schedules to ensure timely dispatch, handling shipping documentation accuracy, and coordinating with logistics providers to prevent delays. Receiving clerks deal with verifying incoming shipments against purchase orders, addressing damaged or incorrect deliveries, and maintaining accurate inventory records to avoid discrepancies. Both roles require meticulous attention to detail and effective communication to minimize errors and enhance supply chain efficiency.
Compliance and Safety Protocols
Shipping clerks ensure compliance with regulations by verifying shipment documentation, labeling, and packaging align with safety standards to prevent damage and hazards. Receiving clerks prioritize safety protocols by inspecting incoming goods for damage, verifying accuracy against purchase orders, and adhering to storage guidelines to maintain workplace safety. Both roles collaborate to uphold regulatory compliance and mitigate risks throughout the transportation supply chain.
Salary and Job Outlook Comparison
Shipping clerks earn a median salary of approximately $38,000 annually, with job growth projected at 2% over the next decade, reflecting stable demand in logistics operations. Receiving clerks typically have a slightly lower median salary near $35,000 but experience a similar job outlook of about 1-3%, tied closely to warehousing and distribution trends. Both positions require attention to detail and accuracy, with salary and employment opportunities influenced by supply chain expansions and e-commerce growth.
Shipping Clerk vs Receiving Clerk Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com