Truck drivers transport goods over long distances, requiring strong navigation skills and the ability to handle heavy cargo safely. Bus drivers focus on passenger safety and comfort, operating routes within cities or regions while maintaining strict schedules. Both roles demand excellent driving skills and adherence to transportation regulations but differ primarily in their cargo and customer interactions.
Table of Comparison
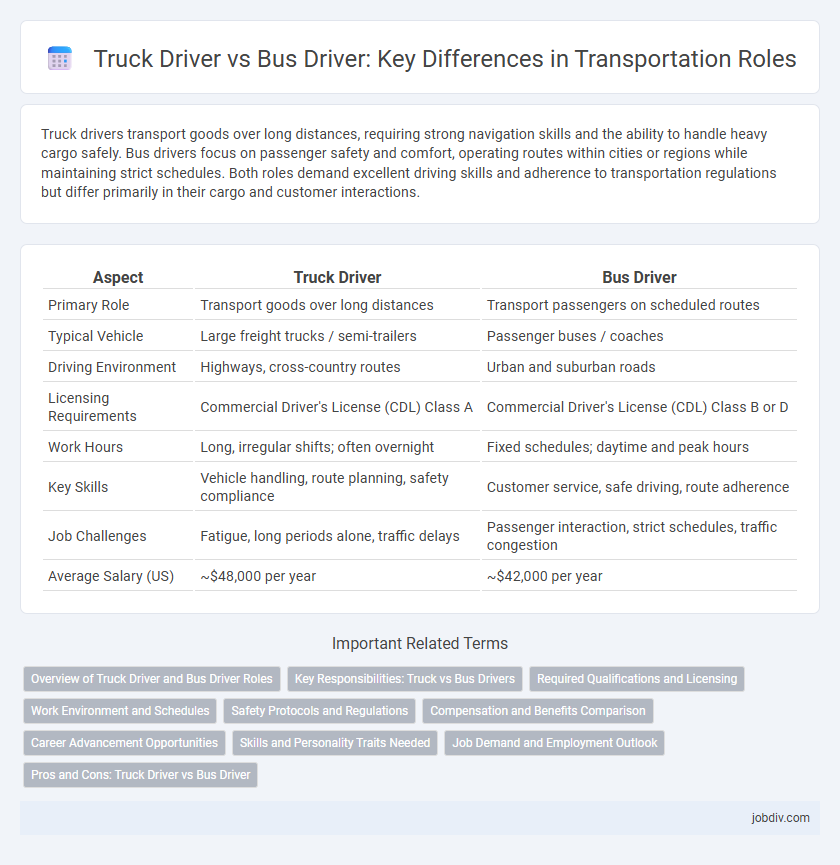
| Aspect | Truck Driver | Bus Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Transport goods over long distances | Transport passengers on scheduled routes |
| Typical Vehicle | Large freight trucks / semi-trailers | Passenger buses / coaches |
| Driving Environment | Highways, cross-country routes | Urban and suburban roads |
| Licensing Requirements | Commercial Driver's License (CDL) Class A | Commercial Driver's License (CDL) Class B or D |
| Work Hours | Long, irregular shifts; often overnight | Fixed schedules; daytime and peak hours |
| Key Skills | Vehicle handling, route planning, safety compliance | Customer service, safe driving, route adherence |
| Job Challenges | Fatigue, long periods alone, traffic delays | Passenger interaction, strict schedules, traffic congestion |
| Average Salary (US) | ~$48,000 per year | ~$42,000 per year |
Overview of Truck Driver and Bus Driver Roles
Truck drivers transport goods over long distances, operating heavy vehicles such as semi-trailers and flatbeds, often requiring extensive knowledge of logistics, safety regulations, and route planning. Bus drivers operate passenger vehicles, focusing on safe transit within urban or suburban areas, emphasizing customer service, adherence to schedules, and managing passenger interactions. Both roles demand commercial driver's licenses (CDLs) but differ significantly in daily responsibilities, work environments, and skill sets related to cargo handling versus passenger safety.
Key Responsibilities: Truck vs Bus Drivers
Truck drivers primarily focus on the transportation of goods, ensuring timely delivery, vehicle maintenance, and safe handling of cargo across long distances. Bus drivers are responsible for safely transporting passengers along fixed routes, managing schedules, and providing customer service. Both roles require adherence to traffic regulations and vehicle inspection, but truck drivers emphasize freight logistics while bus drivers prioritize passenger safety and comfort.
Required Qualifications and Licensing
Truck drivers must obtain a Commercial Driver's License (CDL) with specific endorsements such as hazardous materials (HazMat) or double/triple trailers based on cargo type and vehicle class, often requiring rigorous training and passing both written and road tests. Bus drivers also need a CDL, typically with a passenger (P) endorsement and sometimes a school bus (S) endorsement, emphasizing safe passenger transport and adherence to route schedules. Both professions demand a clean driving record, physical fitness standards, and ongoing certification or training for compliance with federal and state transportation regulations.
Work Environment and Schedules
Truck drivers typically experience solitary and flexible work environments, spending long hours on highways and often operating overnight or on extended shifts. Bus drivers work in more structured environments, interacting frequently with passengers and adhering to fixed schedules within urban or suburban routes. While truck drivers face unpredictable delivery timelines, bus drivers manage consistent, repeatable routes with regular start and end times.
Safety Protocols and Regulations
Truck drivers and bus drivers adhere to strict safety protocols regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), including hours-of-service limits, vehicle inspections, and mandatory rest periods to prevent fatigue-related accidents. Bus drivers follow additional passenger safety regulations, such as ensuring seat belts are used and managing boarding procedures, supervised by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). Both roles require compliance with state-specific licensing requirements and continuous training on emergency response and hazardous material handling.
Compensation and Benefits Comparison
Truck drivers typically earn higher average salaries than bus drivers due to long-haul routes and overtime opportunities, with median annual wages around $48,000 compared to bus drivers' $40,000. Benefits for truck drivers often include per diem allowances, health insurance, and retirement plans, while bus drivers may receive more stable schedules with paid time off and union protections. Variations in compensation depend on factors like employer, route length, and geographic location.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Truck drivers often experience more independent career advancement through certifications such as hazardous materials endorsement or becoming owner-operators, which can lead to higher earnings and business ownership. Bus drivers may advance by obtaining licenses to operate larger vehicles, transitioning into supervisory roles, or moving into transit planning and management positions within public transportation agencies. Both careers offer pathways to specialized driving jobs or training instructor roles, but truck driving frequently provides greater financial growth potential due to the commercial freight industry's expansive demands.
Skills and Personality Traits Needed
Truck drivers require strong spatial awareness, self-discipline, and endurance to manage long hours and navigate diverse routes independently. Bus drivers need excellent interpersonal skills, patience, and a calm demeanor to safely transport passengers and handle frequent stops in urban environments. Both roles demand keen attention to safety regulations and the ability to remain alert under varying road conditions.
Job Demand and Employment Outlook
Truck drivers face a high job demand driven by e-commerce growth and supply chain expansion, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 5% employment increase through 2031. Bus drivers also experience steady demand, particularly in public transportation and school systems, but their growth rate is slower, around 1%. Both roles require commercial driving licenses, though truck driving offers more lucrative opportunities due to long-haul freight needs and increasing trucking industry shortages.
Pros and Cons: Truck Driver vs Bus Driver
Truck drivers benefit from higher earnings and independence on long-haul routes but face irregular schedules and extended periods away from home. Bus drivers enjoy more predictable hours and regular interactions with passengers, enhancing social engagement, but often deal with traffic congestion and lower pay. Both roles require strong safety awareness and responsibility, yet physical demands and job stress vary significantly between them.
Truck Driver vs Bus Driver Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com