Utility meter readers focus on accurately recording consumption data by visually inspecting meters and ensuring data integrity. Utility meter technicians possess advanced skills to install, maintain, and repair meters, often handling complex diagnostics and system calibrations. Both roles are essential for efficient utility management, with technicians providing technical expertise and readers supporting data collection processes.
Table of Comparison
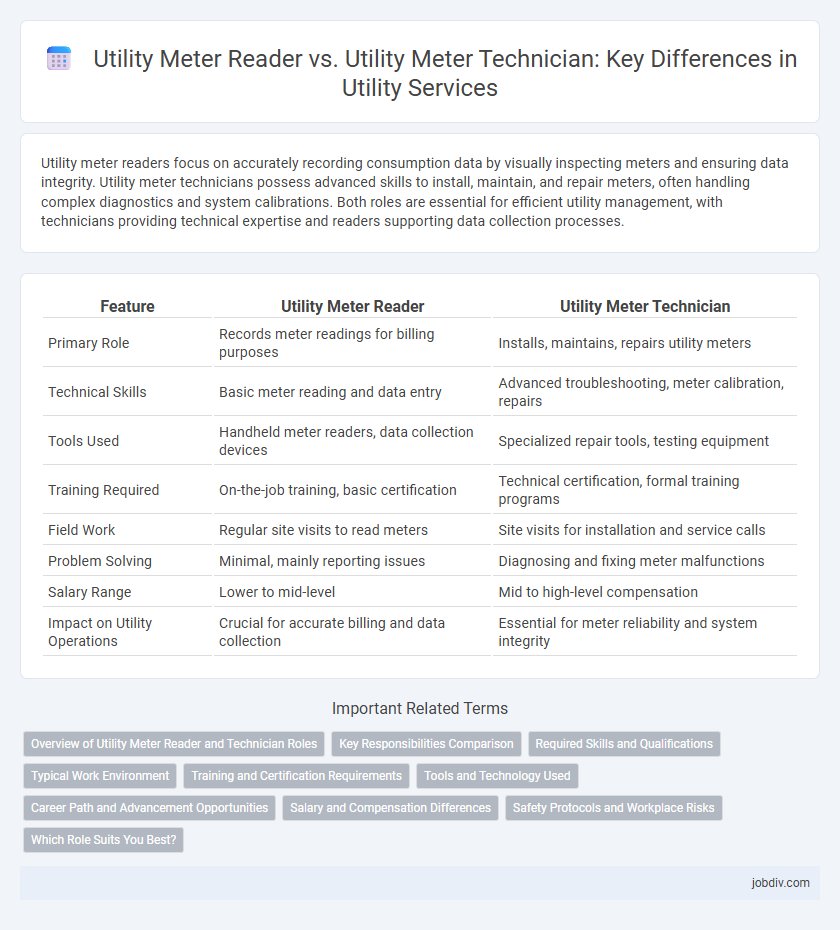
| Feature | Utility Meter Reader | Utility Meter Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Records meter readings for billing purposes | Installs, maintains, repairs utility meters |
| Technical Skills | Basic meter reading and data entry | Advanced troubleshooting, meter calibration, repairs |
| Tools Used | Handheld meter readers, data collection devices | Specialized repair tools, testing equipment |
| Training Required | On-the-job training, basic certification | Technical certification, formal training programs |
| Field Work | Regular site visits to read meters | Site visits for installation and service calls |
| Problem Solving | Minimal, mainly reporting issues | Diagnosing and fixing meter malfunctions |
| Salary Range | Lower to mid-level | Mid to high-level compensation |
| Impact on Utility Operations | Crucial for accurate billing and data collection | Essential for meter reliability and system integrity |
Overview of Utility Meter Reader and Technician Roles
Utility Meter Readers are responsible for accurately recording energy, gas, or water consumption data from residential and commercial meters, ensuring precise billing and usage tracking. Utility Meter Technicians handle more technical aspects, including the installation, maintenance, calibration, and repair of meters and metering equipment to ensure proper functionality and compliance with regulatory standards. Both roles are critical in maintaining the reliability of utility services, with Meter Readers focusing on data collection and Meter Technicians emphasizing equipment performance and troubleshooting.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Utility Meter Readers specialize in accurately recording energy, water, or gas consumption data by physically inspecting meters and inputting readings into digital systems to ensure billing accuracy. Utility Meter Technicians handle maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs of utility meters, calibrating devices to comply with industry standards and ensuring optimal functionality. Both roles require attention to detail, but Technicians possess advanced technical skills for diagnostics and system upgrades, whereas Readers focus primarily on data collection and reporting.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Utility Meter Readers require basic technical skills, proficiency in data recording, and the ability to follow safety protocols while inspecting meters. Utility Meter Technicians need advanced qualifications such as electrical or mechanical certifications, troubleshooting expertise, and the ability to perform complex repairs and installations on utility meters. Both roles demand physical stamina and knowledge of utility regulations, but technicians must possess deeper technical knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Typical Work Environment
Utility Meter Readers typically work outdoors in various weather conditions, visiting residential and commercial properties to manually record utility consumption data. Utility Meter Technicians operate in both field and controlled environments, performing maintenance, repairs, and installations on meter equipment, often in utility company facilities or customer locations. Both roles require physical activity and adherence to safety protocols, though technicians engage more with technical tools and diagnostic equipment compared to readers.
Training and Certification Requirements
Utility Meter Readers typically require basic training on reading various meter types and understanding customer service protocols, often completed through on-the-job training or short-term certification programs. Utility Meter Technicians undergo more extensive training, including coursework in electrical systems, meter maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety protocols, often culminating in formal certifications such as NATE or state-specific utility licenses. Certification requirements for technicians ensure compliance with regulatory standards and technical competencies, whereas meter readers focus on accurate data collection and reporting.
Tools and Technology Used
Utility meter readers primarily use handheld devices such as mobile data terminals (MDTs) and barcode scanners to record consumption data efficiently, relying on automated route mapping software for optimized collection. Utility meter technicians employ advanced diagnostic tools and software, including multimeters, pressure gauges, and specialized calibration equipment, to install, maintain, and troubleshoot meters. Both roles integrate emerging technologies like smart meters and wireless communication systems to enhance accuracy and operational efficiency in utility management.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Utility Meter Readers primarily focus on routine data collection and basic maintenance of meters, providing a foundational role with limited advancement opportunities. Utility Meter Technicians possess advanced skills in installation, troubleshooting, and repair of complex metering systems, offering a broader career path that can lead to supervisory roles or specialized technical positions. Career advancement for technicians often involves additional certifications and training, enhancing job security and earning potential within the utility industry.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Utility Meter Readers earn an average annual salary ranging from $30,000 to $45,000, reflecting entry-level responsibilities focused on data collection from utility meters. Utility Meter Technicians, with advanced skills in meter installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, typically command higher salaries between $50,000 and $70,000 per year. Compensation packages for technicians often include benefits such as overtime pay, certifications bonuses, and opportunities for career advancement, resulting in a more lucrative overall compensation compared to meter readers.
Safety Protocols and Workplace Risks
Utility Meter Technicians adhere to stringent safety protocols, including lockout/tagout procedures and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to handle potentially hazardous electrical components during meter installation or maintenance. Utility Meter Readers primarily face environmental workplace risks such as extreme weather conditions and traffic hazards while accessing meters, necessitating situational awareness and protective clothing. Both roles require compliance with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards to mitigate risks and ensure employee safety in field operations.
Which Role Suits You Best?
Utility meter readers primarily focus on accurately recording consumption data from residential and commercial meters, requiring strong attention to detail and basic technical skills. Utility meter technicians possess advanced expertise, handling installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of meters, which suits those interested in hands-on technical work and problem-solving. Choosing between these roles depends on your preference for routine data collection versus complex technical responsibilities within the utility industry.
Utility Meter Reader vs Utility Meter Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com