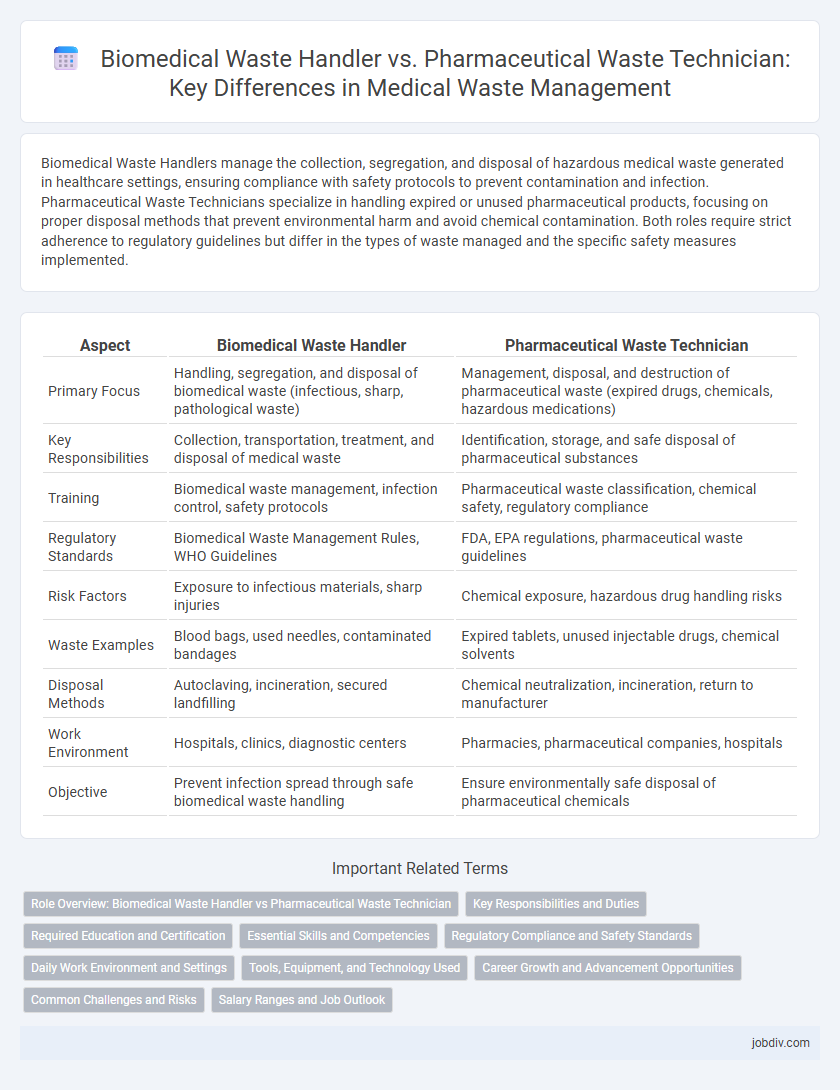
Biomedical Waste Handlers manage the collection, segregation, and disposal of hazardous medical waste generated in healthcare settings, ensuring compliance with safety protocols to prevent contamination and infection. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians specialize in handling expired or unused pharmaceutical products, focusing on proper disposal methods that prevent environmental harm and avoid chemical contamination. Both roles require strict adherence to regulatory guidelines but differ in the types of waste managed and the specific safety measures implemented.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Biomedical Waste Handler | Pharmaceutical Waste Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Handling, segregation, and disposal of biomedical waste (infectious, sharp, pathological waste) | Management, disposal, and destruction of pharmaceutical waste (expired drugs, chemicals, hazardous medications) |
| Key Responsibilities | Collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal of medical waste | Identification, storage, and safe disposal of pharmaceutical substances |
| Training | Biomedical waste management, infection control, safety protocols | Pharmaceutical waste classification, chemical safety, regulatory compliance |
| Regulatory Standards | Biomedical Waste Management Rules, WHO Guidelines | FDA, EPA regulations, pharmaceutical waste guidelines |
| Risk Factors | Exposure to infectious materials, sharp injuries | Chemical exposure, hazardous drug handling risks |
| Waste Examples | Blood bags, used needles, contaminated bandages | Expired tablets, unused injectable drugs, chemical solvents |
| Disposal Methods | Autoclaving, incineration, secured landfilling | Chemical neutralization, incineration, return to manufacturer |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, clinics, diagnostic centers | Pharmacies, pharmaceutical companies, hospitals |
| Objective | Prevent infection spread through safe biomedical waste handling | Ensure environmentally safe disposal of pharmaceutical chemicals |
Role Overview: Biomedical Waste Handler vs Pharmaceutical Waste Technician
Biomedical Waste Handlers manage the collection, segregation, transportation, and disposal of medical waste generated from healthcare facilities, ensuring compliance with health regulations to prevent contamination and infection risks. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians specialize in handling expired, unused, or contaminated pharmaceutical products, applying safe disposal methods to mitigate environmental impact and regulatory non-compliance. Both roles require strict adherence to safety protocols and regulatory guidelines to maintain public health and environmental safety.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Biomedical Waste Handlers primarily focus on the safe collection, segregation, and disposal of clinical and infectious waste generated in healthcare settings, ensuring compliance with biohazard regulations and minimizing contamination risks. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians manage the proper handling, storage, and disposal of expired, unused, or hazardous pharmaceutical products, following strict environmental and safety protocols to prevent chemical hazards and drug diversion. Both roles require knowledge of regulatory standards but differ in the specific waste types they handle and the specialized procedures they employ.
Required Education and Certification
A Biomedical Waste Handler typically requires a high school diploma or equivalent, along with specialized training in hazardous waste management and safety protocols, often certified through OSHA or equivalent health and safety organizations. In contrast, a Pharmaceutical Waste Technician usually needs post-secondary education such as a certificate or associate degree in pharmacy technology or environmental science, coupled with certifications like the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) credential and training in pharmaceutical waste disposal regulations. Both roles demand strict adherence to regulatory compliance, but pharmaceutical waste technicians often face additional requirements due to the complexity of handling cytotoxic and controlled substance wastes.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Biomedical Waste Handlers require proficiency in proper segregation, handling, and disposal techniques of infectious materials, along with strict adherence to health and safety protocols and knowledge of biohazard regulations. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians must possess expertise in handling expired or contaminated drugs, ensuring compliance with pharmaceutical waste disposal laws, and accurate documentation to prevent environmental contamination or drug diversion. Both roles demand strong attention to detail, familiarity with hazardous material guidelines, and the ability to operate specialized equipment safely.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Biomedical Waste Handlers and Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians both adhere to strict regulatory compliance frameworks such as OSHA, EPA, and DOT guidelines, ensuring safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials. Biomedical Waste Handlers specialize in managing infectious waste following CDC and WHO protocols, focusing on infection control and biohazard containment. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians emphasize compliance with FDA and DEA regulations, managing expired or unused medications to prevent environmental contamination and ensure safe destruction.
Daily Work Environment and Settings
Biomedical Waste Handlers typically operate in hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, managing infectious and hazardous waste daily to ensure safe disposal and prevent contamination. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians work primarily in pharmacies, manufacturing plants, and research facilities, handling expired or unused medications and chemical waste under strict regulatory compliance. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols, but their work environments differ significantly in terms of waste types and regulatory considerations.
Tools, Equipment, and Technology Used
Biomedical waste handlers utilize protective gear such as gloves, masks, and biohazard containers alongside tools like trolleys and shredders to safely collect, transport, and manage infectious waste. Pharmaceutical waste technicians employ advanced equipment including autoclaves, incinerators, and chemical neutralizers to treat expired drugs and hazardous chemicals, ensuring compliance with regulatory disposal standards. Both roles leverage tracking software and barcoding systems to monitor waste generation, segregation, and disposal efficiently.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Biomedical Waste Handlers typically focus on the proper collection, segregation, and disposal of infectious and hazardous medical waste, offering career growth through specialized certifications in waste management and health safety compliance. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians specialize in the safe handling and disposal of expired or contaminated medications, with advancement opportunities in regulatory affairs and waste tracking technology integration. Both roles present pathways to supervisory positions and require ongoing education to stay updated with evolving environmental and health regulations.
Common Challenges and Risks
Biomedical waste handlers and pharmaceutical waste technicians both face significant challenges related to the safe management of hazardous substances. Exposure to infectious agents, chemical hazards, and improper disposal methods increases the risk of contamination and environmental pollution in both roles. Strict adherence to regulatory protocols and continuous safety training are critical to minimizing health risks and ensuring compliance with waste management standards.
Salary Ranges and Job Outlook
Biomedical Waste Handlers typically earn between $30,000 and $45,000 annually, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade due to increasing healthcare waste regulations. Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians command higher salaries, ranging from $40,000 to $60,000, driven by the specialized handling of hazardous pharmaceutical materials and stricter environmental compliance standards. Employment opportunities for Pharmaceutical Waste Technicians are expected to grow faster at 7%, reflecting the expanding pharmaceutical industry and stringent waste management policies.
Biomedical Waste Handler vs Pharmaceutical Waste Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com