Biomedical Waste Technicians specialize in the safe handling, segregation, and disposal of infectious and hazardous medical waste to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with health regulations. Solid Waste Technicians manage the collection, transportation, and processing of non-hazardous municipal and industrial waste, focusing on efficient recycling and landfill operations. Both roles require knowledge of waste management protocols but differ significantly in the types of waste handled and safety measures implemented.
Table of Comparison
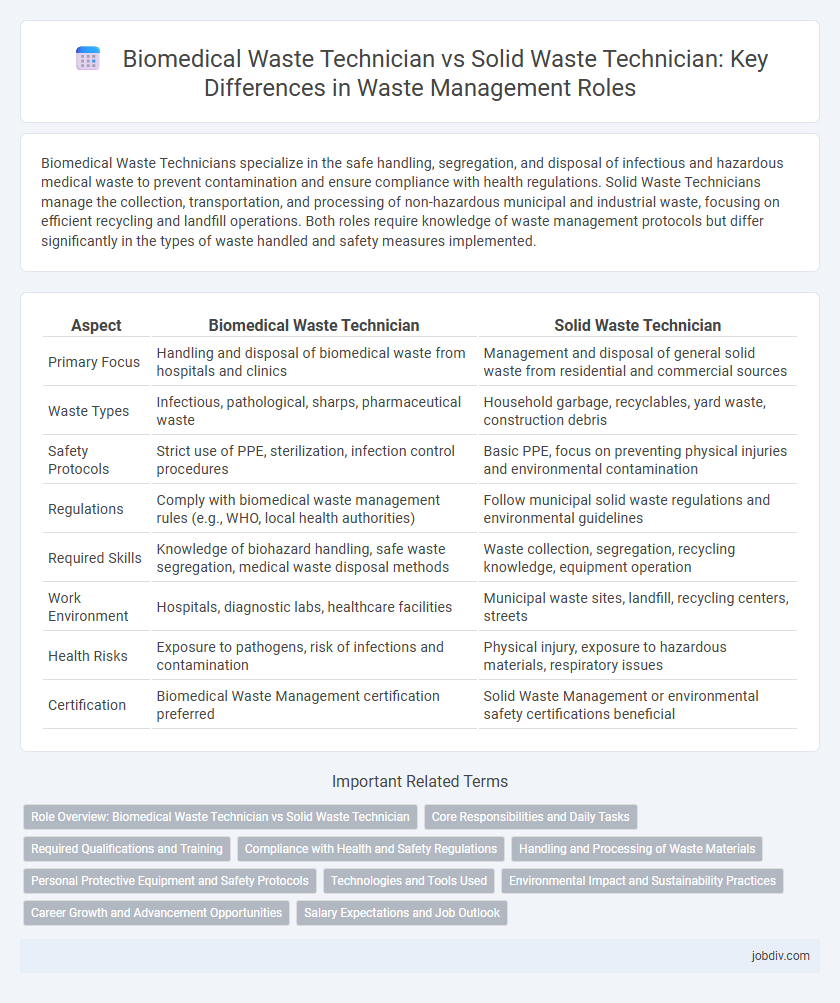
| Aspect | Biomedical Waste Technician | Solid Waste Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Handling and disposal of biomedical waste from hospitals and clinics | Management and disposal of general solid waste from residential and commercial sources |
| Waste Types | Infectious, pathological, sharps, pharmaceutical waste | Household garbage, recyclables, yard waste, construction debris |
| Safety Protocols | Strict use of PPE, sterilization, infection control procedures | Basic PPE, focus on preventing physical injuries and environmental contamination |
| Regulations | Comply with biomedical waste management rules (e.g., WHO, local health authorities) | Follow municipal solid waste regulations and environmental guidelines |
| Required Skills | Knowledge of biohazard handling, safe waste segregation, medical waste disposal methods | Waste collection, segregation, recycling knowledge, equipment operation |
| Work Environment | Hospitals, diagnostic labs, healthcare facilities | Municipal waste sites, landfill, recycling centers, streets |
| Health Risks | Exposure to pathogens, risk of infections and contamination | Physical injury, exposure to hazardous materials, respiratory issues |
| Certification | Biomedical Waste Management certification preferred | Solid Waste Management or environmental safety certifications beneficial |
Role Overview: Biomedical Waste Technician vs Solid Waste Technician
Biomedical Waste Technicians specialize in the safe handling, segregation, and disposal of infectious and hazardous medical waste, ensuring compliance with health regulations to prevent contamination and disease spread. Solid Waste Technicians manage the collection, transportation, and disposal of non-hazardous municipal waste, focusing on efficiency and environmental protection through recycling and landfill operations. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols but differ significantly in the nature of waste materials and regulatory frameworks they navigate.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Biomedical Waste Technicians specialize in the safe collection, segregation, and disposal of infectious and hazardous medical waste to prevent contamination and disease transmission. Solid Waste Technicians focus on managing non-hazardous municipal waste, including collection, transportation, and processing to support recycling and landfill operations. Both roles require adherence to regulatory standards, but Biomedical Waste Technicians handle materials requiring specialized treatment protocols.
Required Qualifications and Training
Biomedical Waste Technicians require specialized training in handling hazardous materials, infection control, and compliance with medical waste regulations such as OSHA and EPA standards. Solid Waste Technicians typically need knowledge of general waste management procedures, including landfill operations and recycling processes, supported by certification in solid waste management or environmental science. Both roles demand safety training, but biomedical technicians emphasize hazardous pathogen containment, while solid waste technicians focus on environmental impact and public health.
Compliance with Health and Safety Regulations
Biomedical Waste Technicians rigorously adhere to stringent health and safety regulations enforced by agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to manage infectious and hazardous medical waste. Solid Waste Technicians comply with federal and local regulations focusing on the safe collection, transportation, and disposal of non-hazardous municipal waste, ensuring environmental protection and public safety. Both roles require specialized training in regulatory compliance, but Biomedical Waste Technicians undergo more intensive protocols due to the biohazardous nature of their materials.
Handling and Processing of Waste Materials
Biomedical Waste Technicians specialize in safely handling and processing infectious and hazardous medical waste using sterilization and containment methods to prevent contamination and disease transmission. Solid Waste Technicians manage general municipal and industrial waste, focusing on sorting, recycling, and landfill operations to minimize environmental impact. Both roles require adherence to regulatory standards, but Biomedical Waste Technicians follow stricter protocols for biohazard disposal and sterilization processes.
Personal Protective Equipment and Safety Protocols
Biomedical Waste Technicians use specialized personal protective equipment (PPE) such as biohazard suits, gloves, masks, and face shields to prevent exposure to infectious materials, following strict safety protocols to handle and dispose of hazardous biological waste. Solid Waste Technicians typically wear durable gloves, steel-toed boots, safety goggles, and high-visibility clothing, adhering to safety procedures designed to minimize risks from physical injuries and chemical exposures during the collection and processing of general municipal waste. The distinct PPE requirements and safety protocols reflect the differing risk profiles and regulatory guidelines governing biomedical versus solid waste management operations.
Technologies and Tools Used
Biomedical Waste Technicians utilize advanced sterilization technologies such as autoclaves and chemical disinfectants, along with specialized containment tools like biohazard bags and sharps containers to safely handle infectious materials. Solid Waste Technicians rely on mechanized equipment including compactors, front-end loaders, and conveyor belts for efficient collection and processing of non-hazardous waste streams. Both roles incorporate GPS tracking systems and waste management software to optimize route planning and ensure regulatory compliance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Practices
Biomedical Waste Technicians manage hazardous medical waste, ensuring proper segregation, treatment, and disposal to prevent contamination and disease transmission, playing a critical role in public health safety. Solid Waste Technicians handle municipal and industrial non-hazardous waste, emphasizing recycling, landfill management, and resource recovery to reduce environmental footprint and promote sustainable material use. Both professions contribute to environmental protection through adherence to regulatory compliance and implementation of eco-friendly waste management practices.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Biomedical Waste Technicians specialize in handling hazardous medical waste, offering career growth through certifications in infection control and biohazard management, which can lead to supervisory roles or specialized compliance positions in healthcare facilities. Solid Waste Technicians manage municipal and industrial non-hazardous waste, with advancement opportunities in waste management operations, recycling program coordination, and environmental compliance roles within public agencies or private companies. Both paths provide distinct career trajectories, with biomedical waste careers often requiring stricter regulatory knowledge and solid waste roles emphasizing logistics and sustainability initiatives.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Biomedical Waste Technicians typically earn higher salaries, averaging $45,000 to $60,000 annually, due to specialized training in handling infectious and hazardous medical materials. Solid Waste Technicians have a median salary range of $35,000 to $50,000, reflecting broader responsibilities in managing municipal and industrial waste streams. Job outlook for Biomedical Waste Technicians is expected to grow 8% over the next decade, driven by healthcare industry expansion, while Solid Waste Technicians face a steady 6% growth supported by increasing environmental regulations and waste management needs.
Biomedical Waste Technician vs Solid Waste Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com