Solid waste engineers specialize in managing and designing systems for the collection, treatment, and disposal of non-liquid waste materials such as municipal garbage, recyclables, and industrial residues. Liquid waste engineers focus on the treatment and management of wastewater, sewage, and industrial effluents to prevent environmental contamination and promote water reclamation. Both specialize in sustainable waste management practices but address distinct challenges associated with solid and liquid waste streams.
Table of Comparison
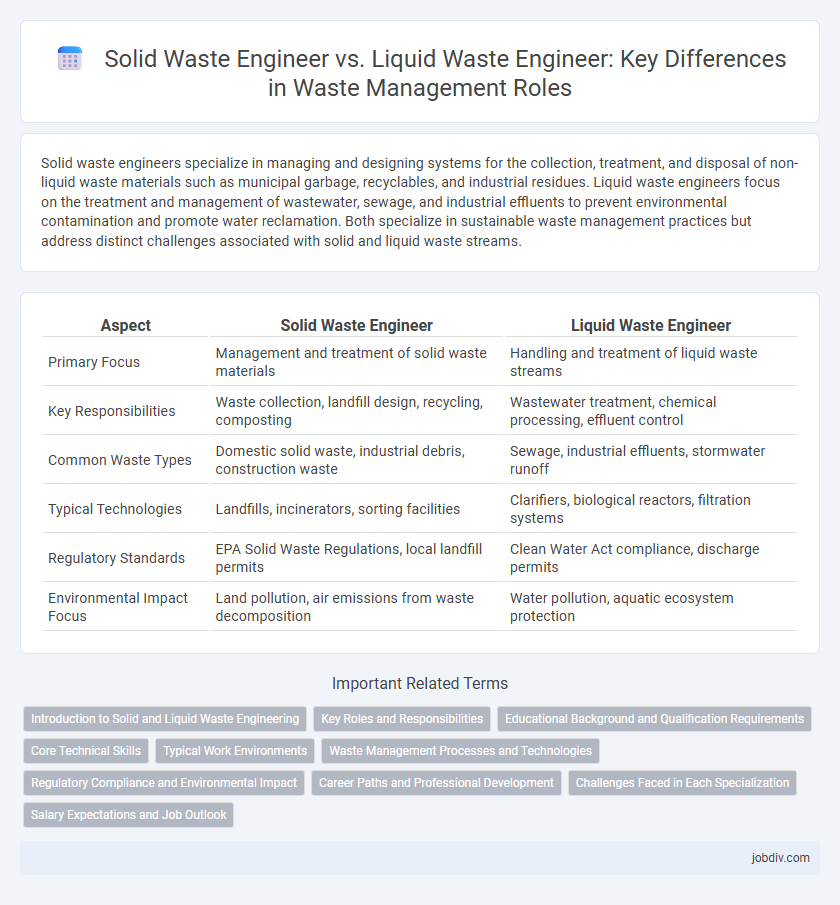
| Aspect | Solid Waste Engineer | Liquid Waste Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Management and treatment of solid waste materials | Handling and treatment of liquid waste streams |
| Key Responsibilities | Waste collection, landfill design, recycling, composting | Wastewater treatment, chemical processing, effluent control |
| Common Waste Types | Domestic solid waste, industrial debris, construction waste | Sewage, industrial effluents, stormwater runoff |
| Typical Technologies | Landfills, incinerators, sorting facilities | Clarifiers, biological reactors, filtration systems |
| Regulatory Standards | EPA Solid Waste Regulations, local landfill permits | Clean Water Act compliance, discharge permits |
| Environmental Impact Focus | Land pollution, air emissions from waste decomposition | Water pollution, aquatic ecosystem protection |
Introduction to Solid and Liquid Waste Engineering
Solid waste engineers specialize in the management, treatment, and disposal of non-liquid waste materials such as municipal garbage, industrial refuse, and construction debris, utilizing techniques like landfill design, recycling, and composting. Liquid waste engineers focus on the treatment and management of wastewater and industrial effluents through processes including biological treatment, chemical neutralization, and sludge dewatering to protect water quality. Both disciplines require expertise in environmental regulations, waste minimization strategies, and sustainable engineering practices to mitigate health risks and environmental impact.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Solid Waste Engineers specialize in the design, management, and optimization of systems for collection, treatment, and disposal of solid materials including municipal waste, construction debris, and hazardous solids, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Liquid Waste Engineers focus on the treatment, recycling, and safe disposal of wastewater and industrial effluents, employing technologies such as biological treatment processes, filtration, and chemical neutralization to prevent water pollution. Both roles require expertise in environmental impact assessment, regulatory standards, and sustainable waste management practices tailored to their respective waste streams.
Educational Background and Qualification Requirements
Solid Waste Engineers typically require a degree in environmental engineering, civil engineering, or related fields with a focus on waste management, landfill design, and recycling processes, emphasizing courses in soil mechanics and waste containment. Liquid Waste Engineers often hold degrees in chemical engineering, environmental engineering, or water resources engineering, specializing in wastewater treatment technologies, fluid mechanics, and contaminant transport. Both roles demand professional engineering licensure and practical experience in specialized waste management systems to address distinct challenges in solid and liquid waste handling.
Core Technical Skills
Solid Waste Engineers specialize in waste management techniques such as landfill design, leachate control, and solid waste collection systems, emphasizing materials characterization and waste compaction technologies. Liquid Waste Engineers focus on wastewater treatment processes, including biological treatment, chemical dosing, and membrane filtration technologies to manage sewage and industrial effluents. Both roles require expertise in environmental regulations, data analysis for pollution control, and the application of sustainable waste treatment methods.
Typical Work Environments
Solid waste engineers typically work in landfills, recycling facilities, and municipal waste management centers where they design systems for waste collection, sorting, and disposal. Liquid waste engineers are often employed at wastewater treatment plants, industrial processing facilities, and environmental agencies focusing on the treatment and management of sewage, industrial effluents, and contaminated water. Both roles require collaboration with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with environmental standards and sustainability goals.
Waste Management Processes and Technologies
Solid waste engineers specialize in the collection, processing, recycling, and disposal of non-liquid materials using technologies like landfills, incineration, and composting. Liquid waste engineers focus on treating wastewater and industrial effluents through processes such as sedimentation, biological treatment, and membrane filtration. Both roles leverage advanced waste management technologies to minimize environmental impact and enhance resource recovery.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Impact
Solid Waste Engineers specialize in managing non-liquid refuse such as municipal, industrial, and hazardous solid wastes, ensuring compliance with regulations like the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and local landfill statutes to minimize soil and groundwater contamination. Liquid Waste Engineers focus on treating wastewater and industrial effluents, adhering to the Clean Water Act (CWA) standards to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems. Both roles prioritize regulatory compliance and environmental impact mitigation, but Solid Waste Engineers primarily address land pollution risks while Liquid Waste Engineers target water quality preservation.
Career Paths and Professional Development
Solid waste engineers specialize in managing landfills, recycling systems, and waste treatment technologies, emphasizing materials handling and environmental compliance. Liquid waste engineers focus on wastewater treatment, sewer system design, and pollution control, requiring expertise in hydraulics and chemical processes. Career development for both roles involves advanced certifications in environmental engineering and opportunities in public infrastructure projects or private sector consulting.
Challenges Faced in Each Specialization
Solid waste engineers confront challenges such as managing large volumes of non-biodegradable materials, optimizing landfill design, and implementing effective recycling and waste diversion strategies to minimize environmental impact. Liquid waste engineers face complex issues involving the treatment and disposal of hazardous effluents, ensuring compliance with water quality regulations, and maintaining advanced wastewater treatment facilities to prevent contamination of water resources. Both specializations require innovative solutions to address evolving regulations, technological advancements, and the sustainability goals of waste management systems.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Solid Waste Engineers typically earn a median salary ranging from $65,000 to $85,000 annually, with job growth projected at 6% due to increasing municipal waste management needs. Liquid Waste Engineers, specializing in wastewater treatment and hazardous liquid disposal, command slightly higher salaries averaging $70,000 to $90,000, driven by stricter environmental regulations and demand for sustainable water solutions. Both fields offer robust job outlooks, but Liquid Waste Engineers may experience faster growth linked to advancements in water purification technology and regulatory compliance.
Solid Waste Engineer vs Liquid Waste Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com