Resellers in wholesale pet markets purchase products in bulk to sell directly to end consumers or smaller retailers, ensuring control over inventory and pricing. Brokers act as intermediaries who connect manufacturers with resellers or retailers without holding stock, facilitating deals while earning commissions. Understanding the distinct roles helps businesses optimize supply chains and negotiate better terms in the pet product industry.
Table of Comparison
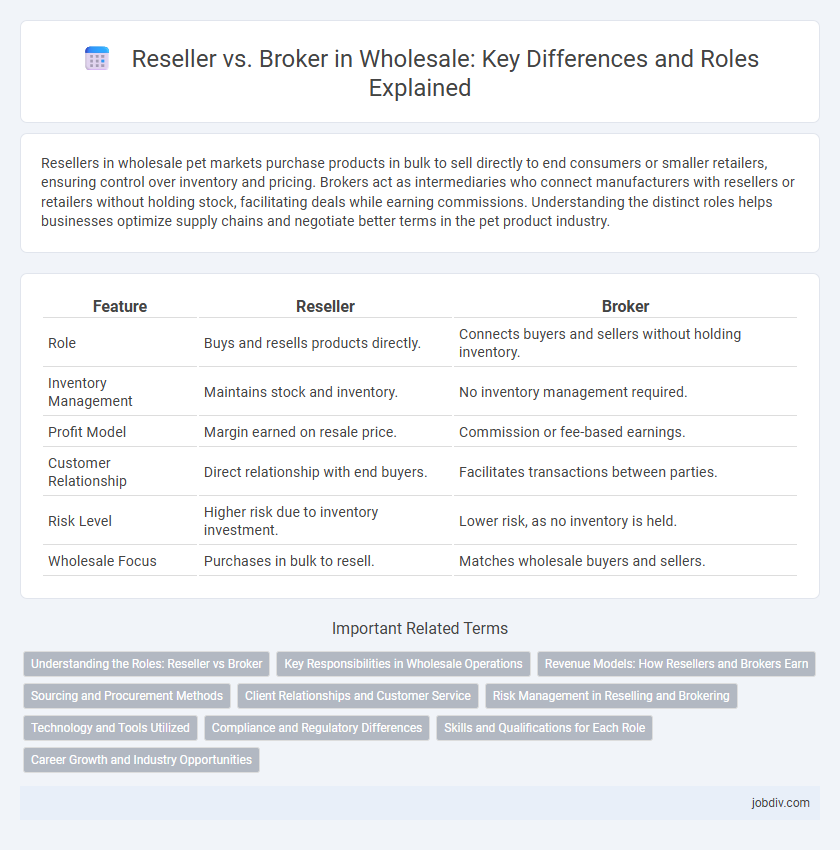
| Feature | Reseller | Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Buys and resells products directly. | Connects buyers and sellers without holding inventory. |
| Inventory Management | Maintains stock and inventory. | No inventory management required. |
| Profit Model | Margin earned on resale price. | Commission or fee-based earnings. |
| Customer Relationship | Direct relationship with end buyers. | Facilitates transactions between parties. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to inventory investment. | Lower risk, as no inventory is held. |
| Wholesale Focus | Purchases in bulk to resell. | Matches wholesale buyers and sellers. |
Understanding the Roles: Reseller vs Broker
Resellers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers or wholesalers and sell them directly to end customers, often adding value through marketing or customer service. Brokers act as intermediaries who facilitate sales between buyers and sellers without taking ownership of the products, earning commissions on successful transactions. Understanding these roles is crucial for businesses to optimize supply chain strategies and reduce overhead costs.
Key Responsibilities in Wholesale Operations
Resellers manage inventory, purchase goods in bulk, and maintain customer relationships to ensure efficient distribution within wholesale operations. Brokers act as intermediaries, facilitating deals between buyers and sellers without holding inventory, focusing on negotiation and market networking. Both roles are integral to optimizing supply chain efficiency and expanding market reach in wholesale distribution.
Revenue Models: How Resellers and Brokers Earn
Resellers earn revenue by purchasing products at wholesale prices and selling them at a markup, often benefiting from volume discounts and inventory management. Brokers generate income through commissions or fees by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers without owning the inventory. The key difference lies in resellers holding stock and assuming risk, while brokers leverage their network and negotiation skills to secure deals and earn commissions.
Sourcing and Procurement Methods
Resellers purchase products directly from manufacturers or distributors, managing inventory and controlling pricing to meet buyer demands. Brokers act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers without holding inventory, facilitating negotiations and securing deals through relationships. Sourcing in reseller models emphasizes bulk purchasing and stock management, while brokers rely on market knowledge and networking to procure goods efficiently.
Client Relationships and Customer Service
Resellers maintain direct client relationships by purchasing goods and managing inventory to fulfill customer orders, enabling personalized customer service and consistent communication. Brokers act as intermediaries, connecting buyers and sellers without holding inventory, which can limit their ability to provide hands-on support or handle after-sales service. Strong client relationships in wholesale depend on responsiveness and reliability, areas where resellers typically have an advantage over brokers.
Risk Management in Reselling and Brokering
Resellers assume inventory risk by purchasing and holding products until sale, requiring efficient stock management and demand forecasting to avoid losses. Brokers mitigate risk by facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers without owning the goods, focusing on negotiation and contract assurance. Effective risk management in reselling centers on inventory control and capital investment, while brokering emphasizes reputation, legal compliance, and transaction security.
Technology and Tools Utilized
Resellers leverage e-commerce platforms, inventory management software, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems to streamline order processing and maintain stock control. Brokers predominantly utilize communication technologies, digital marketplaces, and contract management tools to connect suppliers with buyers without handling physical inventory. Advanced analytics and AI-driven tools increasingly empower both roles to optimize pricing strategies and market insights in the wholesale sector.
Compliance and Regulatory Differences
Resellers purchase wholesale goods to sell directly to end customers, requiring strict adherence to product safety, labeling, and tax regulations to maintain compliance. Brokers facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers without handling the products, focusing on compliance related to licensing, contract laws, and disclosure requirements. Understanding these regulatory distinctions is essential for wholesalers managing legal risks and operational responsibilities in supply chain agreements.
Skills and Qualifications for Each Role
Resellers require strong sales and marketing skills, product knowledge, and customer relationship management to effectively promote and distribute wholesale goods. Brokers must possess excellent negotiation abilities, deep industry expertise, and networking skills to connect buyers and sellers while facilitating deals. Both roles benefit from strong communication and market analysis capabilities to optimize transaction outcomes in wholesale environments.
Career Growth and Industry Opportunities
Resellers typically build career growth through direct sales, inventory management, and customer relationships, gaining expertise in product knowledge and market demand. Brokers excel by connecting buyers and sellers without holding inventory, developing strong negotiation skills and industry networks that open diverse opportunities across sectors. Both roles offer unique pathways in wholesale, with resellers benefiting from operational control and brokers leveraging strategic partnerships for career advancement.
Reseller vs Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com