An Administrative Assistant primarily handles day-to-day clerical tasks such as scheduling, correspondence, and data entry to support organizational operations efficiently. An Administrative Coordinator oversees and manages multiple administrative functions, ensuring coordination between departments and optimizing workflow processes. Their role involves higher-level responsibility, often including project management and staff supervision within the administrative team.
Table of Comparison
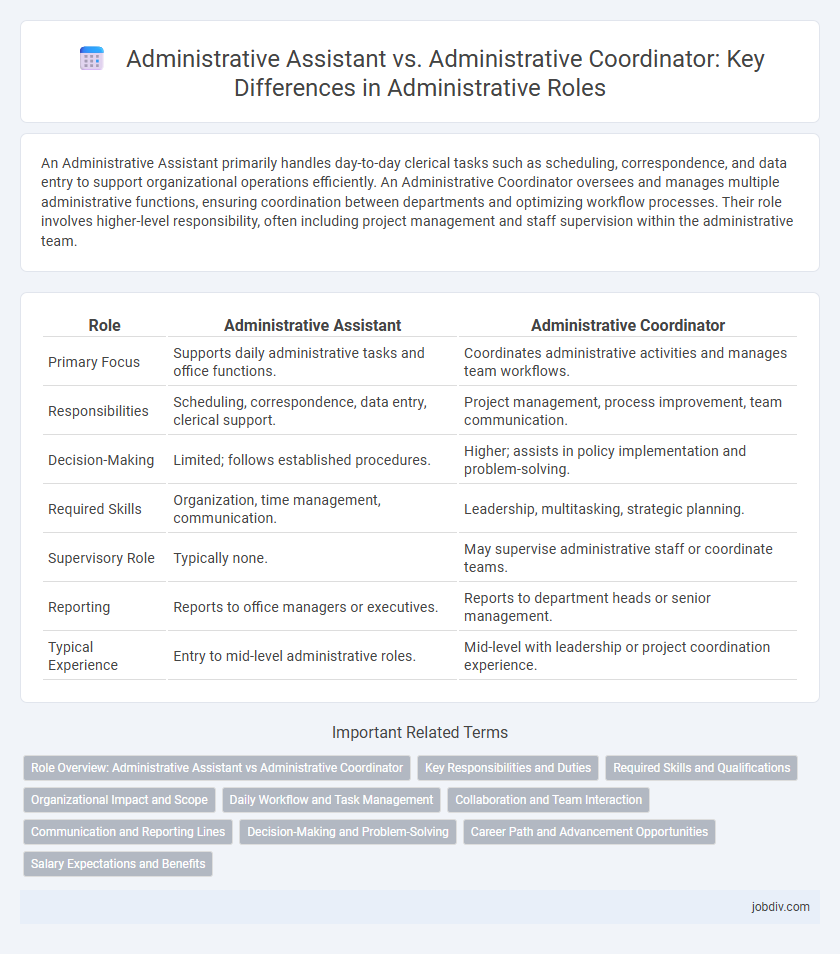
| Role | Administrative Assistant | Administrative Coordinator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Supports daily administrative tasks and office functions. | Coordinates administrative activities and manages team workflows. |
| Responsibilities | Scheduling, correspondence, data entry, clerical support. | Project management, process improvement, team communication. |
| Decision-Making | Limited; follows established procedures. | Higher; assists in policy implementation and problem-solving. |
| Required Skills | Organization, time management, communication. | Leadership, multitasking, strategic planning. |
| Supervisory Role | Typically none. | May supervise administrative staff or coordinate teams. |
| Reporting | Reports to office managers or executives. | Reports to department heads or senior management. |
| Typical Experience | Entry to mid-level administrative roles. | Mid-level with leadership or project coordination experience. |
Role Overview: Administrative Assistant vs Administrative Coordinator
An Administrative Assistant primarily supports daily office operations by managing schedules, handling correspondence, and coordinating meetings to ensure smooth workflow. An Administrative Coordinator takes on a broader scope, overseeing administrative projects, streamlining processes, and liaising between departments to optimize organizational efficiency. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but the coordinator typically assumes higher responsibility for project management and operational oversight.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Administrative Assistants primarily handle clerical tasks such as scheduling appointments, managing correspondence, and maintaining filing systems to support daily office operations. Administrative Coordinators oversee project coordination, workflow organization, and interdepartmental communication to ensure efficient process execution and resource allocation. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but Coordinators typically manage broader responsibilities involving team collaboration and strategic planning.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Administrative Assistants require strong organizational skills, proficiency in office software, and excellent communication abilities to manage daily tasks efficiently. Administrative Coordinators need advanced project management expertise, leadership capabilities, and strategic planning skills to oversee multiple administrative functions. Both roles demand attention to detail, multitasking aptitude, and the ability to coordinate effectively with various departments.
Organizational Impact and Scope
An Administrative Assistant typically handles routine clerical tasks, supporting daily operations and ensuring smooth workflow within a specific team or department. An Administrative Coordinator takes on a broader role, managing complex projects, coordinating between multiple departments, and implementing organizational policies to enhance efficiency. The scope of an Administrative Coordinator impacts cross-functional communication and strategic planning, while an Administrative Assistant focuses on operational support and task execution.
Daily Workflow and Task Management
Administrative Assistants primarily handle routine tasks such as calendar management, correspondence, and basic data entry, streamlining everyday office operations. Administrative Coordinators oversee and organize multiple projects, coordinate between departments, and manage resource allocation to ensure smooth workflow across teams. Their roles differ in scope, with Assistants focusing on task execution and Coordinators on strategic task management and process optimization.
Collaboration and Team Interaction
Administrative Assistants primarily support executives and teams by managing schedules, handling communications, and preparing documents, facilitating efficient individual and small group collaboration. Administrative Coordinators oversee broader office functions, coordinating between departments and leading team projects to ensure cohesive workflow and alignment of organizational goals. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but coordinators often engage in higher-level interaction and strategic collaboration across multiple teams.
Communication and Reporting Lines
Administrative Assistants primarily manage internal communication by acting as the liaison between team members and handling routine correspondence, ensuring efficient information flow. Administrative Coordinators oversee broader communication channels, coordinating between departments and external partners, with responsibilities extending to drafting and managing comprehensive reports. Reporting lines for Administrative Assistants typically involve direct supervision by office managers or department heads, while Administrative Coordinators often report to senior management or project leaders, reflecting their expanded communication and oversight roles.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Administrative Assistants primarily handle routine decision-making by managing schedules, organizing documents, and supporting daily office tasks to ensure smooth operations. Administrative Coordinators engage in higher-level problem-solving, coordinating multiple projects, resolving workflow conflicts, and implementing process improvements to enhance organizational efficiency. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Administrative Coordinators typically exercise greater autonomy in strategic decision-making within administrative functions.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Administrative Assistants typically begin their careers handling clerical tasks such as scheduling, data entry, and communication facilitation, providing a foundation in office management. Administrative Coordinators often advance to roles with increased responsibility, including project oversight, team coordination, and workflow optimization, positioning them for managerial opportunities. Career progression from Assistant to Coordinator involves developing skills in leadership, organization, and multi-departmental collaboration, essential for senior administrative or office management positions.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Administrative Assistant salaries typically range from $35,000 to $50,000 annually, with benefits often including health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans. Administrative Coordinators usually earn between $45,000 and $65,000 per year, reflecting greater responsibility, and their benefits packages may offer enhanced options like professional development stipends and performance bonuses. Both roles provide essential administrative support, but coordinators generally receive higher compensation and more comprehensive benefits due to their expanded duties.
Administrative Assistant vs Administrative Coordinator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com