An HR Administrator manages employee records, recruitment processes, and compliance with labor laws, ensuring smooth human resources operations. A Payroll Administrator specializes in processing employee salaries, tax deductions, and benefits, maintaining accurate payroll data and regulatory compliance. Both roles require attention to detail and understanding of employment regulations but differ in their core responsibilities and focus areas.
Table of Comparison
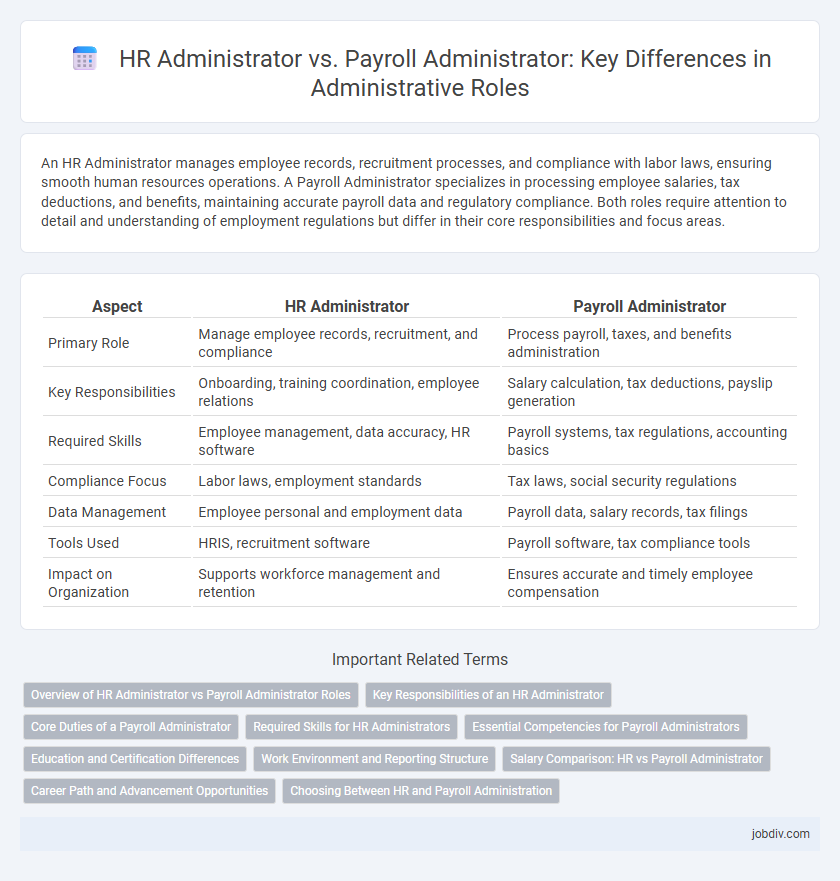
| Aspect | HR Administrator | Payroll Administrator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage employee records, recruitment, and compliance | Process payroll, taxes, and benefits administration |
| Key Responsibilities | Onboarding, training coordination, employee relations | Salary calculation, tax deductions, payslip generation |
| Required Skills | Employee management, data accuracy, HR software | Payroll systems, tax regulations, accounting basics |
| Compliance Focus | Labor laws, employment standards | Tax laws, social security regulations |
| Data Management | Employee personal and employment data | Payroll data, salary records, tax filings |
| Tools Used | HRIS, recruitment software | Payroll software, tax compliance tools |
| Impact on Organization | Supports workforce management and retention | Ensures accurate and timely employee compensation |
Overview of HR Administrator vs Payroll Administrator Roles
HR Administrators manage employee relations, recruitment, training, and compliance with labor laws, ensuring workforce efficiency and engagement. Payroll Administrators specialize in processing employee compensation, tax deductions, benefits management, and maintaining accurate payroll records to ensure timely and compliant salary distribution. Both roles are vital for organizational success, with HR focusing on people management and Payroll concentrating on financial administration.
Key Responsibilities of an HR Administrator
HR Administrators manage employee records, coordinate recruitment processes, and oversee onboarding to ensure compliance with labor laws and company policies. They handle benefits administration, employee relations, and training programs to support workforce development and engagement. Unlike Payroll Administrators, who focus on salary processing and tax compliance, HR Administrators maintain broader responsibilities centered on overall human resource management.
Core Duties of a Payroll Administrator
A Payroll Administrator is responsible for processing employee salaries, managing tax withholdings, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and company policies. Core duties include calculating wages, deductions, benefits, and overtime, as well as maintaining accurate payroll records and preparing payroll reports. This role often involves liaising with tax authorities and providing employees with pay-related information.
Required Skills for HR Administrators
HR Administrators require strong interpersonal and organizational skills to manage employee relations, recruitment, and compliance with labor laws efficiently. Proficiency in HR software, data management, and conflict resolution is essential for maintaining accurate records and supporting workforce development. Payroll Administrators prioritize expertise in payroll processing, tax regulations, and financial reporting, which differ significantly from the broader HR skill set.
Essential Competencies for Payroll Administrators
Payroll Administrators require strong numerical proficiency, attention to detail, and comprehensive knowledge of tax regulations and compliance standards to accurately process employee salaries and deductions. Mastery of payroll software and data confidentiality practices ensures secure and efficient handling of sensitive financial information. Effective communication skills are essential for resolving payroll discrepancies and liaising with tax authorities and internal departments.
Education and Certification Differences
HR Administrators typically require a bachelor's degree in human resources, business administration, or a related field, with certifications such as SHRM-CP or PHR enhancing their credentials. Payroll Administrators often hold degrees in accounting, finance, or business, and benefit from certifications like the Certified Payroll Professional (CPP) which focus on payroll laws and tax regulations. The distinction in education centers on HR management versus financial accuracy and compliance in payroll processing.
Work Environment and Reporting Structure
HR Administrators typically work within human resources departments, collaborating closely with recruitment, training, and employee relations teams, often reporting to the HR Manager or Director. Payroll Administrators are usually situated in finance or payroll departments, focusing on salary processing, tax compliance, and benefits administration, with direct reporting lines to the Payroll Manager or Finance Director. Both roles require coordination with multiple departments, but HR Administrators emphasize employee lifecycle management while Payroll Administrators prioritize payroll accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Salary Comparison: HR vs Payroll Administrator
Salary comparison between an HR Administrator and a Payroll Administrator reveals that Payroll Administrators typically earn a higher median salary due to specialized expertise in payroll processing, tax regulations, and compliance. HR Administrators handle broader responsibilities including employee relations, recruitment, and benefits management, which may result in slightly lower compensation compared to the more technical payroll role. Variations in salary depend on industry, location, and company size, with Payroll Administrators often commanding premiums for their critical role in ensuring accurate employee compensation.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
HR Administrators typically have a broader scope of responsibilities, including employee relations, recruitment, and compliance, which positions them for advancement into roles such as HR Manager or Talent Acquisition Specialist. Payroll Administrators focus on processing wages, benefits, and tax deductions, developing expertise that can lead to senior payroll management or compensation and benefits analyst roles. Career progression in HR administration often involves expanding strategic skills, while payroll administrators advance by deepening technical payroll knowledge and regulatory compliance expertise.
Choosing Between HR and Payroll Administration
Choosing between an HR Administrator and a Payroll Administrator depends on organizational needs; HR Administrators manage employee relations, recruitment, and compliance while Payroll Administrators focus on salary processing, tax deductions, and benefits administration. Companies prioritizing workforce management and policy enforcement benefit from HR administration, whereas those emphasizing accurate compensation and regulatory payroll compliance require specialized payroll administration. Assessing company size, complexity of benefits, and regulatory demands helps determine the optimal role for efficient administration.
HR Administrator vs Payroll Administrator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com