School administrators oversee the overall management and strategic planning of educational institutions, including staff supervision, budget allocation, and policy implementation. School secretaries handle daily administrative tasks such as managing communications, maintaining records, and supporting both staff and students with organizational needs. While administrators focus on leadership and decision-making, secretaries ensure smooth operational functions within the school environment.
Table of Comparison
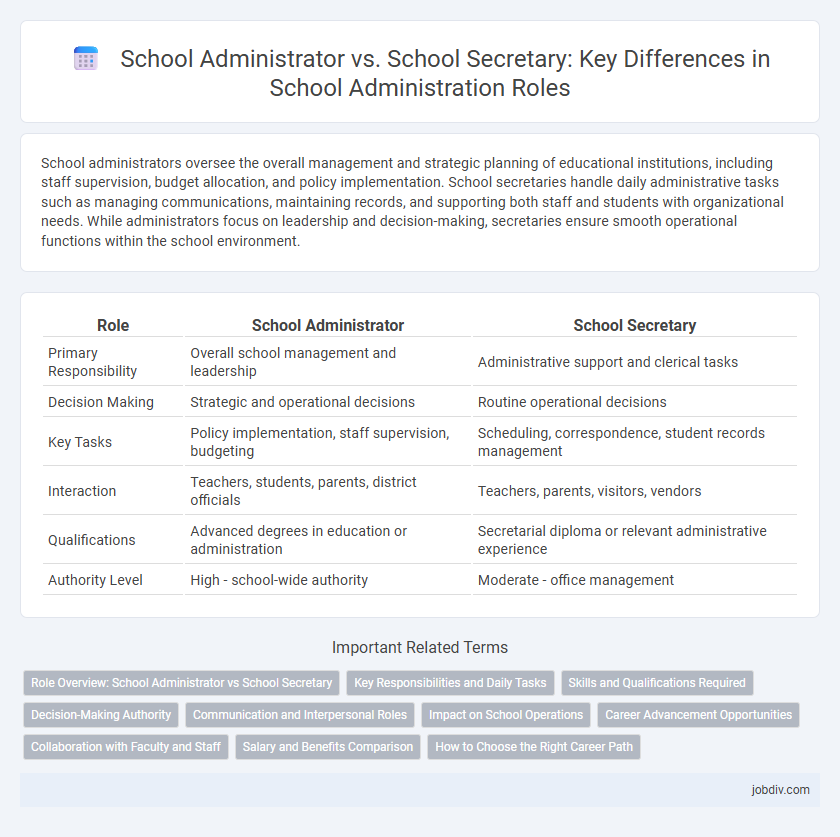
| Role | School Administrator | School Secretary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Overall school management and leadership | Administrative support and clerical tasks |
| Decision Making | Strategic and operational decisions | Routine operational decisions |
| Key Tasks | Policy implementation, staff supervision, budgeting | Scheduling, correspondence, student records management |
| Interaction | Teachers, students, parents, district officials | Teachers, parents, visitors, vendors |
| Qualifications | Advanced degrees in education or administration | Secretarial diploma or relevant administrative experience |
| Authority Level | High - school-wide authority | Moderate - office management |
Role Overview: School Administrator vs School Secretary
School administrators oversee the overall management of educational institutions, including policy implementation, staff coordination, and budgeting, ensuring smooth school operations. School secretaries focus on administrative support tasks such as managing communications, scheduling appointments, maintaining student records, and facilitating office functions. Both roles are essential for effective school administration, with administrators handling strategic leadership and secretaries managing daily clerical duties.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
School administrators oversee the overall management of educational institutions, including policy implementation, staff supervision, and student discipline, ensuring a conducive learning environment. School secretaries handle daily clerical tasks such as managing correspondence, maintaining student records, scheduling appointments, and supporting communication between staff, students, and parents. Both roles are essential for smooth school operations but differ significantly in scope, with administrators focusing on strategic leadership and secretaries on administrative support.
Skills and Qualifications Required
School administrators typically require advanced degrees in education leadership or administration, strong organizational skills, and experience in policy implementation and staff management. School secretaries need proficiency in office software, excellent communication abilities, and skills in scheduling, record-keeping, and customer service. Both roles demand attention to detail and effective multitasking, but administrators focus more on leadership and decision-making, whereas secretaries prioritize clerical and operational support.
Decision-Making Authority
School administrators possess significant decision-making authority, overseeing policies, disciplinary actions, and resource allocation to shape the school's educational environment. In contrast, school secretaries primarily execute administrative support tasks, managing records and communications without the power to make high-level decisions. The distinction in authority ensures that strategic and operational choices are guided by trained administrators rather than clerical staff.
Communication and Interpersonal Roles
School administrators lead communication by setting policies, coordinating with staff, and liaising with parents to ensure smooth school operations. School secretaries serve as the primary point of contact, managing daily communication, scheduling, and supporting interpersonal interactions among teachers, students, and parents. Both roles are essential for maintaining effective communication channels and fostering a collaborative educational environment.
Impact on School Operations
School administrators oversee strategic planning, policy implementation, and coordination of educational programs, significantly shaping school operations and overall academic success. School secretaries manage daily administrative tasks such as scheduling, communication, and record-keeping, ensuring smooth front-office operations and supporting staff and students efficiently. Both roles are critical; administrators drive decision-making and leadership, while secretaries maintain organizational functionality vital for effective school management.
Career Advancement Opportunities
School administrators have broader career advancement opportunities, often progressing to roles such as principals, district managers, or educational consultants due to their leadership responsibilities and decision-making authority. School secretaries typically advance within administrative support roles, moving toward senior secretarial positions or office management but face limitations in leadership pathways compared to administrators. Professional development and higher education significantly enhance career mobility for both roles, with administrators benefiting more from advanced degrees in education leadership.
Collaboration with Faculty and Staff
School administrators coordinate with faculty to develop academic programs, manage staff schedules, and implement school policies ensuring a cohesive educational environment. School secretaries facilitate communication between teachers, administrators, and parents by managing correspondence, organizing meetings, and maintaining records. Effective collaboration between school administrators and secretaries enhances organizational efficiency and supports student success.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
School administrators typically earn higher salaries than school secretaries due to their greater responsibilities, with average annual pay ranging from $60,000 to $95,000 compared to $30,000 to $45,000 for secretaries. Benefits for school administrators often include comprehensive health insurance, retirement plans, and performance bonuses, whereas school secretaries usually receive basic health coverage and standard retirement benefits. Salary and benefits vary by district size and geographic location, significantly influencing overall compensation packages.
How to Choose the Right Career Path
Choosing between a school administrator and school secretary career path depends on leadership aspirations and administrative responsibilities. School administrators oversee operations, policy implementation, and student outcomes, requiring advanced education and decision-making skills. School secretaries focus on clerical tasks, communication, and office management, offering entry-level opportunities with less emphasis on leadership roles.
School Administrator vs School Secretary Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com