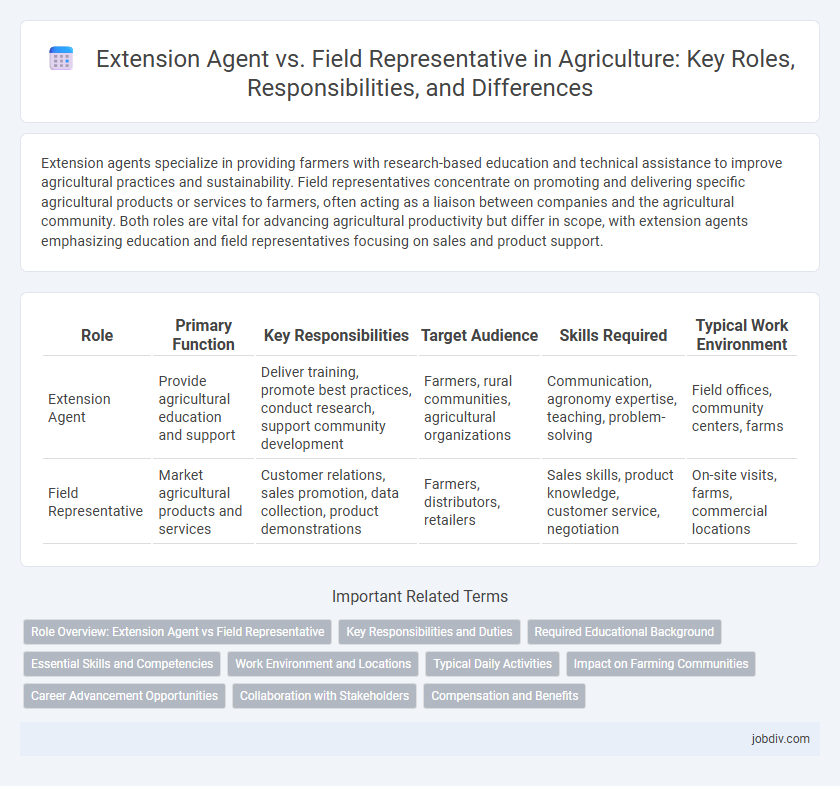
Extension agents specialize in providing farmers with research-based education and technical assistance to improve agricultural practices and sustainability. Field representatives concentrate on promoting and delivering specific agricultural products or services to farmers, often acting as a liaison between companies and the agricultural community. Both roles are vital for advancing agricultural productivity but differ in scope, with extension agents emphasizing education and field representatives focusing on sales and product support.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Primary Function | Key Responsibilities | Target Audience | Skills Required | Typical Work Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extension Agent | Provide agricultural education and support | Deliver training, promote best practices, conduct research, support community development | Farmers, rural communities, agricultural organizations | Communication, agronomy expertise, teaching, problem-solving | Field offices, community centers, farms |
| Field Representative | Market agricultural products and services | Customer relations, sales promotion, data collection, product demonstrations | Farmers, distributors, retailers | Sales skills, product knowledge, customer service, negotiation | On-site visits, farms, commercial locations |
Role Overview: Extension Agent vs Field Representative
Extension agents provide expert guidance and training to farmers on crop management, pest control, and sustainable practices, facilitating knowledge transfer from research institutions to agricultural communities. Field representatives focus on promoting agricultural products and services, gathering market feedback, and supporting client relationships within specific geographic regions. Both roles are integral to enhancing agricultural productivity, but extension agents emphasize education and community outreach, while field representatives prioritize sales and customer engagement.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Extension agents provide farmers with education on crop management, pest control, and sustainable practices through workshops and on-site visits, aiming to improve agricultural productivity and community well-being. Field representatives act as liaisons between agricultural companies and farmers, promoting products such as seeds, fertilizers, and machinery while gathering market feedback to support product development and sales strategies. Both roles require strong communication skills but differ in focus: extension agents prioritize knowledge transfer and advisory services, whereas field representatives emphasize sales and customer relationship management.
Required Educational Background
Extension agents typically require a bachelor's degree in agriculture, horticulture, or a related field emphasizing scientific knowledge and community education skills. Field representatives often hold degrees in agricultural business, agronomy, or marketing, highlighting expertise in sales and client relations within the agricultural sector. Both roles prioritize practical agricultural experience coupled with formal education aligned to their specific responsibilities.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Extension Agents require strong communication and educational skills to effectively transfer scientific knowledge to farmers and rural communities, emphasizing training in sustainable agricultural practices and resource management. Field Representatives must possess in-depth technical knowledge of agricultural products and market trends, along with negotiation and customer service skills to facilitate sales and client relationships. Both roles demand problem-solving abilities, adaptability to field conditions, and proficiency in data collection and reporting for informed decision-making.
Work Environment and Locations
Extension Agents primarily operate within rural communities, farms, and agricultural research centers, providing direct support and education to farmers in the field. Field Representatives often work for agribusiness companies, spending considerable time at farms, trade shows, and corporate offices to promote products and gather market insights. Both roles require significant travel but differ as Extension Agents focus on public agricultural outreach, while Field Representatives emphasize commercial relationships and sales.
Typical Daily Activities
Extension agents conduct educational workshops, provide technical advice to farmers, and assess crop and livestock conditions to promote best agricultural practices. Field representatives focus on monitoring product performance, managing client relationships, and delivering field demonstrations to support agricultural suppliers. Both roles involve data collection, reporting, and facilitating communication between agricultural stakeholders for improved productivity.
Impact on Farming Communities
Extension agents provide essential education and resources directly to farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural practices and improving crop yields. Field representatives serve as vital links between agricultural companies and farming communities, facilitating the adoption of new technologies and input supplies. Both roles significantly enhance farm productivity and community resilience by promoting knowledge exchange and access to innovations.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Extension agents typically have broader career advancement opportunities due to their roles in education, research, and community engagement within agricultural sectors, allowing progression into specialized or administrative positions. Field representatives often advance by developing expertise in specific crops or products, moving into senior sales, marketing, or technical advisory roles within agribusiness firms. Both career paths benefit from continuous professional development and networking within agricultural organizations to enhance progression potential.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Extension agents collaborate closely with farmers, researchers, and government agencies to implement sustainable agricultural practices and deliver educational resources effectively. Field representatives engage directly with agribusinesses, suppliers, and community leaders to facilitate the adoption of new technologies and market access initiatives. Both roles require strong communication skills and stakeholder management to drive innovation and improve agricultural productivity.
Compensation and Benefits
Extension Agents typically receive higher compensation packages compared to Field Representatives due to their advanced education and specialized expertise in agricultural practices. Benefits for Extension Agents often include professional development opportunities, health insurance, retirement plans, and performance-based bonuses, reflecting their role in community education and research. Field Representatives generally have more modest salary scales but may receive travel allowances, commissions, and job-related expense reimbursements tied to their direct sales and client engagement activities.
Extension Agent vs Field Representative Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com