Aquaponics operators manage integrated systems combining fish farming and plant cultivation, optimizing nutrient cycles to enhance sustainability and reduce waste. Hydroponics operators focus solely on soilless plant growth using nutrient-rich water, emphasizing precise control over environmental factors for maximum yield. Both roles require expertise in water management and plant science, but aquaponics adds an aquatic ecosystem component that demands additional skills in fish care.
Table of Comparison
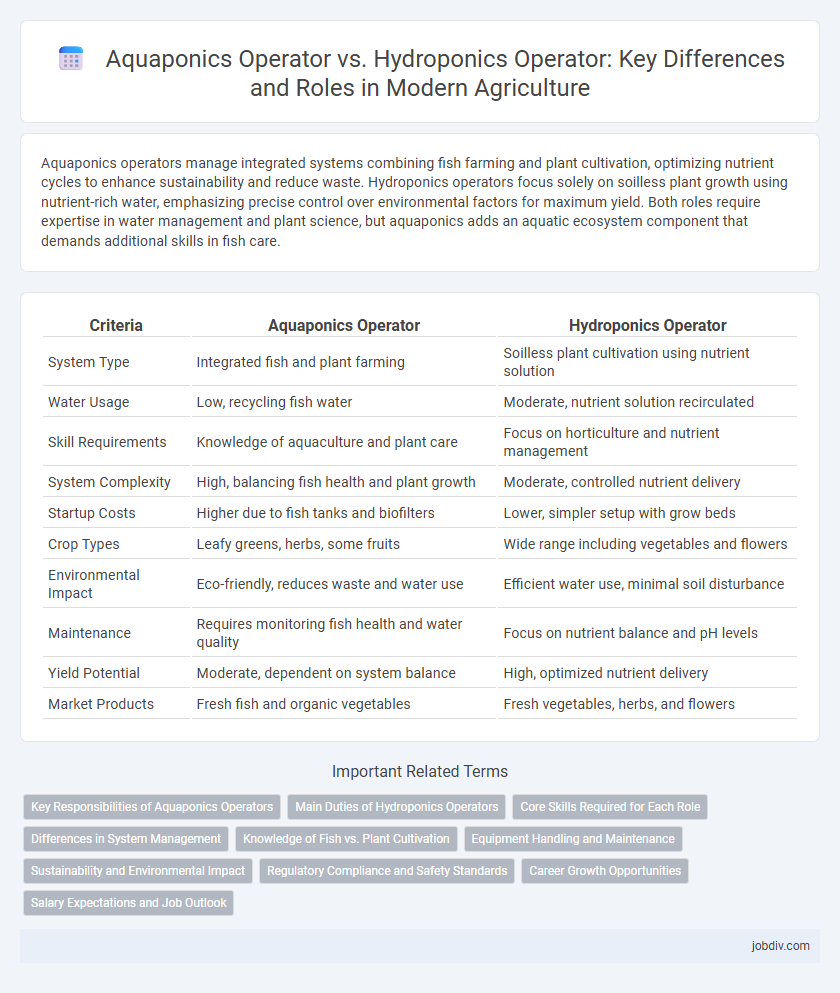
| Criteria | Aquaponics Operator | Hydroponics Operator |
|---|---|---|
| System Type | Integrated fish and plant farming | Soilless plant cultivation using nutrient solution |
| Water Usage | Low, recycling fish water | Moderate, nutrient solution recirculated |
| Skill Requirements | Knowledge of aquaculture and plant care | Focus on horticulture and nutrient management |
| System Complexity | High, balancing fish health and plant growth | Moderate, controlled nutrient delivery |
| Startup Costs | Higher due to fish tanks and biofilters | Lower, simpler setup with grow beds |
| Crop Types | Leafy greens, herbs, some fruits | Wide range including vegetables and flowers |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces waste and water use | Efficient water use, minimal soil disturbance |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring fish health and water quality | Focus on nutrient balance and pH levels |
| Yield Potential | Moderate, dependent on system balance | High, optimized nutrient delivery |
| Market Products | Fresh fish and organic vegetables | Fresh vegetables, herbs, and flowers |
Key Responsibilities of Aquaponics Operators
Aquaponics operators manage integrated systems combining fish farming and plant cultivation, ensuring optimal water quality, nutrient cycling, and system balance. They continually monitor water parameters like pH, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates, adjusting feeding and filtration to maintain healthy aquatic livestock and robust plant growth. Regular maintenance of pumps, tanks, and bio-filters is essential to sustain a stable aquaponic environment, distinguishing their role from hydroponics operators who focus solely on soil-less plant cultivation without animal husbandry.
Main Duties of Hydroponics Operators
Hydroponics operators manage nutrient solution formulation and monitor water quality to optimize plant growth in soil-less systems. They calibrate and maintain equipment such as pumps, lighting, and climate control to ensure ideal environmental conditions. Regularly inspecting plant health and adjusting nutrient delivery schedules are essential duties to maximize yield and prevent diseases.
Core Skills Required for Each Role
Aquaponics operators require expertise in managing symbiotic relationships between aquatic animals and plants, including water quality monitoring, fish health management, and nutrient cycling. Hydroponics operators focus on skills related to soilless plant cultivation, such as nutrient solution formulation, pH and EC control, and precise environmental regulation. Both roles demand strong knowledge of plant biology, system maintenance, and problem-solving abilities tailored to their specific cultivation methods.
Differences in System Management
Aquaponics operators manage a symbiotic system combining fish farming and plant cultivation, requiring expertise in water quality, fish health, and nutrient cycling to maintain balance. Hydroponics operators focus exclusively on soilless plant growth, optimizing nutrient solutions and environmental conditions for maximum crop yield. The key distinction lies in aquaponics demanding continuous monitoring of both aquatic life and plants, whereas hydroponics centers solely on precise nutrient and pH management for plants.
Knowledge of Fish vs. Plant Cultivation
An Aquaponics Operator requires comprehensive knowledge in fish biology, water quality management, and aquatic ecosystem balance to sustain healthy fish populations, alongside plant cultivation expertise. In contrast, a Hydroponics Operator focuses primarily on optimizing nutrient solutions, light conditions, and plant growth media without managing aquatic animals. Mastery of fish health and behavior distinctly differentiates aquaponics operations, while hydroponics emphasizes plant physiology and controlled environment agriculture techniques.
Equipment Handling and Maintenance
Aquaponics operators manage integrated systems combining fish tanks and plant beds, requiring expertise in maintaining water quality equipment, pumps, and biofilters to balance aquatic and plant health. Hydroponics operators focus on nutrient delivery systems, such as pumps, grow trays, and lighting, ensuring precise control of water pH and nutrient concentration for optimal plant growth. Both roles demand regular monitoring and calibration of equipment to prevent system failures and maximize crop yields.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Aquaponics operators integrate fish farming with plant cultivation, creating a closed-loop system that recycles water and nutrients, significantly reducing waste and conserving resources. Hydroponics operators grow plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, offering efficient water use but typically relying on synthetic nutrients, which can raise sustainability concerns. Both systems reduce land use and pesticide reliance, but aquaponics generally delivers higher environmental benefits through sustainable fish waste recycling and minimal fertilizer inputs.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Aquaponics operators must comply with regulations governing both aquaculture and horticulture, including water quality, fish health standards, and organic certification requirements, which often makes their regulatory landscape more complex than that of hydroponics operators. Hydroponics operators focus primarily on plant nutrient delivery and greenhouse safety standards, with fewer regulations related to animal welfare or water discharge. Both roles demand adherence to local agricultural laws, food safety protocols such as GAP (Good Agricultural Practices), and workplace safety standards governed by OSHA or equivalent agencies.
Career Growth Opportunities
Aquaponics operators benefit from expanding interest in sustainable agriculture, combining fish farming with plant cultivation to create diverse skill sets that enhance job market resilience. Hydroponics operators experience strong demand driven by urban farming and resource-efficient crop production, with careers advancing toward specialized roles in system design and crop management. Both fields offer promising career growth, but aquaponics provides unique interdisciplinary opportunities appealing to innovative agricultural technologies.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Aquaponics operators typically earn between $40,000 and $60,000 annually due to the integrated nature of fish and plant systems, while hydroponics operators generally make $35,000 to $55,000, reflecting the widespread adoption of soil-less farming techniques. Job outlook for aquaponics is growing as sustainable agriculture gains traction, with a projected employment increase of 10% over the next decade, whereas hydroponics operators see a steady 7% growth driven by advancements in controlled-environment agriculture. Both fields benefit from the rising demand for efficient food production, but aquaponics offers niche opportunities in sustainability-focused markets.
Aquaponics Operator vs Hydroponics Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com