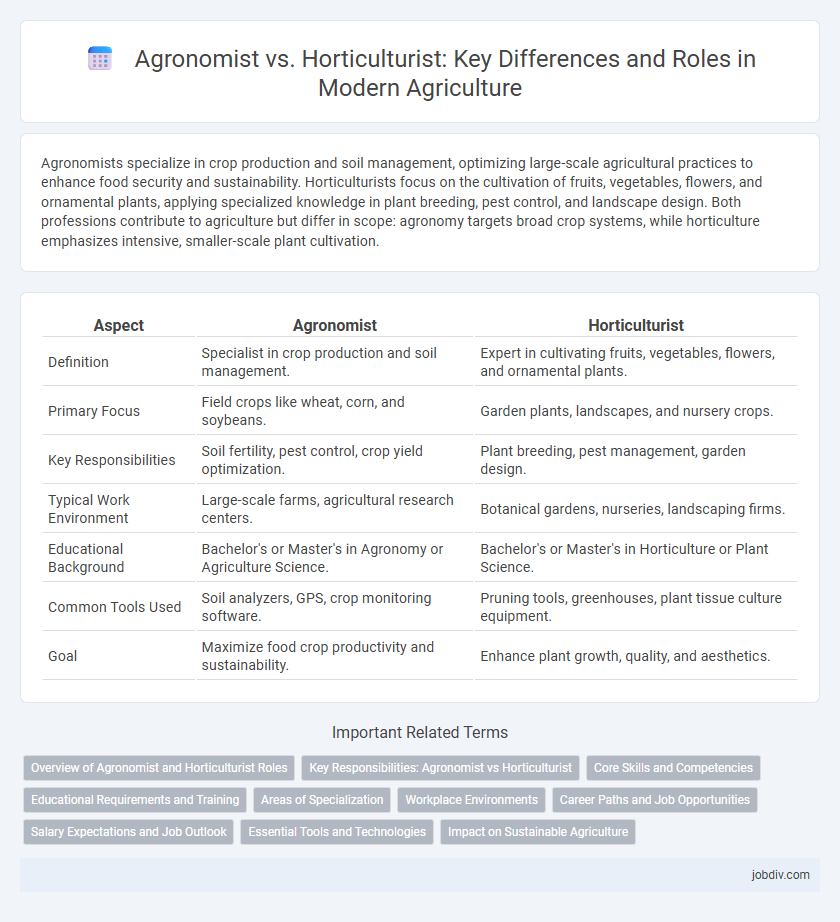
Agronomists specialize in crop production and soil management, optimizing large-scale agricultural practices to enhance food security and sustainability. Horticulturists focus on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants, applying specialized knowledge in plant breeding, pest control, and landscape design. Both professions contribute to agriculture but differ in scope: agronomy targets broad crop systems, while horticulture emphasizes intensive, smaller-scale plant cultivation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Agronomist | Horticulturist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialist in crop production and soil management. | Expert in cultivating fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants. |
| Primary Focus | Field crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans. | Garden plants, landscapes, and nursery crops. |
| Key Responsibilities | Soil fertility, pest control, crop yield optimization. | Plant breeding, pest management, garden design. |
| Typical Work Environment | Large-scale farms, agricultural research centers. | Botanical gardens, nurseries, landscaping firms. |
| Educational Background | Bachelor's or Master's in Agronomy or Agriculture Science. | Bachelor's or Master's in Horticulture or Plant Science. |
| Common Tools Used | Soil analyzers, GPS, crop monitoring software. | Pruning tools, greenhouses, plant tissue culture equipment. |
| Goal | Maximize food crop productivity and sustainability. | Enhance plant growth, quality, and aesthetics. |
Overview of Agronomist and Horticulturist Roles
Agronomists specialize in crop production and soil management, aiming to improve agricultural yield and sustainability through scientific research and field experiments. Horticulturists focus on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants, enhancing plant growth, quality, and aesthetics for commercial and recreational use. Both professionals contribute to agriculture but differ in scope, with agronomists addressing large-scale crop systems and horticulturists concentrating on intensive cultivation and plant care.
Key Responsibilities: Agronomist vs Horticulturist
Agronomists specialize in crop production and soil management, focusing on enhancing yield and sustainability through scientific research and field experiments. Horticulturists concentrate on the cultivation, breeding, and maintenance of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, emphasizing plant health, aesthetics, and productivity. Both professions utilize plant science but differ in scope, with agronomists addressing large-scale farming systems and horticulturists specializing in garden and greenhouse environments.
Core Skills and Competencies
Agronomists possess expertise in soil management, crop production, and sustainable farming practices, emphasizing large-scale agricultural systems and crop yield optimization. Horticulturists specialize in plant propagation, pest control, and landscape design, focusing on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants. Both professions require strong knowledge of plant biology, but agronomists prioritize field-scale agricultural techniques while horticulturists excel in detailed plant care and decorative cultivation.
Educational Requirements and Training
Agronomists typically require a bachelor's degree in agronomy, crop science, or soil science, with advanced positions often needing a master's or doctoral degree focusing on plant genetics, soil management, or agricultural technology. Horticulturists generally pursue degrees in horticulture, botany, or plant sciences, emphasizing training in plant cultivation, greenhouse management, and landscape design during their studies. Both careers benefit from hands-on internships, research projects, and certifications such as Certified Crop Adviser (CCA) for agronomists or Certified Professional Horticulturist (CPH) for horticulturists to enhance practical expertise and industry credibility.
Areas of Specialization
Agronomists specialize in crop production and soil management, focusing on large-scale agriculture to improve field crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans. Horticulturists concentrate on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants, emphasizing plant breeding, pest control, and landscape design. Both experts play crucial roles in sustainable agriculture but differ in their approach to plant science and crop management.
Workplace Environments
Agronomists primarily work in large-scale agricultural settings such as farms, research institutions, and government agencies, focusing on crop production, soil management, and sustainable farming practices. Horticulturists are often found in botanical gardens, nurseries, greenhouses, and landscape design companies, specializing in the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants. Both professions may also collaborate in academic or extension services to improve plant health and productivity.
Career Paths and Job Opportunities
Agronomists primarily focus on large-scale crop production, soil management, and sustainable farming techniques, making them essential in agricultural research, farm management, and government agencies. Horticulturists specialize in the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants, offering career opportunities in landscape design, greenhouse management, and botanical gardens. Both career paths provide roles in academia, agri-business companies, and environmental consulting, with agronomy emphasizing field-based crop systems while horticulture centers on plant cultivation and garden aesthetics.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Agronomists typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $55,000 to $80,000, driven by demand in crop production, soil management, and sustainable farming practices, with job growth projected at 5% over the next decade according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Horticulturists, specializing in plant cultivation, landscape design, and greenhouse management, have slightly lower median salaries around $45,000 to $65,000 but benefit from increasing opportunities in urban farming and botanical research, contributing to a steady employment growth rate of approximately 4%. Both careers offer strong prospects in agriculture, yet agronomists tend to have broader applications in large-scale farming operations compared to horticulturists' niche focus on plant science and ornamental crops.
Essential Tools and Technologies
Agronomists rely heavily on soil testing kits, GPS-guided equipment, and crop modeling software to optimize large-scale field production and enhance sustainable farming practices. Horticulturists utilize precision irrigation systems, controlled environment agriculture tools like greenhouses, and plant disease diagnostic technologies to improve the quality and yield of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. Both professions integrate advanced data analytics and remote sensing technologies to monitor plant health and productivity efficiently.
Impact on Sustainable Agriculture
Agronomists specialize in optimizing crop production on a large scale by improving soil health, enhancing nutrient management, and promoting efficient water use, which directly supports sustainable agriculture practices. Horticulturists focus on the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, advancing sustainable techniques through integrated pest management, genetic plant improvement, and biodiversity conservation. Both roles are essential for enhancing agricultural sustainability by balancing productivity with environmental stewardship and resource conservation.
Agronomist vs Horticulturist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com