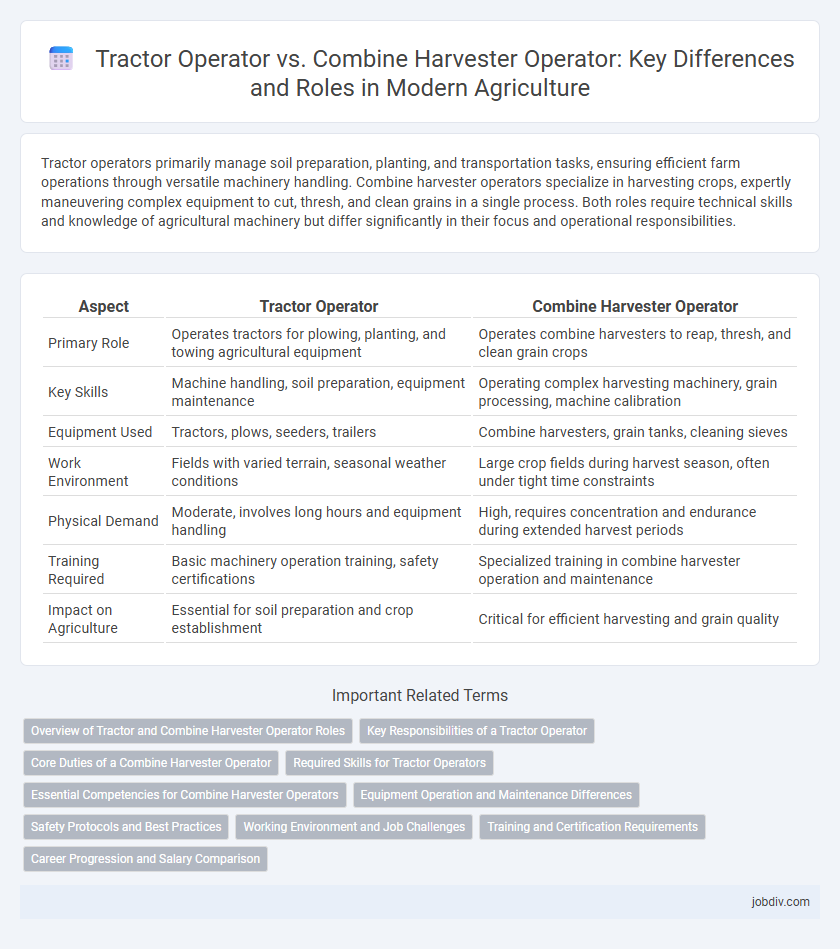
Tractor operators primarily manage soil preparation, planting, and transportation tasks, ensuring efficient farm operations through versatile machinery handling. Combine harvester operators specialize in harvesting crops, expertly maneuvering complex equipment to cut, thresh, and clean grains in a single process. Both roles require technical skills and knowledge of agricultural machinery but differ significantly in their focus and operational responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tractor Operator | Combine Harvester Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Operates tractors for plowing, planting, and towing agricultural equipment | Operates combine harvesters to reap, thresh, and clean grain crops |
| Key Skills | Machine handling, soil preparation, equipment maintenance | Operating complex harvesting machinery, grain processing, machine calibration |
| Equipment Used | Tractors, plows, seeders, trailers | Combine harvesters, grain tanks, cleaning sieves |
| Work Environment | Fields with varied terrain, seasonal weather conditions | Large crop fields during harvest season, often under tight time constraints |
| Physical Demand | Moderate, involves long hours and equipment handling | High, requires concentration and endurance during extended harvest periods |
| Training Required | Basic machinery operation training, safety certifications | Specialized training in combine harvester operation and maintenance |
| Impact on Agriculture | Essential for soil preparation and crop establishment | Critical for efficient harvesting and grain quality |
Overview of Tractor and Combine Harvester Operator Roles
Tractor operators manage and maneuver agricultural tractors to perform tasks like plowing, planting, and transporting materials, ensuring efficient field preparation and maintenance. Combine harvester operators specialize in operating complex harvesting machines that simultaneously reap, thresh, and clean grain crops, maximizing yield and minimizing crop loss. Both roles require technical skill and knowledge of machinery to support productive farming operations.
Key Responsibilities of a Tractor Operator
A Tractor Operator is responsible for operating heavy machinery to prepare fields by plowing, tilling, and planting crops, ensuring optimal soil conditions for growth. They maintain and inspect tractors regularly to prevent mechanical failures during critical farming periods. Efficient management of fuel consumption and adherence to safety protocols are also essential to maximize productivity and minimize downtime.
Core Duties of a Combine Harvester Operator
A Combine Harvester Operator is responsible for efficiently operating the combine harvester to ensure proper harvesting of crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans while minimizing grain loss and damage. Key duties include monitoring machine performance, adjusting settings for varying field conditions, and performing routine maintenance to prevent downtime. This role requires strong knowledge of crop characteristics, machine mechanics, and safety protocols to optimize harvesting productivity.
Required Skills for Tractor Operators
Tractor operators must have strong mechanical skills to manage and maintain complex farming machinery, ensuring efficient fieldwork and reducing downtime. Proficiency in GPS technology and precision farming tools enhances their ability to operate tractors accurately, optimizing crop planting and soil management. Physical stamina and attention to safety protocols are critical for handling long hours in varying weather conditions while minimizing risks on the farm.
Essential Competencies for Combine Harvester Operators
Combine Harvester Operators must possess advanced mechanical skills to efficiently operate complex harvesting machinery, ensuring minimal crop loss and maximum yield. Proficiency in monitoring grain moisture levels, adjusting concave clearance, and managing threshing speed is essential for maintaining grain quality and machine performance. Strong spatial awareness and quick decision-making enable operators to navigate varying field conditions and optimize harvest efficiency.
Equipment Operation and Maintenance Differences
Tractor operators primarily manage versatile machinery used for plowing, planting, and towing, requiring routine maintenance such as engine checks, lubrication, and tire inspections to ensure optimal performance. Combine harvester operators focus on complex harvesting equipment involving components like threshers and sieves, demanding specialized upkeep including cleaning grain tanks, adjusting cutting blades, and calibrating sensors for precision harvesting. Both roles necessitate mechanical proficiency, but combine operators require deeper knowledge of electronic systems and crop-specific maintenance protocols to maximize efficiency during harvesting seasons.
Safety Protocols and Best Practices
Tractor operators must prioritize regular equipment inspections, safe driving speeds, and proper use of rollover protection systems (ROPS) to prevent accidents during fieldwork. Combine harvester operators should follow strict maintenance schedules, ensure grain tank and unloading auger safety, and wear protective gear to reduce exposure to dust and machinery hazards. Both roles require adherence to training on emergency shut-down procedures and clear communication to enhance overall farm safety.
Working Environment and Job Challenges
Tractor operators typically work in diverse agricultural settings, managing tasks like plowing, planting, and towing equipment, often exposed to varying weather conditions and uneven terrains. Combine harvester operators face the unique challenge of operating large, complex machinery during the critical harvesting period, requiring precision and endurance amid dusty environments and time-sensitive deadlines. Both roles demand physical stamina and technical skill, but combine harvester operators encounter higher pressure due to crop perishability and machinery complexity.
Training and Certification Requirements
Tractor operators typically require basic training and certification focused on machinery operation, maintenance, and safety protocols, often obtainable through vocational schools or on-the-job programs. Combine harvester operators need specialized certification emphasizing advanced equipment handling, grain harvesting techniques, and system troubleshooting, usually provided by agricultural training centers or manufacturers. Both roles benefit from hands-on experience and adherence to agricultural safety standards to ensure efficient and secure farm operations.
Career Progression and Salary Comparison
Tractor operators typically start with basic fieldwork and can progress to senior equipment operator roles or agricultural machinery supervisors, earning an average salary of $35,000 to $50,000 annually. Combine harvester operators often require specialized skills for harvesting and grain handling, leading to higher seniority positions like harvest managers or machinery instructors with salaries ranging from $45,000 to $65,000 per year. Salary growth in combine harvester operation generally outpaces tractor operators due to the complexity and critical role in crop yield optimization.
Tractor Operator vs Combine Harvester Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com