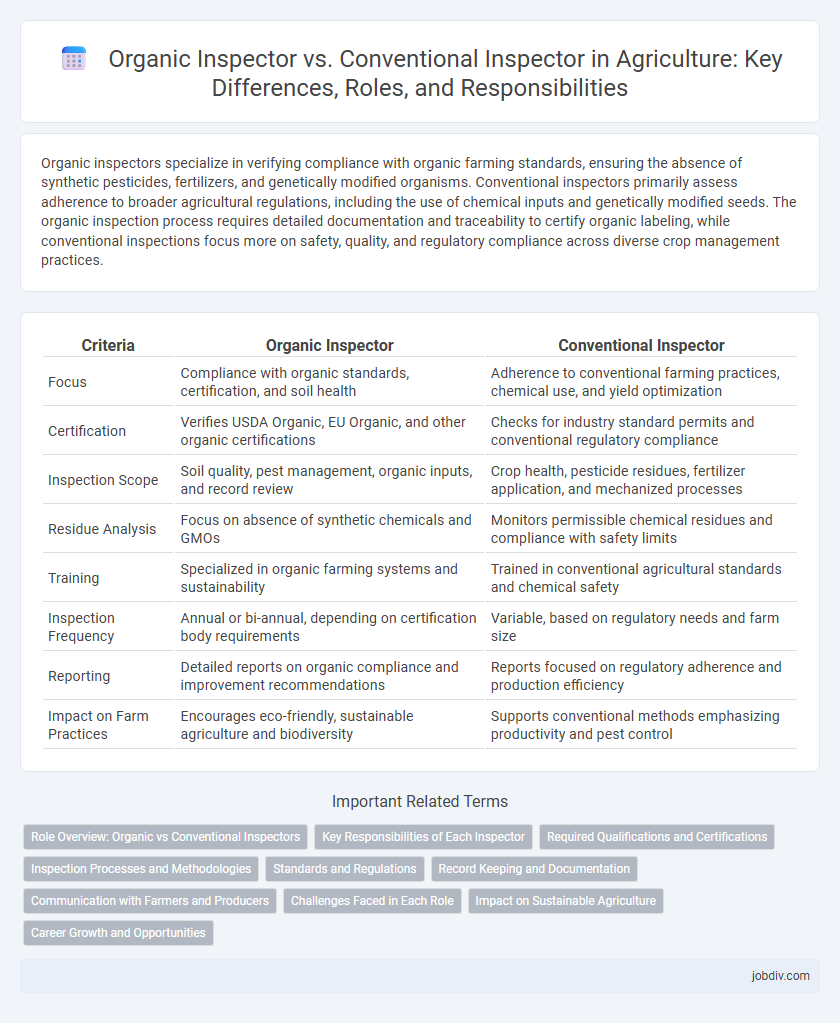
Organic inspectors specialize in verifying compliance with organic farming standards, ensuring the absence of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms. Conventional inspectors primarily assess adherence to broader agricultural regulations, including the use of chemical inputs and genetically modified seeds. The organic inspection process requires detailed documentation and traceability to certify organic labeling, while conventional inspections focus more on safety, quality, and regulatory compliance across diverse crop management practices.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Organic Inspector | Conventional Inspector |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Compliance with organic standards, certification, and soil health | Adherence to conventional farming practices, chemical use, and yield optimization |
| Certification | Verifies USDA Organic, EU Organic, and other organic certifications | Checks for industry standard permits and conventional regulatory compliance |
| Inspection Scope | Soil quality, pest management, organic inputs, and record review | Crop health, pesticide residues, fertilizer application, and mechanized processes |
| Residue Analysis | Focus on absence of synthetic chemicals and GMOs | Monitors permissible chemical residues and compliance with safety limits |
| Training | Specialized in organic farming systems and sustainability | Trained in conventional agricultural standards and chemical safety |
| Inspection Frequency | Annual or bi-annual, depending on certification body requirements | Variable, based on regulatory needs and farm size |
| Reporting | Detailed reports on organic compliance and improvement recommendations | Reports focused on regulatory adherence and production efficiency |
| Impact on Farm Practices | Encourages eco-friendly, sustainable agriculture and biodiversity | Supports conventional methods emphasizing productivity and pest control |
Role Overview: Organic vs Conventional Inspectors
Organic inspectors specialize in verifying compliance with organic farming standards, ensuring the absence of synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. Conventional inspectors focus on adherence to traditional agricultural practices, emphasizing pesticide usage, crop rotation, and soil health management. Both roles require thorough record-keeping and site assessments but differ fundamentally in regulatory frameworks and certification criteria.
Key Responsibilities of Each Inspector
Organic inspectors ensure compliance with organic standards by verifying that farms avoid synthetic pesticides, GMOs, and non-organic fertilizers through thorough on-site inspections and detailed record reviews. Conventional inspectors focus on enforcing regulatory requirements related to pesticide use, soil management, and crop health to maximize yield and safety. Both inspectors play critical roles in maintaining agricultural standards, but organic inspectors prioritize natural and sustainable practices while conventional inspectors emphasize efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Organic inspectors must possess specialized knowledge of USDA organic regulations, often requiring certification from bodies like the National Organic Program (NOP) and completion of organic-specific training programs. Conventional inspectors typically hold qualifications related to general agricultural practices or food safety standards without the stringent organic certification requirements. Both roles demand strong expertise in compliance, but organic inspectors undergo more rigorous vetting to verify adherence to organic standards.
Inspection Processes and Methodologies
Organic inspectors employ rigorous protocols emphasizing compliance with organic standards, including detailed verification of prohibited substances and seed origins, whereas conventional inspectors assess adherence to general agricultural regulations with less focus on chemical restrictions. Organic inspection processes involve comprehensive documentation reviews, residue testing, and farm system audits to ensure integrity throughout the supply chain. Conventional inspections prioritize pest management, fertilizer application rates, and overall crop health, typically relying on visual assessments and regulatory checklists.
Standards and Regulations
Organic inspectors enforce strict adherence to USDA National Organic Program standards, ensuring farms use no synthetic pesticides, GMOs, or prohibited substances. Conventional inspectors follow broader agricultural regulations, primarily focusing on food safety, pesticide application, and environmental compliance without the stringent organic certification criteria. Differences in certification processes impact how inspectors verify practices, documentation, and residue testing to meet either organic or conventional agricultural standards.
Record Keeping and Documentation
Organic inspectors prioritize meticulous record keeping to ensure compliance with organic standards, verifying detailed documentation like input usage, production methods, and transaction certificates. Conventional inspectors review records primarily for regulatory adherence, focusing on pesticide applications, chemical use, and safety protocols. The organic inspection process demands more comprehensive traceability and transparency, reflecting the stricter certification requirements.
Communication with Farmers and Producers
Organic inspectors prioritize transparent communication, ensuring farmers understand compliance with strict organic standards and certification requirements. Conventional inspectors focus on discussing pest management, fertilizer use, and crop yields, emphasizing efficiency and regulatory adherence. Both roles require clear dialogue, but organic inspectors engage more in educating about sustainability and eco-friendly practices.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Organic inspectors face challenges such as verifying compliance with strict organic standards, managing diverse crop rotations, and monitoring for prohibited substances, which require in-depth knowledge of organic certification processes. Conventional inspectors encounter difficulties related to assessing adherence to pesticide regulations, ensuring proper fertilizer application, and detecting environmental impacts from intensive farming practices. Both roles demand rigorous documentation review and on-site evaluations to uphold agricultural integrity and food safety.
Impact on Sustainable Agriculture
Organic inspectors assess farms based on strict compliance with organic certification standards, ensuring the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to promote soil health and biodiversity, which are crucial for sustainable agriculture. Conventional inspectors focus on adherence to regulatory requirements related to chemical use and crop yield optimization, often emphasizing short-term productivity over ecological balance. The organic inspection process significantly supports sustainable agriculture by fostering practices that enhance ecosystem services and long-term farm resilience.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Organic inspectors often experience expanding career growth due to increasing global demand for certified organic products, leading to higher job availability and specialized roles in sustainability. Conventional inspectors benefit from established career paths within large-scale agricultural operations, with opportunities for advancement in regulatory agencies, quality control, and agribusiness firms. Both roles require strong knowledge of agricultural practices, but organic inspectors typically engage more with environmental compliance and evolving organic standards, influencing future market trends.
Organic Inspector vs Conventional Inspector Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com