Farm managers oversee crop production, soil health, and irrigation systems to maximize agricultural yields, while ranch managers focus on livestock breeding, grazing management, and animal health to ensure sustainable herd productivity. Both roles require strong leadership skills and knowledge of agricultural best practices but differ in their primary responsibilities related to plant or animal agriculture. Efficient management in either position directly impacts the economic viability and environmental sustainability of the operation.
Table of Comparison
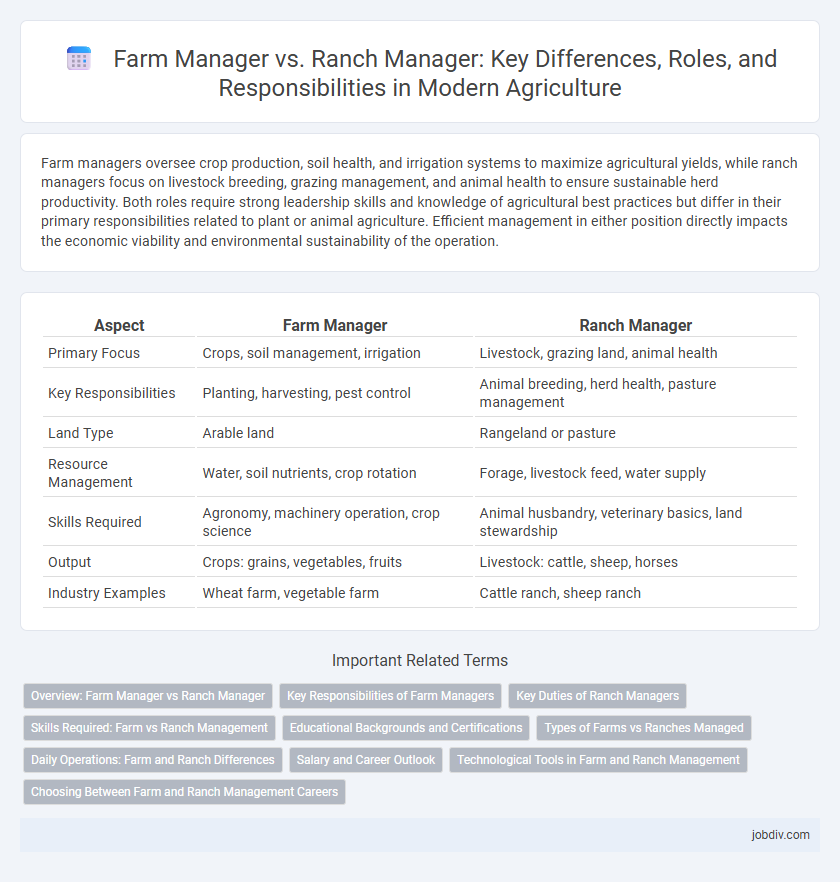
| Aspect | Farm Manager | Ranch Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Crops, soil management, irrigation | Livestock, grazing land, animal health |
| Key Responsibilities | Planting, harvesting, pest control | Animal breeding, herd health, pasture management |
| Land Type | Arable land | Rangeland or pasture |
| Resource Management | Water, soil nutrients, crop rotation | Forage, livestock feed, water supply |
| Skills Required | Agronomy, machinery operation, crop science | Animal husbandry, veterinary basics, land stewardship |
| Output | Crops: grains, vegetables, fruits | Livestock: cattle, sheep, horses |
| Industry Examples | Wheat farm, vegetable farm | Cattle ranch, sheep ranch |
Overview: Farm Manager vs Ranch Manager
Farm managers primarily oversee crop production, soil management, and irrigation strategies to maximize agricultural yield. Ranch managers focus on livestock care, grazing management, and pasture maintenance to ensure animal health and sustainable land use. Both roles require strong leadership skills, knowledge of agricultural technology, and efficient resource allocation for optimal farm or ranch operations.
Key Responsibilities of Farm Managers
Farm managers oversee crop production, soil health, irrigation, pest control, and labor management to maximize agricultural yield and profitability. They coordinate planting schedules, monitor equipment maintenance, manage budgets, and ensure compliance with agricultural regulations. Effective farm management requires knowledge of crop rotation, fertilization techniques, and market trends to optimize resource use and farm productivity.
Key Duties of Ranch Managers
Ranch managers oversee the daily operations of livestock production, including breeding, grazing management, and animal health monitoring. They coordinate feeding schedules, manage pasture rotation to prevent overgrazing, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Their responsibilities also involve hiring and supervising ranch hands, maintaining equipment, and budgeting for feed, veterinary care, and infrastructure maintenance.
Skills Required: Farm vs Ranch Management
Farm managers require expertise in crop production techniques, soil health management, irrigation systems, and pest control to maximize yield and ensure sustainable agriculture. Ranch managers prioritize animal husbandry skills, livestock breeding, pasture management, and veterinary knowledge to maintain herd health and optimize meat or dairy production. Both roles demand strong leadership, financial planning, and resource management abilities but differ significantly in their technical and operational skill sets.
Educational Backgrounds and Certifications
Farm managers typically possess degrees in agricultural science, agribusiness, or crop production, often supplemented by certifications such as Certified Crop Adviser (CCA) or pesticide applicator licenses. Ranch managers, on the other hand, often have educational backgrounds in animal science, range management, or livestock production, with certifications including Certified Ranch Manager (CRM) or range management certifications. Both roles emphasize specialized training, but farm management leans towards crop and soil knowledge, while ranch management prioritizes livestock and land stewardship expertise.
Types of Farms vs Ranches Managed
Farm managers oversee crop farms, horticultural operations, and mixed farms focusing on soil cultivation, planting, irrigation, and harvest processes. Ranch managers specialize in livestock operations such as cattle, sheep, or horse ranches, emphasizing animal health, breeding, grazing management, and pasture maintenance. Both roles require tailored strategies aligned with the specific agricultural production systems and resource management inherent to farms or ranches.
Daily Operations: Farm and Ranch Differences
Farm managers oversee daily crop production tasks such as planting, irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting, ensuring efficient use of resources and machinery to optimize yields. Ranch managers focus on livestock care, including feeding, breeding, pasture maintenance, and health monitoring, prioritizing animal welfare and grazing land sustainability. Both roles require strategic planning and coordination, but farm operations emphasize plant cultivation while ranch operations center on animal husbandry.
Salary and Career Outlook
Farm managers typically earn an annual salary ranging from $50,000 to $90,000, influenced by farm size and location, while ranch managers often command salaries between $55,000 and $95,000 due to the specialized skills required for livestock management. Career outlook for both roles is positive, with a projected growth rate of 5-7% over the next decade driven by increasing demand for efficient agricultural operations and sustainable livestock production. Advanced education and experience in agricultural science, livestock management, and business administration significantly enhance earning potential and career advancement opportunities in both professions.
Technological Tools in Farm and Ranch Management
Farm managers leverage precision agriculture technologies such as GPS-guided machinery, soil sensors, and drone surveillance to optimize crop production and resource management. Ranch managers utilize advanced monitoring systems including GPS tracking for livestock, automated feeding systems, and health management software to improve herd productivity and animal welfare. Both roles increasingly rely on integrated farm management software to analyze data and make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency.
Choosing Between Farm and Ranch Management Careers
Farm managers oversee crop production, irrigation systems, and soil health, emphasizing efficient planting, harvesting, and pest control to maximize yields. Ranch managers focus on livestock care, grazing management, breeding programs, and maintaining pasture quality for sustainable animal production. Choosing between farm and ranch management careers depends on interest in crop cultivation versus animal husbandry and the specific skills required for each discipline.
Farm Manager vs Ranch Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com