Irrigation specialists design and manage water delivery systems to optimize crop hydration and enhance agricultural productivity, focusing on efficient water use and soil moisture maintenance. Drainage specialists concentrate on removing excess water from fields to prevent waterlogging, soil erosion, and salinity issues, ensuring healthy root development and effective land use. Both roles are essential for sustainable water management in agriculture, but their expertise targets opposite water balance challenges on the farm.
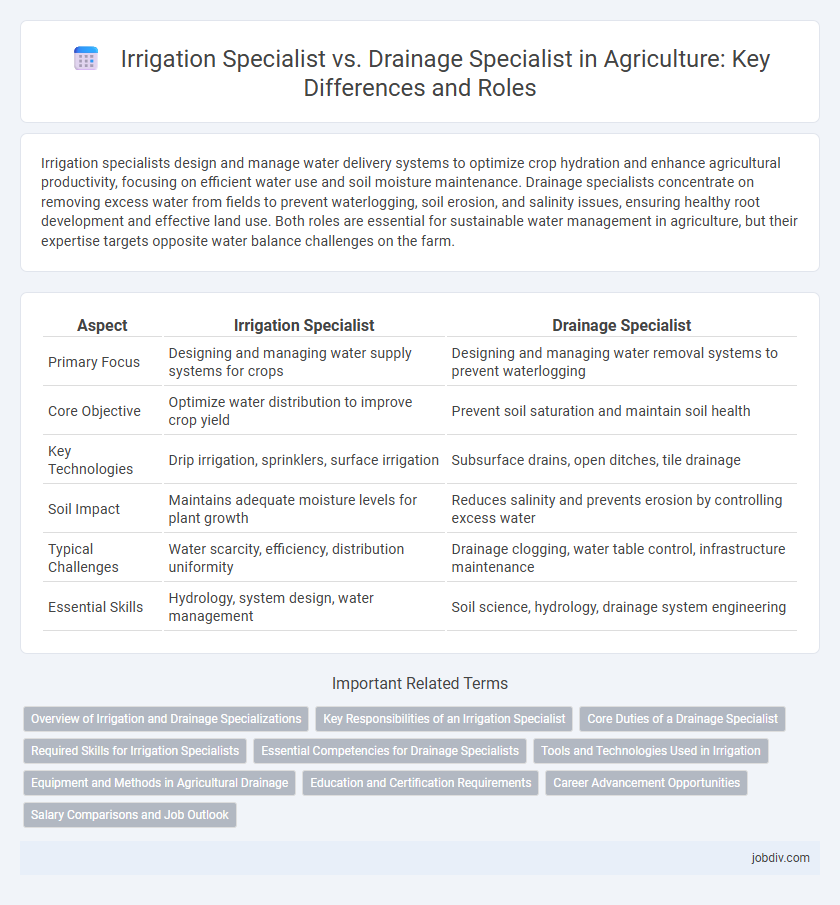
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Irrigation Specialist | Drainage Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Designing and managing water supply systems for crops | Designing and managing water removal systems to prevent waterlogging |
| Core Objective | Optimize water distribution to improve crop yield | Prevent soil saturation and maintain soil health |
| Key Technologies | Drip irrigation, sprinklers, surface irrigation | Subsurface drains, open ditches, tile drainage |
| Soil Impact | Maintains adequate moisture levels for plant growth | Reduces salinity and prevents erosion by controlling excess water |
| Typical Challenges | Water scarcity, efficiency, distribution uniformity | Drainage clogging, water table control, infrastructure maintenance |
| Essential Skills | Hydrology, system design, water management | Soil science, hydrology, drainage system engineering |
Overview of Irrigation and Drainage Specializations
Irrigation specialists focus on designing and managing water delivery systems to optimize crop growth and conserve water resources, employing techniques such as drip irrigation and sprinkler systems. Drainage specialists concentrate on removing excess water from soil through subsurface and surface drainage solutions to prevent waterlogging and soil degradation. Both specializations are critical for maintaining soil health, improving agricultural productivity, and ensuring sustainable water management practices.
Key Responsibilities of an Irrigation Specialist
An Irrigation Specialist designs, implements, and maintains efficient water distribution systems to optimize crop growth and conserve water resources. They analyze soil types, climate conditions, and crop requirements to develop tailored irrigation schedules and select appropriate technologies such as drip or sprinkler systems. Their expertise includes monitoring system performance, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations to enhance agricultural productivity.
Core Duties of a Drainage Specialist
A Drainage Specialist in agriculture focuses on designing and implementing effective water removal systems to prevent soil waterlogging and enhance crop growth conditions. Core duties include assessing soil moisture levels, planning subsurface and surface drainage solutions, and maintaining drainage infrastructure to ensure optimal soil aeration and nutrient availability. This role is critical for improving field productivity by managing excess water and preventing root diseases caused by poor drainage.
Required Skills for Irrigation Specialists
Irrigation specialists require expertise in water management techniques, soil science, and hydraulic systems to design efficient irrigation plans that optimize water use. They must possess skills in evaluating soil moisture levels, understanding crop water requirements, and operating irrigation technologies such as drip, sprinkler, and surface systems. Proficiency in field data analysis, use of irrigation scheduling software, and knowledge of environmental regulations is essential to ensure sustainable water resource management in agriculture.
Essential Competencies for Drainage Specialists
Drainage specialists possess essential competencies in designing effective water removal systems to prevent soil salinization and waterlogging, ensuring optimal crop growth. Their expertise includes soil hydrology analysis, subsurface drainage installation, and managing surface runoff to maintain soil structure and fertility. Proficiency in surveying techniques and knowledge of environmental regulations are critical for implementing sustainable drainage solutions in agricultural landscapes.
Tools and Technologies Used in Irrigation
Irrigation specialists primarily utilize advanced technologies such as drip irrigation systems, automated sprinklers, soil moisture sensors, and remote monitoring software to optimize water distribution and crop yield. These tools enable precise water management, reduce wastage, and improve irrigation efficiency based on real-time data. In contrast, drainage specialists focus on tools like subsurface drainage pipes, open ditches, and water control structures to manage excess water but rely less on irrigation-specific technologies.
Equipment and Methods in Agricultural Drainage
Irrigation specialists focus on equipment such as sprinkler systems, drip emitters, and center pivots designed to deliver precise water application for crop growth, while drainage specialists utilize subsurface tile drains, open ditches, and French drains to manage excess water and prevent soil waterlogging. Methods employed by drainage specialists include contour drainage, mole drainage, and surface grading to enhance soil permeability and optimize water removal. Both rely on advanced technologies like remote sensors and GIS mapping to monitor soil moisture levels and water flow for sustainable agriculture.
Education and Certification Requirements
Irrigation specialists typically require a degree in agricultural engineering, soil science, or water resource management, along with certifications such as Certified Irrigation Designer (CID) or Certified Irrigation Contractor (CIC). Drainage specialists often hold degrees in civil or agricultural engineering, environmental science, or hydrology, with certifications like Certified Professional in Erosion and Sediment Control (CPESC) or Certified Drainage Designer (CDD). Both roles benefit from training in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and water management software to enhance their expertise in sustainable agricultural water practices.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Irrigation specialists advance by mastering water management technologies and precision irrigation systems, leading to roles in agricultural consulting and water resource management. Drainage specialists progress through expertise in soil hydrology and drainage infrastructure design, often moving into environmental engineering and land reclamation projects. Both careers benefit from certifications and hands-on experience, which open pathways to leadership positions in sustainable agriculture and farm management.
Salary Comparisons and Job Outlook
Irrigation specialists typically earn an average salary ranging from $55,000 to $75,000 annually, with demand driven by increasing water-efficient farming practices. Drainage specialists generally have a slightly higher salary range between $60,000 and $80,000, owing to the critical role they play in managing soil moisture and preventing crop damage. Both careers show steady job growth projected at 5-7% over the next decade, reflecting the agricultural sector's emphasis on sustainable water management solutions.
Irrigation Specialist vs Drainage Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com