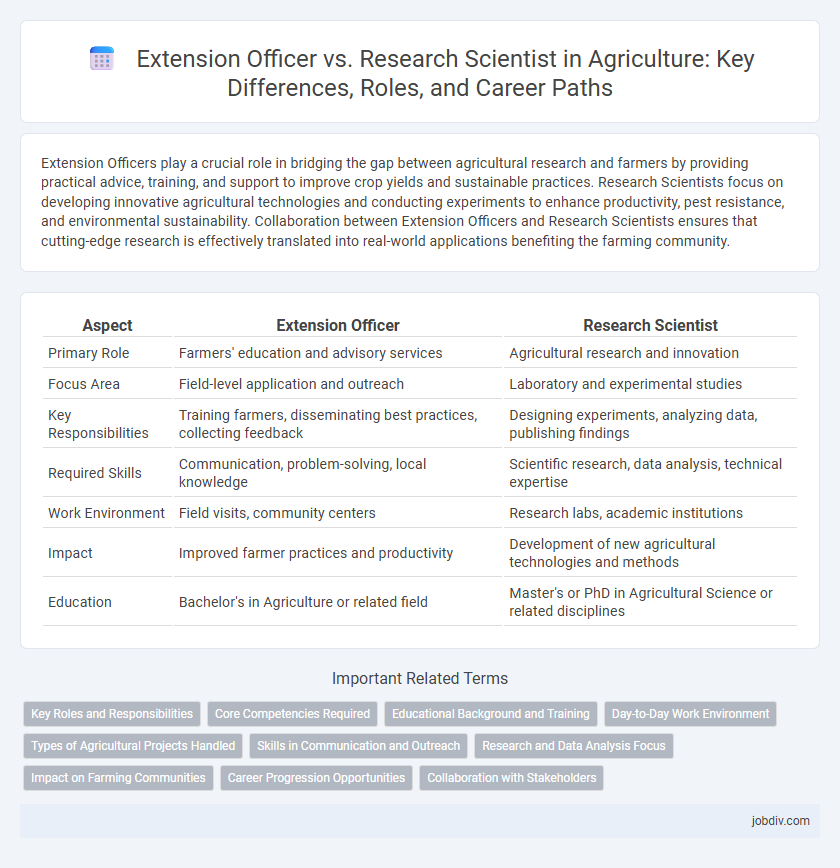
Extension Officers play a crucial role in bridging the gap between agricultural research and farmers by providing practical advice, training, and support to improve crop yields and sustainable practices. Research Scientists focus on developing innovative agricultural technologies and conducting experiments to enhance productivity, pest resistance, and environmental sustainability. Collaboration between Extension Officers and Research Scientists ensures that cutting-edge research is effectively translated into real-world applications benefiting the farming community.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Extension Officer | Research Scientist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Farmers' education and advisory services | Agricultural research and innovation |
| Focus Area | Field-level application and outreach | Laboratory and experimental studies |
| Key Responsibilities | Training farmers, disseminating best practices, collecting feedback | Designing experiments, analyzing data, publishing findings |
| Required Skills | Communication, problem-solving, local knowledge | Scientific research, data analysis, technical expertise |
| Work Environment | Field visits, community centers | Research labs, academic institutions |
| Impact | Improved farmer practices and productivity | Development of new agricultural technologies and methods |
| Education | Bachelor's in Agriculture or related field | Master's or PhD in Agricultural Science or related disciplines |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Extension Officers facilitate the transfer of agricultural knowledge and technology from research institutions to farmers, providing on-field training and support to improve crop management and sustainability. Research Scientists conduct experimental studies to develop innovative agricultural techniques, crop varieties, and pest management solutions through systematic investigation and data analysis. Both roles collaborate to enhance agricultural productivity, with Extension Officers implementing practical solutions and Research Scientists advancing scientific understanding.
Core Competencies Required
Extension Officers require strong communication and interpersonal skills to effectively transfer agricultural knowledge and practices to farmers, alongside problem-solving abilities tailored to field conditions. Research Scientists need advanced analytical skills, expertise in experimental design, and proficiency in data interpretation to drive innovation in crop improvement and sustainable farming techniques. Both roles demand a solid understanding of agronomy, but Extension Officers focus on practical application while Research Scientists prioritize scientific investigation.
Educational Background and Training
Extension Officers typically hold a bachelor's degree in agricultural science, agronomy, or related fields, with specialized training in communication, community engagement, and applied agricultural practices. Research Scientists often possess advanced degrees such as a master's or Ph.D. in agricultural science, plant biology, or genetics, with extensive training in experimental design, data analysis, and laboratory techniques. Both roles require continuous professional development, but Research Scientists emphasize innovation and discovery, while Extension Officers focus on practical implementation and farmer education.
Day-to-Day Work Environment
Extension Officers engage directly with farmers, providing practical advice, conducting field visits, and organizing workshops to implement agricultural innovations in real-world settings. Research Scientists primarily work in laboratories or experimental plots, designing studies, collecting data, and analyzing results to develop new crop varieties or pest control methods. Extension Officers bridge the gap between scientific research and farm application, while Research Scientists focus on generating foundational knowledge within controlled environments.
Types of Agricultural Projects Handled
Extension Officers primarily manage farmer-centric agricultural projects focused on technology transfer, training, and community engagement to improve crop yields and sustainable practices. Research Scientists handle experimental and innovative projects involving crop genetics, pest resistance, and soil health aimed at developing new agricultural technologies and scientific knowledge. Both roles contribute to agricultural advancement but differ in project scope, with Extension Officers focusing on practical application and Research Scientists emphasizing experimental research.
Skills in Communication and Outreach
Extension Officers excel in communication and outreach by directly engaging with farmers, conducting workshops, and translating complex agricultural research into practical advice. Research Scientists focus on technical proficiency and data analysis, requiring strong written communication to publish findings but typically have less direct interaction with end-users. Effective agricultural development depends on the collaboration between Extension Officers' community engagement and the Research Scientists' specialized expertise.
Research and Data Analysis Focus
Extension Officers apply research findings directly to farming practices, emphasizing practical data interpretation and farmer engagement to improve crop yields and sustainability. Research Scientists concentrate on experimental design and advanced data analysis to develop innovative agricultural technologies and solutions. Their work generates the foundational knowledge that Extension Officers translate into actionable strategies for local agricultural communities.
Impact on Farming Communities
Extension Officers directly engage with farming communities by providing practical training, timely advice, and support, which leads to immediate improvements in crop management and livestock care. Research Scientists contribute by developing innovative agricultural technologies and sustainable practices that, once validated, enhance productivity and resilience in farming systems over time. The combined efforts of both roles drive transformational change, boosting farm incomes and food security in rural areas.
Career Progression Opportunities
Extension Officers typically advance by gaining specialized certifications and taking leadership roles in community outreach programs, which enhance their expertise in practical agricultural applications. Research Scientists progress by publishing research, securing grants, and contributing to innovations in crop improvement, leading to roles such as senior scientist or research director. Career progression for Extension Officers centers on field impact and education, while Research Scientists focus on scientific discovery and academic achievements.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Extension Officers collaborate directly with farmers, local communities, and agricultural organizations to implement research findings and provide practical guidance for improving crop yields and sustainability. Research Scientists engage with academic institutions, government agencies, and industry partners to conduct experiments and develop innovative agricultural technologies. Together, their collaboration ensures the translation of scientific discoveries into effective on-the-ground solutions, promoting agricultural development and stakeholder engagement.
Extension Officer vs Research Scientist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com