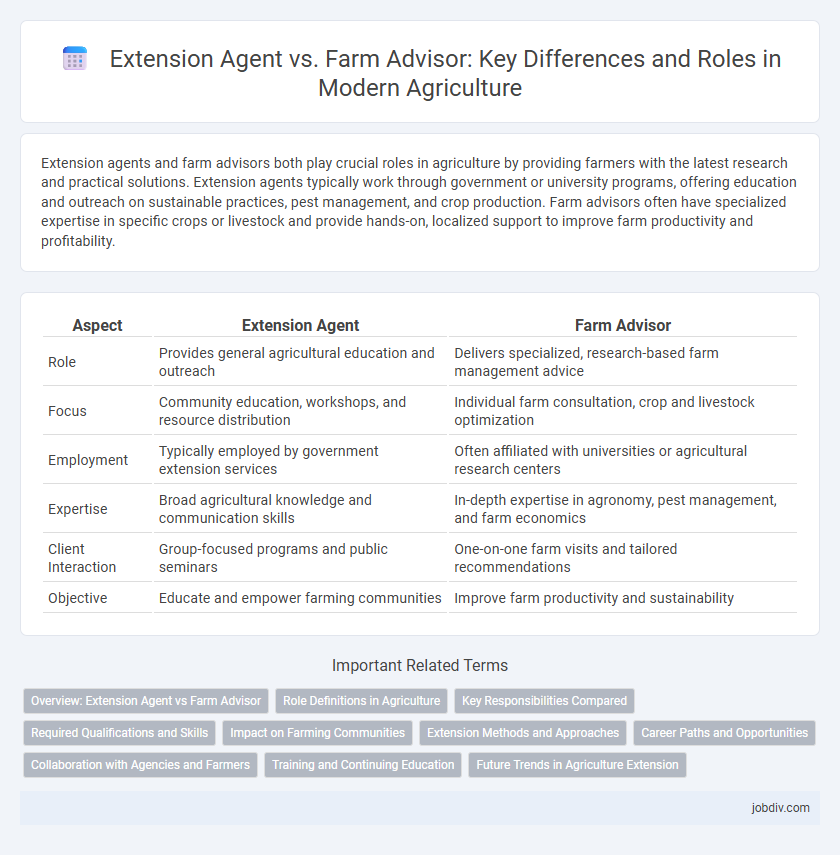
Extension agents and farm advisors both play crucial roles in agriculture by providing farmers with the latest research and practical solutions. Extension agents typically work through government or university programs, offering education and outreach on sustainable practices, pest management, and crop production. Farm advisors often have specialized expertise in specific crops or livestock and provide hands-on, localized support to improve farm productivity and profitability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Extension Agent | Farm Advisor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides general agricultural education and outreach | Delivers specialized, research-based farm management advice |
| Focus | Community education, workshops, and resource distribution | Individual farm consultation, crop and livestock optimization |
| Employment | Typically employed by government extension services | Often affiliated with universities or agricultural research centers |
| Expertise | Broad agricultural knowledge and communication skills | In-depth expertise in agronomy, pest management, and farm economics |
| Client Interaction | Group-focused programs and public seminars | One-on-one farm visits and tailored recommendations |
| Objective | Educate and empower farming communities | Improve farm productivity and sustainability |
Overview: Extension Agent vs Farm Advisor
Extension Agents and Farm Advisors both play crucial roles in agricultural support, with Extension Agents typically representing government or university programs to deliver research-based education to farmers and communities. Farm Advisors often work directly with farmers to apply practical solutions on-site, offering tailored advice on crop management, pest control, and sustainable practices. The primary distinction lies in Extension Agents focusing on broad outreach and education while Farm Advisors emphasize personalized, technical assistance for optimizing farm production.
Role Definitions in Agriculture
Extension Agents provide crucial outreach by delivering research-based agricultural education directly to farmers, focusing on practical solutions for crop management, pest control, and sustainable practices. Farm Advisors specialize in offering expert consultation tailored to specific farm operations, integrating scientific research with local conditions to optimize productivity and resource management. Both roles collaborate to enhance farm efficiency, promote innovation, and support rural community development through knowledge transfer and problem-solving.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Extension Agents primarily deliver educational programs and provide technical support to farmers on best practices, pest management, and sustainable agriculture. Farm Advisors focus on applied research, translating scientific findings into practical recommendations to improve crop yields, soil health, and farm profitability. Both roles collaborate closely with agricultural institutions but differ in their emphasis on outreach versus research-based guidance.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Extension Agents typically require a bachelor's degree in agriculture, education, or related fields, with strong communication and community outreach skills to effectively disseminate research-based information. Farm Advisors often hold advanced degrees, such as a master's or doctorate in agricultural sciences, and possess expertise in research, problem-solving, and technical knowledge to provide specialized, evidence-based recommendations. Both roles demand proficiency in agricultural practices and the ability to engage with diverse farming communities, but Farm Advisors focus more on applied research and innovation.
Impact on Farming Communities
Extension agents and farm advisors play critical roles in enhancing farming communities by delivering tailored agricultural knowledge and practices that improve crop yields and sustainability. Extension agents focus on education and outreach programs, facilitating farmer training and resource access, while farm advisors provide direct, on-site consultation and technical solutions to individual farm challenges. Their combined efforts drive innovation adoption, boost farm productivity, and strengthen rural economies by fostering resilience against environmental and market fluctuations.
Extension Methods and Approaches
Extension Agents primarily use direct, face-to-face methods such as workshops, on-farm visits, and demonstration plots to engage with farmers and disseminate research-based agricultural practices. Farm Advisors emphasize participatory approaches, incorporating farmer feedback through field days, group meetings, and farmer networks to tailor advice and ensure relevance to local conditions. Both roles utilize digital tools and multimedia resources increasingly, but Extension Agents focus more on structured educational programs, while Farm Advisors lean towards adaptive, collaborative decision-making processes.
Career Paths and Opportunities
Extension Agents typically work with community education programs to deliver research-based agricultural knowledge, focusing on public outreach and farmer assistance. Farm Advisors often engage in applied research and direct farm consultation, providing specialized expertise in crop management, soil health, and sustainable practices. Career paths for Extension Agents commonly lead to roles in education and public policy, while Farm Advisors may advance into research positions or agribusiness consultancy.
Collaboration with Agencies and Farmers
Extension Agents and Farm Advisors collaborate closely with agricultural agencies and farmers to deliver tailored educational programs and practical solutions. Extension Agents often serve as a liaison between research institutions and local farming communities, facilitating the dissemination of innovative practices. Farm Advisors contribute specialized expertise by conducting on-farm research and providing direct support to enhance crop productivity and sustainable farming methods.
Training and Continuing Education
Extension Agents participate in comprehensive training programs focused on community outreach, agricultural techniques, and educational methods to support farmers effectively. Farm Advisors undergo specialized continuing education that emphasizes the latest agronomic research, pest management strategies, and sustainable farming practices to provide expert technical guidance. Both roles prioritize ongoing professional development to enhance knowledge transfer and improve farm productivity through evidence-based recommendations.
Future Trends in Agriculture Extension
Extension agents and farm advisors will increasingly integrate digital technologies such as remote sensing, precision agriculture tools, and data analytics to enhance decision-making for farmers. Artificial intelligence and machine learning models will support personalized recommendations, improving crop yields and resource management. Emphasis on sustainability and climate-smart practices will drive their collaboration with policymakers to promote resilient and adaptive agricultural systems.
Extension Agent vs Farm Advisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com