Matte painters create highly detailed, photorealistic environments that enhance visual storytelling by blending digital painting techniques with real-world imagery. Background artists concentrate on designing the mood and atmosphere of scenes, crafting stylized or illustrative backdrops that complement character actions and narrative tone. Both roles require strong artistic skills but differ in their approach to realism and abstraction within visual production.
Table of Comparison
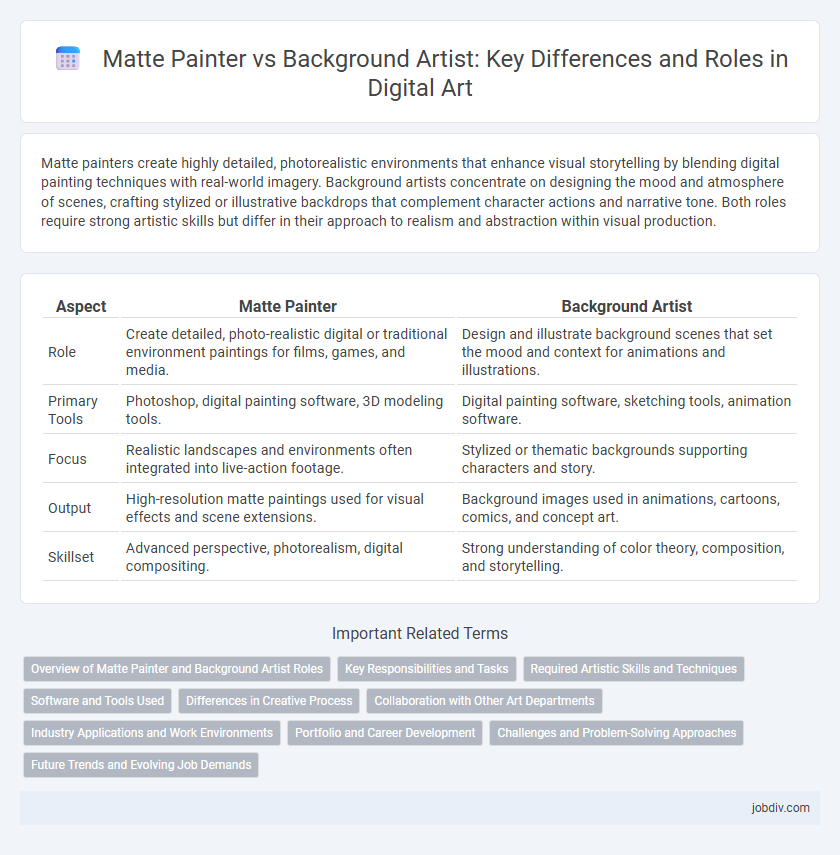
| Aspect | Matte Painter | Background Artist |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Create detailed, photo-realistic digital or traditional environment paintings for films, games, and media. | Design and illustrate background scenes that set the mood and context for animations and illustrations. |
| Primary Tools | Photoshop, digital painting software, 3D modeling tools. | Digital painting software, sketching tools, animation software. |
| Focus | Realistic landscapes and environments often integrated into live-action footage. | Stylized or thematic backgrounds supporting characters and story. |
| Output | High-resolution matte paintings used for visual effects and scene extensions. | Background images used in animations, cartoons, comics, and concept art. |
| Skillset | Advanced perspective, photorealism, digital compositing. | Strong understanding of color theory, composition, and storytelling. |
Overview of Matte Painter and Background Artist Roles
Matte painters create detailed, photorealistic environments that blend seamlessly with live-action footage or digital scenes, often using digital tools such as Photoshop and 3D software to compose expansive landscapes or intricate visual effects backgrounds. Background artists focus on designing stylized or detailed static backgrounds that set the mood and atmosphere for animated films, using traditional painting or digital illustration techniques to enhance storytelling. Both roles require strong artistic skills, but matte painters emphasize realism and integration within visual effects pipelines, while background artists prioritize consistency with the animation style and narrative tone.
Key Responsibilities and Tasks
Matte painters specialize in creating photorealistic or stylized digital environments that serve as seamless extensions of live-action footage or 3D scenes, using software like Photoshop and Nuke to craft detailed backgrounds, skies, or large-scale landscapes. Background artists focus on designing and illustrating the backgrounds for animated productions, ensuring the artistic style, color palette, and mood complement the characters and story, often working within 2D or 3D animation pipelines. Both roles require strong artistic skills, but matte painters emphasize integrating digital imagery with visual effects, while background artists concentrate on storytelling through environment design in animation.
Required Artistic Skills and Techniques
Matte painters require advanced skills in digital painting, perspective, and photorealistic rendering to create seamless environmental extensions that blend convincingly with live-action footage. Background artists focus on mastering composition, color theory, and traditional painting techniques to craft visually compelling and stylistically consistent scenes for animation or illustration. Both roles demand expertise in software tools like Photoshop and a strong understanding of lighting and texture to achieve the desired artistic impact.
Software and Tools Used
Matte painters primarily utilize software such as Adobe Photoshop, Corel Painter, and Nuke for detailed digital painting and compositing, enabling the creation of highly realistic environmental backdrops. Background artists often rely on a combination of Adobe Photoshop, Toon Boom Harmony, and Clip Studio Paint to craft stylized and animated backgrounds for various media formats. Both roles benefit from tools like Wacom tablets and digital brushes, but matte painters focus more on photorealistic textures, while background artists emphasize style and animation integration.
Differences in Creative Process
Matte painters typically create highly detailed, photorealistic environments that blend seamlessly with live-action footage using digital tools such as Photoshop and 3D software. Background artists focus on designing stylized, illustrative scenes that establish mood and complement character animation, often working hand-in-hand with the overall art direction. The creative process of matte painters prioritizes technical precision and realism, whereas background artists emphasize artistic expression and storytelling through color, composition, and texture.
Collaboration with Other Art Departments
Matte painters closely collaborate with visual effects and concept art teams to seamlessly integrate painted elements into live-action footage, ensuring consistency in lighting, perspective, and color. Background artists work hand-in-hand with character designers and animators to create immersive environments that enhance narrative flow and support character interaction. Both roles require strong communication and coordination with layout and compositing departments to achieve a cohesive visual storytelling experience.
Industry Applications and Work Environments
Matte Painters create highly detailed digital or traditional landscapes used in film and video game productions to extend or enhance environments seamlessly. Background Artists predominantly work in animation and game studios, crafting stylized backdrops that support character interaction and storytelling. Both roles require collaboration with art directors and use advanced software, but Matte Painters often contribute to live-action visual effects, while Background Artists focus on animated or illustrated narratives.
Portfolio and Career Development
A Matte Painter's portfolio showcases highly detailed, digitally created environmental scenes that blend photorealistic and imaginative elements, demonstrating strong skills in 2D and 3D software like Photoshop and Nuke. Background Artists emphasize traditional and digital painting techniques to create cohesive, stylistic backdrops that support animation and character work, often highlighting versatility across different settings and moods. Career development for Matte Painters leans towards roles in visual effects and film production, while Background Artists frequently progress within animation studios and game development, both requiring continuous portfolio updates with diverse project samples.
Challenges and Problem-Solving Approaches
Matte painters face challenges in seamlessly integrating digital and traditional painting techniques to create realistic, immersive environments, requiring strong skills in texture blending and perspective accuracy. Background artists must resolve issues related to maintaining visual consistency and mood across various scenes, often adapting quickly to changes in storyboards and animation styles. Both roles rely heavily on problem-solving approaches that involve iterative feedback, precise color correction, and collaboration with directors and visual effects teams to achieve cohesive visual narratives.
Future Trends and Evolving Job Demands
Matte painters and background artists must adapt to increasing integration of AI tools and real-time rendering technologies that enhance workflow efficiency and visual fidelity. Future trends emphasize cross-disciplinary skills, requiring artists to combine traditional painting expertise with 3D modeling and VR environment creation. Evolving job demands prioritize versatility, with matte painters expanding into dynamic scene creation while background artists embrace interactive and immersive media projects.
Matte Painter vs Background Artist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com