Motion Graphics Artists specialize in creating dynamic visual content through animated graphic design, often incorporating text, shapes, and effects to convey messages or enhance storytelling. In contrast, 2D Animators focus on crafting frame-by-frame illustrations and character animations that bring stories and characters to life with fluid motion. Both roles require strong artistic skills, but motion graphics emphasizes design and typography, while 2D animation centers on traditional drawing and narrative movement.
Table of Comparison
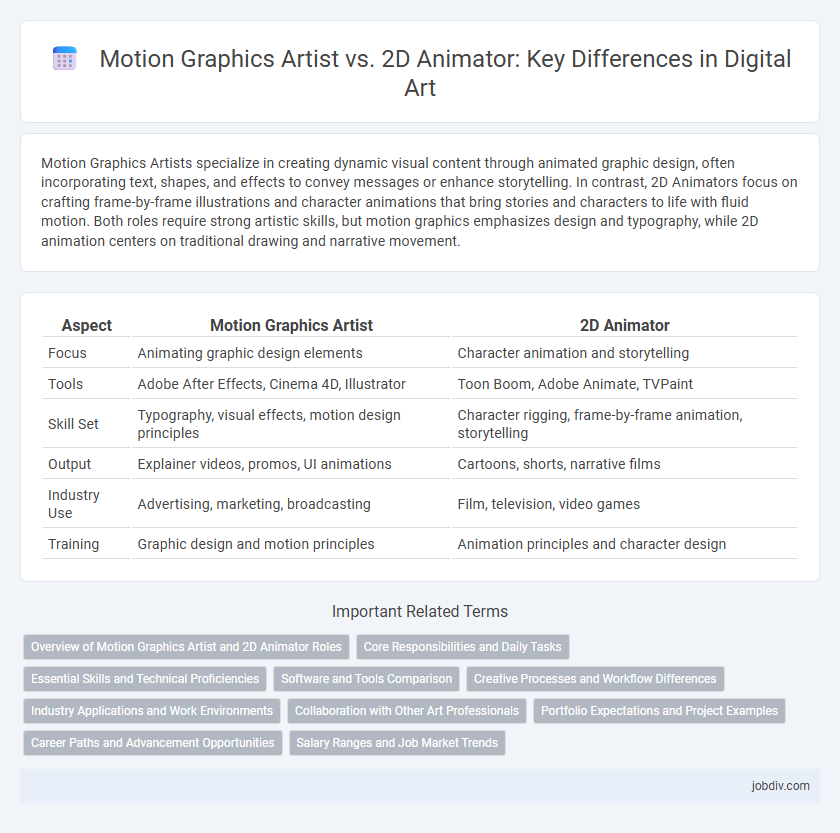
| Aspect | Motion Graphics Artist | 2D Animator |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Animating graphic design elements | Character animation and storytelling |
| Tools | Adobe After Effects, Cinema 4D, Illustrator | Toon Boom, Adobe Animate, TVPaint |
| Skill Set | Typography, visual effects, motion design principles | Character rigging, frame-by-frame animation, storytelling |
| Output | Explainer videos, promos, UI animations | Cartoons, shorts, narrative films |
| Industry Use | Advertising, marketing, broadcasting | Film, television, video games |
| Training | Graphic design and motion principles | Animation principles and character design |
Overview of Motion Graphics Artist and 2D Animator Roles
Motion Graphics Artists specialize in creating animated graphic design elements using digital tools like Adobe After Effects to enhance visual storytelling in media such as advertisements, films, and user interfaces. 2D Animators focus on crafting hand-drawn or digitally created frame-by-frame animations that bring characters and scenes to life, commonly employed in traditional cartoons, explainer videos, and games. Both roles require strong artistic skills and software proficiency, but Motion Graphics Artists emphasize graphic design and motion effects, while 2D Animators prioritize character movement and narrative animation.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Motion Graphics Artists specialize in creating dynamic visual content by combining graphic design, animation, and video effects, often working with software like After Effects and Cinema 4D to produce engaging multimedia presentations. 2D Animators focus on crafting frame-by-frame animations or rig-based character movements using tools such as Adobe Animate and Toon Boom Harmony to bring illustrations to life in a linear storytelling format. Daily tasks for Motion Graphics Artists include designing animated logos, title sequences, and promotional videos, while 2D Animators primarily develop character animation, background art, and storyboarding for films, TV shows, and video games.
Essential Skills and Technical Proficiencies
Motion Graphics Artists excel in software like Adobe After Effects and Cinema 4D, emphasizing dynamic visual storytelling through animated graphic elements and motion design principles. 2D Animators primarily master frame-by-frame techniques in programs such as Toon Boom Harmony and Adobe Animate, focusing on character animation, timing, and traditional drawing skills. Both roles require a strong understanding of visual composition, color theory, and storytelling, but Motion Graphics Artists lean towards manipulating digital assets, while 2D Animators specialize in handcrafted animation workflows.
Software and Tools Comparison
Motion Graphics Artists primarily utilize software such as Adobe After Effects, Cinema 4D, and Blender to create dynamic visual effects and animated graphics, emphasizing layered compositions and 3D elements. In contrast, 2D Animators focus on frame-by-frame animation using tools like Adobe Animate, Toon Boom Harmony, and TVPaint, which specialize in character animation and traditional drawing techniques. Both roles require proficiency in digital illustration and timing, but their software choices reflect distinct approaches to animation workflows and visual storytelling.
Creative Processes and Workflow Differences
Motion Graphics Artists leverage software like After Effects and Cinema 4D to create dynamic visuals often incorporating 3D elements, typography, and abstract animation, emphasizing timed effects and compositional layering. In contrast, 2D Animators focus on character animation and storytelling using frame-by-frame techniques in programs such as Toon Boom Harmony or Adobe Animate, prioritizing fluidity and expressiveness in traditional animation principles. Workflow differences include Motion Graphics Artists working extensively with pre-designed assets and iterative refinement, while 2D Animators invest time in sketching, keyframing, and inbetweening to build seamless narrative motion sequences.
Industry Applications and Work Environments
Motion Graphics Artists create dynamic visuals often used in advertising, film, and digital media, employing software like After Effects to design engaging title sequences and promotional content. 2D Animators specialize in frame-by-frame animation for television, video games, and animated films, using tools such as Toon Boom Harmony and Adobe Animate to bring characters and stories to life. Both roles operate in collaborative studio environments but differ in their artistic focus and project types, with motion graphics emphasizing visual effects and branding, while 2D animation centers on narrative storytelling.
Collaboration with Other Art Professionals
Motion graphics artists often collaborate closely with graphic designers, video editors, and sound designers to create dynamic multimedia content. In contrast, 2D animators typically work alongside storyboard artists, character designers, and layout artists to produce frame-by-frame animation sequences. Both roles require seamless teamwork with directors and producers to ensure the artistic vision aligns with storytelling and project goals.
Portfolio Expectations and Project Examples
A Motion Graphics Artist portfolio emphasizes dynamic visual storytelling using software like After Effects and Cinema 4D, showcasing projects such as animated logos, explainer videos, and kinetic typography that highlight proficiency in motion design and compositing. In contrast, a 2D Animator's portfolio centers on frame-by-frame character animation, storyboarding, and traditional animation techniques demonstrated through short films, character walks, and lip-sync animations using tools like Toon Boom Harmony or Adobe Animate. Both portfolios require clear examples of timing, creativity, and technical skill, but Motion Graphics Artists focus on graphic manipulation and effects while 2D Animators prioritize fluid character movement and narrative development.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Motion graphics artists specialize in creating visual effects and animated graphics for multimedia projects, often working with software like After Effects to enhance digital storytelling. 2D animators focus on character and scene animation using frame-by-frame techniques or rigging in programs such as Toon Boom Harmony, emphasizing traditional animation skills. Career advancement for motion graphics artists typically leads to roles in creative direction or multimedia design, while 2D animators often progress toward lead animator positions or storyboard artists in animation studios.
Salary Ranges and Job Market Trends
Motion graphics artists earn an average salary ranging from $50,000 to $85,000 annually, with job growth driven by demand in advertising, digital marketing, and multimedia platforms. In comparison, 2D animators typically make between $45,000 and $75,000, seeing steady opportunities in film, television, and gaming industries. The job market trend favors motion graphics due to increasing digital content consumption, while 2D animation maintains niche demand for storytelling and traditional animation styles.
Motion Graphics Artist vs 2D Animator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com