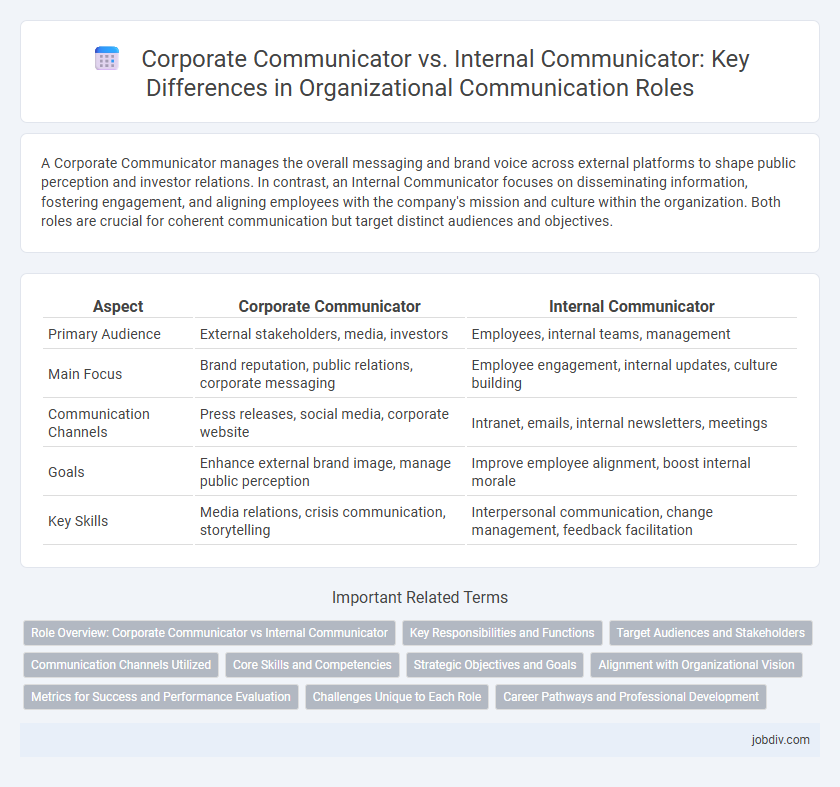
A Corporate Communicator manages the overall messaging and brand voice across external platforms to shape public perception and investor relations. In contrast, an Internal Communicator focuses on disseminating information, fostering engagement, and aligning employees with the company's mission and culture within the organization. Both roles are crucial for coherent communication but target distinct audiences and objectives.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Corporate Communicator | Internal Communicator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Audience | External stakeholders, media, investors | Employees, internal teams, management |
| Main Focus | Brand reputation, public relations, corporate messaging | Employee engagement, internal updates, culture building |
| Communication Channels | Press releases, social media, corporate website | Intranet, emails, internal newsletters, meetings |
| Goals | Enhance external brand image, manage public perception | Improve employee alignment, boost internal morale |
| Key Skills | Media relations, crisis communication, storytelling | Interpersonal communication, change management, feedback facilitation |
Role Overview: Corporate Communicator vs Internal Communicator
A Corporate Communicator manages external messaging to shape brand reputation, handle media relations, and craft public-facing content, ensuring consistent communication across stakeholders and the public. An Internal Communicator focuses on engaging employees, disseminating organizational updates, and fostering a unified workplace culture through targeted internal channels. Both roles require strategic communication skills but differ primarily in audience focus and message delivery objectives.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Corporate communicators oversee external messaging, brand reputation management, and media relations to ensure consistent public perception. Internal communicators focus on employee engagement, information dissemination, and fostering organizational culture through channels like intranets and internal newsletters. Both roles collaborate to align communication strategies with overall business objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Target Audiences and Stakeholders
Corporate communicators primarily engage external stakeholders such as investors, customers, media, and industry partners, ensuring consistent brand messaging and reputation management. Internal communicators target employees and management within the organization, focusing on workforce alignment, culture building, and information dissemination. Both roles collaborate to maintain cohesive communication strategies that address the distinct needs of internal and external audiences, enhancing overall organizational effectiveness.
Communication Channels Utilized
Corporate communicators primarily utilize external communication channels such as press releases, social media platforms, corporate websites, and investor relations portals to engage with stakeholders, media, and the public. Internal communicators focus on intranet systems, email newsletters, team collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams or Slack, and town hall meetings to facilitate information flow and employee engagement within the organization. The strategic deployment of these communication channels ensures targeted messaging aligns with the intended audience, maximizing clarity and organizational impact.
Core Skills and Competencies
Corporate communicators excel in strategic messaging, media relations, and brand management, ensuring consistent external communications aligned with organizational goals. Internal communicators specialize in employee engagement, change management, and fostering a collaborative culture through tailored internal messaging platforms. Both roles require strong writing, interpersonal skills, and an understanding of audience segmentation to optimize information flow and drive organizational effectiveness.
Strategic Objectives and Goals
Corporate communicators prioritize aligning messaging with overarching business goals to enhance brand reputation and stakeholder engagement. Internal communicators focus on fostering employee alignment and engagement by crafting targeted communications that support organizational culture and drive productivity. Both roles contribute to strategic objectives, with corporate communicators addressing external perceptions and internal communicators reinforcing internal cohesion.
Alignment with Organizational Vision
Corporate communicators align messaging with the organization's overarching vision to ensure consistency across all external and internal channels. Internal communicators focus on reinforcing that vision within the workforce, promoting engagement and understanding among employees. This alignment fosters a unified corporate culture and drives strategic objectives effectively.
Metrics for Success and Performance Evaluation
Corporate communicators measure success through brand perception, media coverage, and stakeholder engagement metrics, leveraging tools like sentiment analysis and share-of-voice tracking. Internal communicators focus on employee engagement scores, message reach, and feedback mechanisms such as pulse surveys and intranet analytics to evaluate performance. Both roles utilize data-driven insights but prioritize different audiences and KPIs to align communication efforts with organizational goals.
Challenges Unique to Each Role
Corporate communicators often face challenges related to managing brand reputation across diverse external stakeholders, ensuring consistent messaging during crises, and navigating complex media landscapes. Internal communicators primarily tackle issues like fostering employee engagement, overcoming information silos, and aligning communication strategies with organizational culture and change management initiatives. Both roles require tailored approaches to address the distinct demands of external transparency versus internal cohesion effectively.
Career Pathways and Professional Development
Corporate communicators often advance through roles in public relations, marketing, and media relations, gaining skills in brand management and stakeholder engagement, while internal communicators typically develop expertise in employee engagement, organizational culture, and change management. Career pathways for corporate communicators may include positions such as Communications Director or Chief Communications Officer, with professional development focused on external messaging and crisis communication. Internal communicators progress towards roles like Internal Communications Manager or Employee Experience Lead, emphasizing training in internal communication strategies, employee feedback systems, and leadership communication.
Corporate Communicator vs Internal Communicator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com