Cost engineers specialize in budgeting, cost control, and financial management throughout the construction project lifecycle, ensuring projects are delivered within allocated budgets. Value engineers focus on optimizing project value by analyzing functions and recommending design or process improvements to reduce costs without compromising quality or performance. Both roles collaborate closely to balance budget constraints and maximize overall project efficiency in construction.
Table of Comparison
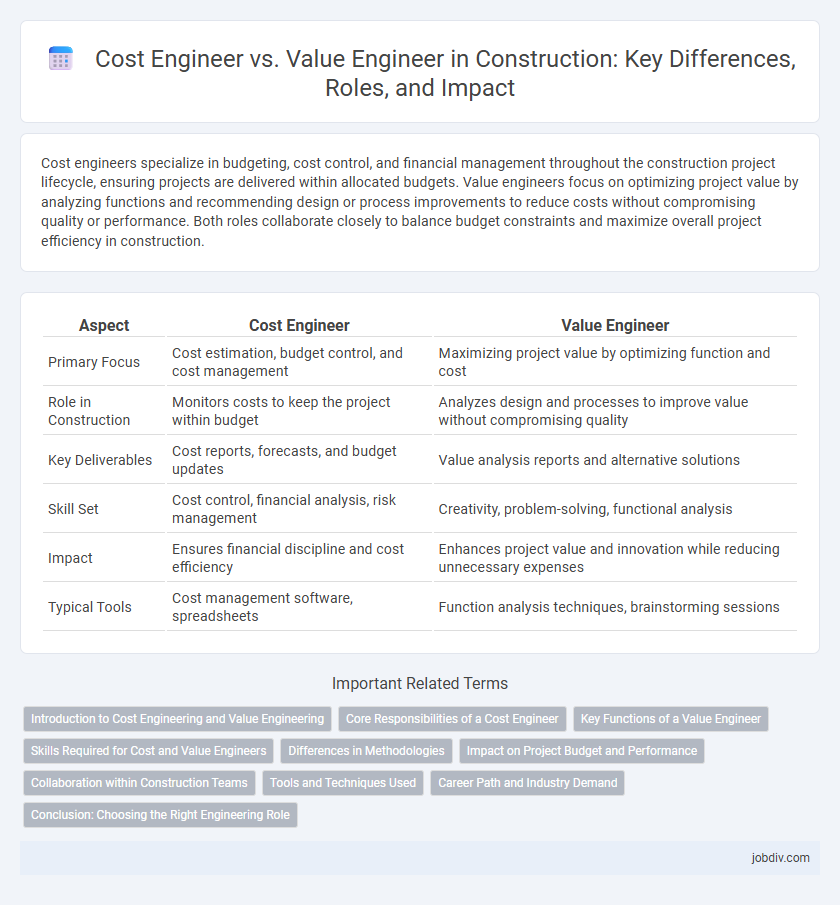
| Aspect | Cost Engineer | Value Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cost estimation, budget control, and cost management | Maximizing project value by optimizing function and cost |
| Role in Construction | Monitors costs to keep the project within budget | Analyzes design and processes to improve value without compromising quality |
| Key Deliverables | Cost reports, forecasts, and budget updates | Value analysis reports and alternative solutions |
| Skill Set | Cost control, financial analysis, risk management | Creativity, problem-solving, functional analysis |
| Impact | Ensures financial discipline and cost efficiency | Enhances project value and innovation while reducing unnecessary expenses |
| Typical Tools | Cost management software, spreadsheets | Function analysis techniques, brainstorming sessions |
Introduction to Cost Engineering and Value Engineering
Cost Engineering focuses on project cost estimation, budgeting, and financial control to ensure construction projects are completed within allocated budgets while maintaining quality standards. Value Engineering emphasizes improving project value by analyzing functions, reducing costs without compromising performance, and enhancing overall project efficiency. Both disciplines collaborate to optimize resources, balancing cost control and functional value in construction projects.
Core Responsibilities of a Cost Engineer
A Cost Engineer specializes in estimating, controlling, and monitoring project costs to ensure budgets are met and financial risks minimized throughout the construction lifecycle. They analyze cost data, prepare detailed reports, and develop cost-effective strategies for resource allocation and procurement management. Their core duties include conducting cost forecasting, cost control, and financial performance assessment to optimize project profitability and avoid cost overruns.
Key Functions of a Value Engineer
Value Engineers focus on optimizing project value by analyzing functions to reduce costs while maintaining quality and performance. Their key functions include function analysis, cost-benefit evaluation, and proposing alternative solutions that enhance project efficiency and sustainability. They collaborate closely with design and construction teams to ensure value maximization throughout the project lifecycle.
Skills Required for Cost and Value Engineers
Cost engineers require expertise in cost estimation, budgeting, risk analysis, and financial reporting to accurately forecast and control project expenditures. Value engineers focus on skills such as functional analysis, creative problem-solving, and multidisciplinary collaboration to optimize project value without compromising quality. Both roles demand strong communication, analytical thinking, and proficiency in project management software for effective decision-making.
Differences in Methodologies
Cost engineers primarily focus on budgeting, cost estimation, and financial control throughout the construction project lifecycle, employing quantitative methods such as cost-benefit analysis and risk assessment. Value engineers emphasize functional analysis to improve project value by optimizing design, materials, and processes, often using techniques like function-cost ratio evaluation and alternative solution workshops. The methodologies of cost engineering are centered on minimizing expenses while maintaining project scope, whereas value engineering seeks to enhance overall project performance and client satisfaction by balancing cost, quality, and functionality.
Impact on Project Budget and Performance
Cost Engineers focus on accurately estimating, controlling, and reducing project costs to keep the budget on track and avoid financial overruns. Value Engineers analyze project functions and materials to improve efficiency and quality, aiming to enhance overall project performance while maintaining or reducing costs. The synergy of cost control and value improvement directly impacts project profitability and successful delivery.
Collaboration within Construction Teams
Cost Engineers focus on budget control, cost estimation, and financial risk management, while Value Engineers prioritize maximizing project value through function analysis and design optimization. Effective collaboration between Cost Engineers and Value Engineers within construction teams enhances project efficiency by aligning cost control with value-driven solutions, ensuring optimal resource allocation. Integrating their expertise fosters transparent communication and innovative problem-solving, leading to improved project outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction.
Tools and Techniques Used
Cost Engineers primarily utilize tools such as cost estimating software, risk analysis models, and Earned Value Management Systems (EVMS) to monitor project budgets and forecast expenses accurately. Value Engineers employ techniques like Function Analysis System Technique (FAST), Life Cycle Costing (LCC), and Value Stream Mapping to optimize project value by improving function while minimizing cost. Both disciplines integrate Building Information Modeling (BIM) to enhance collaboration and decision-making in construction projects.
Career Path and Industry Demand
Cost engineers specialize in project budgeting, cost control, and financial risk management, with career paths in construction management, project control, and consultancy roles. Value engineers focus on optimizing project value by analyzing function, materials, and design alternatives to reduce costs without compromising quality, leading to opportunities in design management, procurement, and quality assurance. Industry demand favors cost engineers in large-scale infrastructure projects due to stringent budget controls, while value engineers are increasingly sought after in sustainable construction and innovative development sectors to enhance project efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Engineering Role
Selecting between a Cost Engineer and a Value Engineer depends on project priorities such as budget control or maximizing value. Cost Engineers specialize in accurate cost estimation, budgeting, and financial risk management to ensure projects stay within financial limits. Value Engineers focus on optimizing project functions and improving quality while reducing costs, delivering enhanced value without compromising performance.
Cost Engineer vs Value Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com