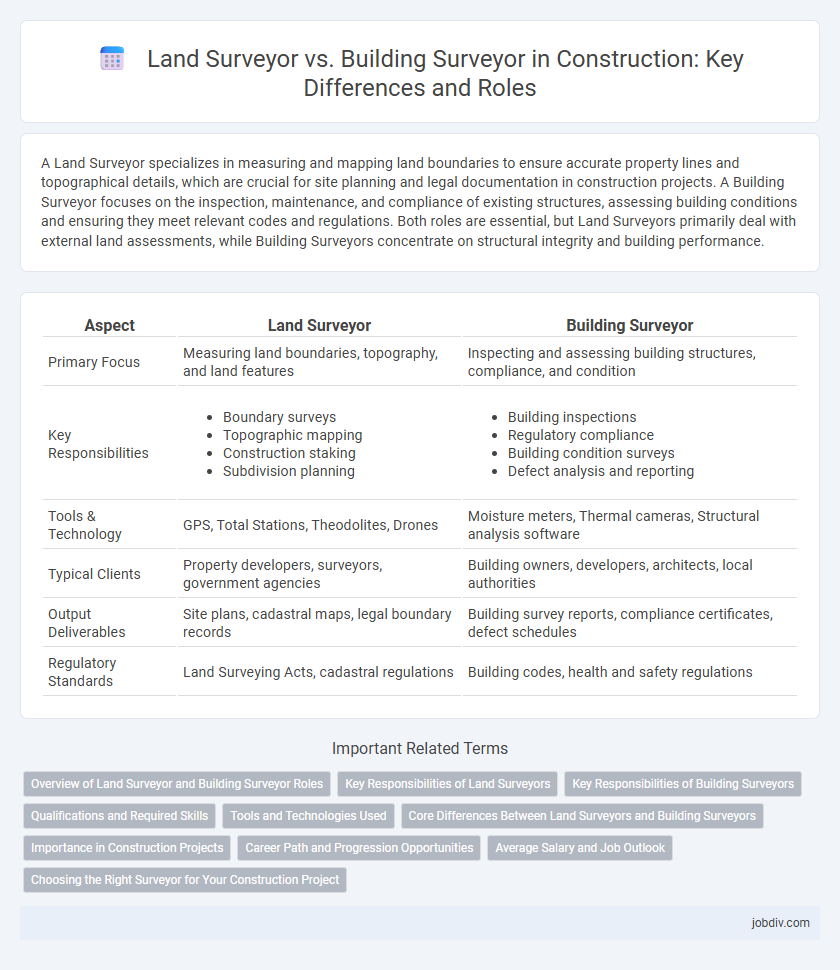
A Land Surveyor specializes in measuring and mapping land boundaries to ensure accurate property lines and topographical details, which are crucial for site planning and legal documentation in construction projects. A Building Surveyor focuses on the inspection, maintenance, and compliance of existing structures, assessing building conditions and ensuring they meet relevant codes and regulations. Both roles are essential, but Land Surveyors primarily deal with external land assessments, while Building Surveyors concentrate on structural integrity and building performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Land Surveyor | Building Surveyor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Measuring land boundaries, topography, and land features | Inspecting and assessing building structures, compliance, and condition |
| Key Responsibilities |
|
|
| Tools & Technology | GPS, Total Stations, Theodolites, Drones | Moisture meters, Thermal cameras, Structural analysis software |
| Typical Clients | Property developers, surveyors, government agencies | Building owners, developers, architects, local authorities |
| Output Deliverables | Site plans, cadastral maps, legal boundary records | Building survey reports, compliance certificates, defect schedules |
| Regulatory Standards | Land Surveying Acts, cadastral regulations | Building codes, health and safety regulations |
Overview of Land Surveyor and Building Surveyor Roles
Land surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping land boundaries, topography, and physical features to support construction projects and legal documentation. Building surveyors focus on inspecting and assessing the condition, design, and safety of existing structures, ensuring compliance with building regulations and standards. Both roles are critical in construction, with land surveyors providing groundwork data and building surveyors overseeing structural integrity and regulatory adherence.
Key Responsibilities of Land Surveyors
Land surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping land boundaries, topography, and features using advanced tools like GPS and total stations to ensure accurate spatial data for construction projects. Their key responsibilities include establishing property lines, preparing site plans, conducting land subdivision surveys, and providing legal documentation for land ownership and development. These precise measurements are crucial for architects, engineers, and builders to design and construct structures within regulatory compliance and avoid disputes.
Key Responsibilities of Building Surveyors
Building surveyors specialize in assessing the condition, structure, and safety of buildings, conducting detailed inspections to identify defects, damage, or compliance issues with building regulations. Their key responsibilities include advising on repairs, maintenance, and renovations, managing construction contracts, and ensuring projects meet health and safety standards. Unlike land surveyors who focus on measuring land and property boundaries, building surveyors bridge design and construction phases to maintain structural integrity and regulatory adherence.
Qualifications and Required Skills
Land surveyors require a degree in geomatics, surveying, or civil engineering, with expertise in GPS technology, GIS mapping, and data analysis to measure land boundaries accurately. Building surveyors typically possess qualifications in building surveying or construction management, emphasizing skills in structural assessment, regulatory compliance, and property inspection. Both professions demand strong problem-solving abilities and proficiency in specialized software, but their technical focus and certification bodies differ significantly.
Tools and Technologies Used
Land surveyors utilize advanced GPS equipment, total stations, and drone technology to measure and map land boundaries with high precision. Building surveyors rely on laser scanners, thermal imaging cameras, and CAD software to assess structural integrity and provide detailed building diagnostics. Both professionals integrate Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for data analysis and visualization, enhancing accuracy in their respective surveys.
Core Differences Between Land Surveyors and Building Surveyors
Land surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping land boundaries, topography, and property lines using tools like GPS and total stations, essential for construction site planning and legal documentation. Building surveyors focus on inspecting, assessing, and ensuring compliance of structures, dealing with building regulations, safety standards, and maintenance issues throughout the construction lifecycle. While land surveyors establish precise land data critical for project design, building surveyors manage structural integrity and regulatory adherence during and after construction.
Importance in Construction Projects
Land surveyors provide precise measurements and boundary determinations essential for site planning and legal documentation, ensuring construction projects begin on a stable and compliant foundation. Building surveyors assess structural integrity, compliance with building codes, and identify defects, playing a crucial role in maintaining safety and quality throughout the construction process. The collaboration between land surveyors and building surveyors optimizes project accuracy, reduces risks, and supports regulatory adherence from site acquisition to project completion.
Career Path and Progression Opportunities
Land surveyors primarily focus on measuring and mapping land boundaries using advanced technologies like GPS and GIS, which opens career paths in civil engineering firms, government agencies, and construction companies. Building surveyors specialize in inspecting structural integrity, compliance, and maintenance of buildings, leading to roles in property consultancy, project management, and urban planning. Progression for land surveyors often involves becoming licensed surveyors or geographic information system (GIS) specialists, while building surveyors can advance to senior surveyor roles, consultancy positions, or chartered surveyor status.
Average Salary and Job Outlook
Land surveyors earn an average salary of around $65,000 annually, with job growth projected at 6% over the next decade due to increasing infrastructure projects. Building surveyors typically make slightly more, averaging $70,000 per year, driven by demand in property inspection and compliance sectors. Both professions offer stable career prospects, but building surveyors benefit from broader opportunities in real estate and construction management.
Choosing the Right Surveyor for Your Construction Project
Choosing the right surveyor for your construction project depends on the specific expertise required; land surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping land boundaries, topography, and site layout, ensuring accurate property lines and legal documentation. Building surveyors focus on assessing building structures, compliance with regulations, condition reports, and advising on construction or renovation processes. Selecting a land surveyor is crucial for site planning and legal land disputes, whereas a building surveyor is essential for structural integrity and regulatory adherence in construction.
Land Surveyor vs Building Surveyor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com