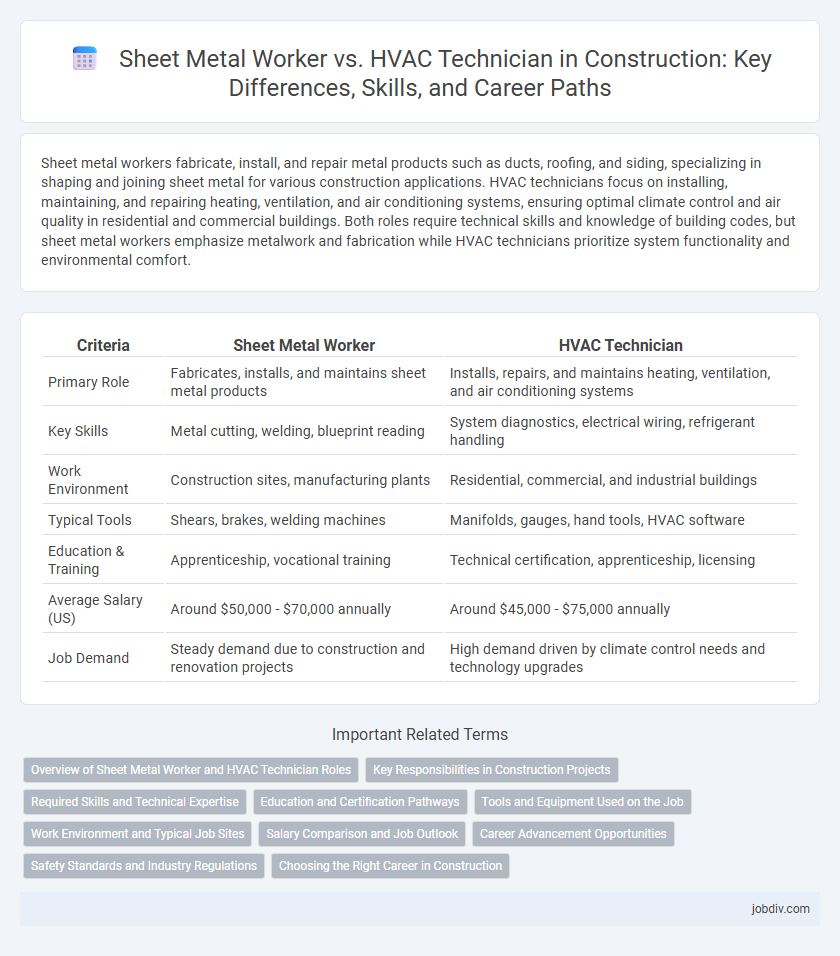
Sheet metal workers fabricate, install, and repair metal products such as ducts, roofing, and siding, specializing in shaping and joining sheet metal for various construction applications. HVAC technicians focus on installing, maintaining, and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, ensuring optimal climate control and air quality in residential and commercial buildings. Both roles require technical skills and knowledge of building codes, but sheet metal workers emphasize metalwork and fabrication while HVAC technicians prioritize system functionality and environmental comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Sheet Metal Worker | HVAC Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Fabricates, installs, and maintains sheet metal products | Installs, repairs, and maintains heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems |
| Key Skills | Metal cutting, welding, blueprint reading | System diagnostics, electrical wiring, refrigerant handling |
| Work Environment | Construction sites, manufacturing plants | Residential, commercial, and industrial buildings |
| Typical Tools | Shears, brakes, welding machines | Manifolds, gauges, hand tools, HVAC software |
| Education & Training | Apprenticeship, vocational training | Technical certification, apprenticeship, licensing |
| Average Salary (US) | Around $50,000 - $70,000 annually | Around $45,000 - $75,000 annually |
| Job Demand | Steady demand due to construction and renovation projects | High demand driven by climate control needs and technology upgrades |
Overview of Sheet Metal Worker and HVAC Technician Roles
Sheet metal workers fabricate, install, and maintain metal components such as ductwork, roofing, and siding essential for building structures. HVAC technicians specialize in installing, repairing, and servicing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure climate control and air quality. Both roles require knowledge of blueprints, tools, and safety standards but focus on different aspects of construction and maintenance.
Key Responsibilities in Construction Projects
Sheet metal workers specialize in fabricating, installing, and maintaining metal ducts, roofs, and siding components essential for building envelopes and HVAC systems in construction projects. HVAC technicians focus on installing, repairing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, ensuring optimal climate control and air quality within buildings. Both roles require precise skills in interpreting blueprints, safety compliance, and coordination with other construction trades to ensure project efficiency and system integration.
Required Skills and Technical Expertise
Sheet Metal Workers require expertise in fabricating and installing metal sheets, involving skills in measuring, cutting, bending, and joining metals with precision tools and machinery. HVAC Technicians must possess technical knowledge in heating, ventilation, air conditioning systems, including electrical components, refrigeration cycles, and diagnostics for system maintenance and repair. Proficiency in reading blueprints and compliance with safety standards are critical for both professions, but HVAC Technicians need additional certification in handling refrigerants and troubleshooting complex climate control systems.
Education and Certification Pathways
Sheet metal workers typically complete an apprenticeship combining on-the-job training with technical instruction, often earning certifications such as the NCCER Core Curriculum or OSHA safety credentials. HVAC technicians usually pursue formal education through technical schools or community colleges, obtaining certifications like EPA Section 608 for refrigerant handling and NATE (North American Technician Excellence) credentials. Both careers require strong technical skills, but HVAC technicians often need additional certifications specific to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Tools and Equipment Used on the Job
Sheet metal workers utilize specialized tools such as metal shears, bending brakes, seamers, and hand tools like hammers and snips to cut, shape, and assemble sheet metal components. HVAC technicians rely on diagnostic instruments including manifold gauges, refrigerant recovery machines, vacuum pumps, and leak detectors to install, service, and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Both professions require proficiency with power tools and safety equipment tailored to their specific tasks for precision and efficiency in construction projects.
Work Environment and Typical Job Sites
Sheet metal workers primarily operate in manufacturing plants, industrial sites, and construction areas where they fabricate, install, and repair metal products such as ductwork and roofing. HVAC technicians frequently work inside residential, commercial, and industrial buildings to install, maintain, and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. While sheet metal workers often handle heavy materials and work outdoors or in partially enclosed spaces, HVAC technicians typically perform tasks in confined indoor areas requiring precise system diagnostics and adjustments.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Sheet metal workers earn a median annual wage of approximately $52,000, with job outlook growth projected at 6% over the next decade, reflecting steady demand in construction and manufacturing. HVAC technicians typically have a higher median salary around $55,000 to $60,000, with a faster expected job growth rate of about 13%, driven by increasing demand for climate control systems and energy-efficient installations. Both careers offer strong employment opportunities, but HVAC technicians tend to command higher wages and stronger growth due to specialization in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Sheet Metal Workers can advance by specializing in areas like architectural sheet metal or becoming supervisors, gaining expertise in fabrication and installation of ductwork, roofing, and siding systems. HVAC Technicians often progress through certifications in refrigeration, system controls, or energy efficiency, leading to roles in system design, maintenance management, or technical sales. Both careers offer union apprenticeship programs that provide structured training and pathways to higher wages and leadership positions.
Safety Standards and Industry Regulations
Sheet Metal Workers adhere to OSHA standards for handling sharp metal edges and operating heavy machinery, emphasizing the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and eye protection to prevent injuries. HVAC Technicians follow EPA regulations regarding refrigerant handling and are required to comply with safety protocols like lockout/tagout procedures to mitigate electrical and chemical hazards. Both professions must stay updated on ANSI and NFPA codes relevant to their tasks to ensure compliance with evolving industry safety standards.
Choosing the Right Career in Construction
Sheet metal workers specialize in fabricating and installing metal products for roofing, siding, and ductwork, requiring skills in welding, cutting, and blueprint reading. HVAC technicians focus on installing, maintaining, and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, demanding knowledge in refrigeration, electrical components, and climate control technology. Choosing the right career depends on your interest in structural metalwork versus climate system mechanics, as well as desired work environments and specialized certifications.
Sheet Metal Worker vs HVAC Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com