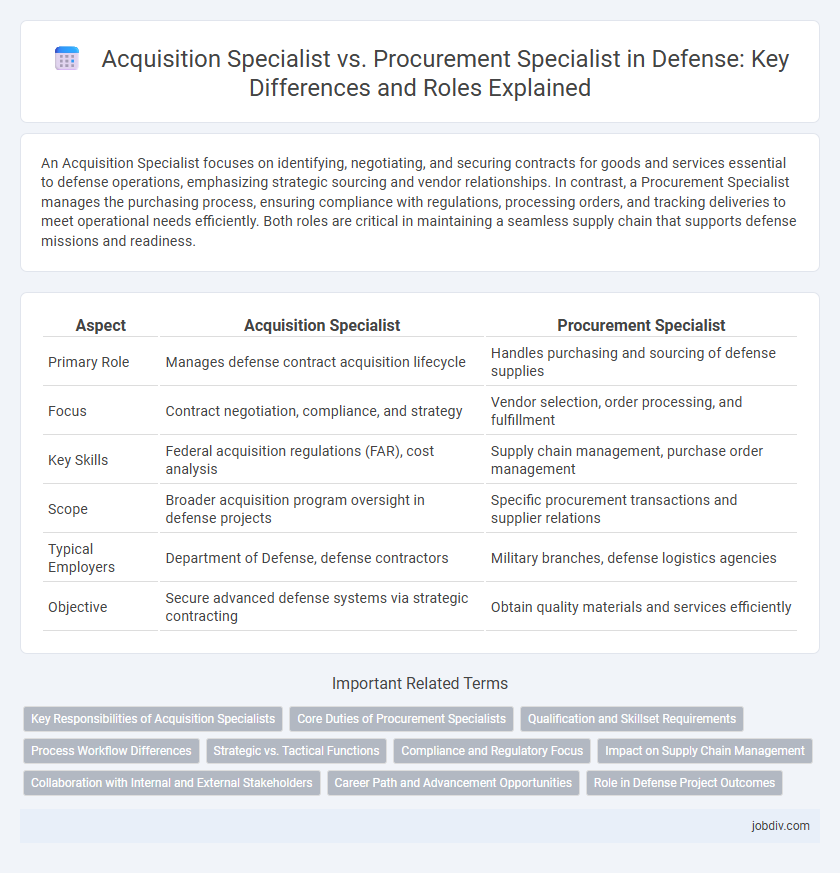
An Acquisition Specialist focuses on identifying, negotiating, and securing contracts for goods and services essential to defense operations, emphasizing strategic sourcing and vendor relationships. In contrast, a Procurement Specialist manages the purchasing process, ensuring compliance with regulations, processing orders, and tracking deliveries to meet operational needs efficiently. Both roles are critical in maintaining a seamless supply chain that supports defense missions and readiness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Acquisition Specialist | Procurement Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages defense contract acquisition lifecycle | Handles purchasing and sourcing of defense supplies |
| Focus | Contract negotiation, compliance, and strategy | Vendor selection, order processing, and fulfillment |
| Key Skills | Federal acquisition regulations (FAR), cost analysis | Supply chain management, purchase order management |
| Scope | Broader acquisition program oversight in defense projects | Specific procurement transactions and supplier relations |
| Typical Employers | Department of Defense, defense contractors | Military branches, defense logistics agencies |
| Objective | Secure advanced defense systems via strategic contracting | Obtain quality materials and services efficiently |
Key Responsibilities of Acquisition Specialists
Acquisition Specialists in defense focus on managing complex contracts, ensuring compliance with federal acquisition regulations (FAR), and coordinating with multiple stakeholders to meet mission-critical requirements. They conduct market research, develop acquisition strategies, and oversee the entire procurement lifecycle from requirements definition to contract closeout. These specialists play a pivotal role in cost analysis, risk management, and negotiating terms to support defense programs efficiently.
Core Duties of Procurement Specialists
Procurement Specialists in defense manage the acquisition of goods and services essential for military operations, ensuring compliance with federal regulations and defense contracting standards. Their core duties include evaluating supplier capabilities, negotiating contracts, and managing supply chain risks to maintain operational readiness. They also coordinate with acquisition specialists to align procurement strategies with broader defense acquisition programs and budget constraints.
Qualification and Skillset Requirements
Acquisition Specialists in defense typically require expertise in contract law, government acquisition regulations (FAR/DFARS), and project management certifications such as PMP or DAWIA. Procurement Specialists focus on supplier relationship management, cost analysis, and inventory control, often holding certifications like CPSM or CPPM. Both roles demand strong negotiation skills, familiarity with defense logistics, and compliance with federal acquisition policies, but Acquisition Specialists emphasize strategic sourcing and contract administration more heavily.
Process Workflow Differences
Acquisition specialists in defense manage end-to-end contracting processes, including requirements analysis, solicitation, negotiation, and contract award, ensuring compliance with federal acquisition regulations. Procurement specialists focus on the purchasing phase, emphasizing supplier selection, purchase order issuance, and transaction processing within established contracts. The acquisition specialist oversees the strategic workflow from need identification to contract execution, while the procurement specialist handles tactical execution and supply chain coordination under those contracts.
Strategic vs. Tactical Functions
Acquisition Specialists in defense focus on strategic functions such as long-term planning, contract negotiation, and aligning procurement with overarching military goals and compliance standards. Procurement Specialists perform tactical tasks including order placement, supplier management, and day-to-day logistics ensuring timely delivery of defense materials. The strategic role of Acquisition Specialists drives policy and resource allocation, while Procurement Specialists execute operational purchasing activities within those strategic frameworks.
Compliance and Regulatory Focus
Acquisition Specialists in defense prioritize compliance with federal acquisition regulations (FAR) and Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) to ensure contract awards meet stringent legal standards. Procurement Specialists focus on regulatory adherence related to supply chain management and vendor qualifications, ensuring all purchases comply with defense acquisition policies and cybersecurity mandates. Both roles require expert knowledge of government contracting laws but diverge in their emphasis on acquisition strategy versus operational purchasing compliance.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
Acquisition Specialists in defense focus on strategic sourcing, contract negotiation, and vendor performance to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery of critical defense materials, directly enhancing supply chain resilience and mission readiness. Procurement Specialists handle the transactional aspects of purchasing, including order processing and supplier coordination, which supports the efficient flow of goods but may have less influence on long-term supply chain strategy. Their combined efforts streamline defense supply chains by balancing strategic oversight with operational execution, reducing risks of delays and shortages in essential equipment.
Collaboration with Internal and External Stakeholders
Acquisition specialists coordinate closely with contract managers, legal teams, and defense project leaders to ensure compliance with federal acquisition regulations and streamline procurement processes. Procurement specialists collaborate with suppliers, vendors, and logistics partners to secure materials and services that meet defense specifications and delivery schedules. Both roles require effective communication and negotiation skills to align internal requirements with external capabilities, enhancing operational readiness and cost-efficiency.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Acquisition Specialists in defense typically pursue career advancement through specialized roles in contract management, negotiations, and compliance, often progressing to senior acquisition officer or program manager positions. Procurement Specialists focus on sourcing, purchasing strategies, and supplier relationship management, with career paths leading to procurement manager or supply chain director roles. Both roles offer opportunities for certification such as DAWIA or CPSM, enhancing prospects for leadership positions within the defense acquisition workforce.
Role in Defense Project Outcomes
Acquisition Specialists in defense projects manage the end-to-end process of securing complex systems and technology, ensuring compliance with federal regulations and aligning purchases with strategic military objectives. Procurement Specialists focus on the tactical purchasing aspects, negotiating contracts and managing supplier relationships to guarantee timely delivery and cost efficiency of materials and services. Both roles are critical to defense project outcomes, with Acquisition Specialists shaping project direction through long-term planning and Procurement Specialists optimizing operational execution.
Acquisition Specialist vs Procurement Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com