A Counterintelligence Agent focuses on identifying and neutralizing espionage threats and protecting sensitive information from foreign intelligence services. In contrast, a Counterterrorism Specialist concentrates on preventing, responding to, and investigating terrorist activities and networks. Both roles require advanced analytical skills and collaboration with law enforcement to safeguard national security.
Table of Comparison
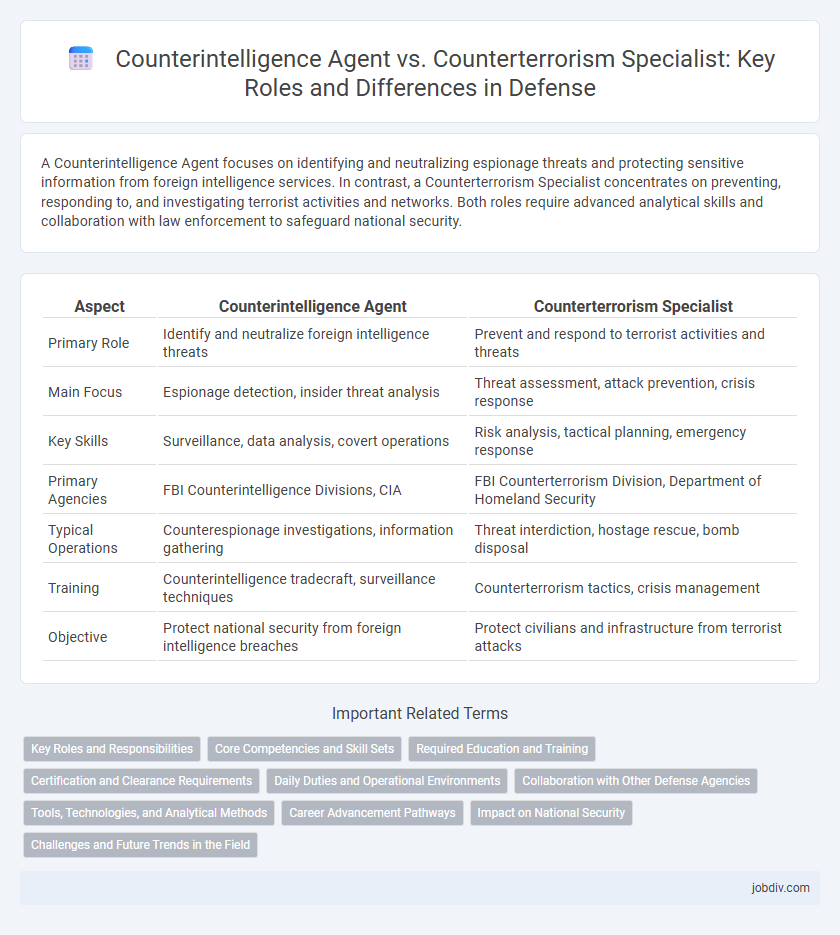
| Aspect | Counterintelligence Agent | Counterterrorism Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Identify and neutralize foreign intelligence threats | Prevent and respond to terrorist activities and threats |
| Main Focus | Espionage detection, insider threat analysis | Threat assessment, attack prevention, crisis response |
| Key Skills | Surveillance, data analysis, covert operations | Risk analysis, tactical planning, emergency response |
| Primary Agencies | FBI Counterintelligence Divisions, CIA | FBI Counterterrorism Division, Department of Homeland Security |
| Typical Operations | Counterespionage investigations, information gathering | Threat interdiction, hostage rescue, bomb disposal |
| Training | Counterintelligence tradecraft, surveillance techniques | Counterterrorism tactics, crisis management |
| Objective | Protect national security from foreign intelligence breaches | Protect civilians and infrastructure from terrorist attacks |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Counterintelligence Agents specialize in identifying and neutralizing threats posed by foreign intelligence services, employing surveillance, analysis, and covert operations to protect national security information. Counterterrorism Specialists focus on preventing, detecting, and responding to terrorist activities by gathering intelligence, conducting risk assessments, and coordinating with law enforcement agencies to thwart attacks. Both roles demand expertise in threat analysis and strategic intervention but differ in target focus: counterintelligence targets espionage, while counterterrorism addresses terrorist threats.
Core Competencies and Skill Sets
Counterintelligence Agents specialize in identifying, assessing, and neutralizing espionage threats through skills in surveillance detection, intelligence analysis, and covert operations. Counterterrorism Specialists focus on preventing and responding to terrorist activities by leveraging expertise in threat assessment, crisis management, tactical response, and interagency coordination. Both roles require proficiency in intelligence collection and security protocols, but Counterintelligence Agents prioritize defensive measures against foreign intelligence, whereas Counterterrorism Specialists emphasize proactive measures against violent extremism.
Required Education and Training
Counterintelligence Agents typically require a bachelor's degree in criminal justice, political science, or international relations, followed by specialized training at agencies like the FBI or CIA in intelligence analysis, surveillance, and threat identification. Counterterrorism Specialists often hold degrees in homeland security, forensic science, or cybersecurity and undergo rigorous training in tactical response, explosives detection, and crisis management through federal or military programs. Both roles demand continuous education in evolving security threats, with Counterintelligence focusing more on espionage prevention and Counterterrorism emphasizing proactive counterattacks and threat mitigation.
Certification and Clearance Requirements
Counterintelligence agents typically require Department of Defense (DoD) security clearances, often at the Top Secret level with Sensitive Compartmented Information (SCI) access, and certifications such as the Certified Counterintelligence Professional (CCIP) credential. Counterterrorism specialists generally hold security clearances ranging from Secret to Top Secret with SCI, complemented by specialized counterterrorism certifications like the Certified Protection Professional (CPP) or training in counterterrorism tactics and intelligence analysis. Both roles demand rigorous background investigations, with counterintelligence positions emphasizing security clearance due to the sensitive nature of espionage prevention.
Daily Duties and Operational Environments
Counterintelligence agents focus on identifying and neutralizing foreign espionage threats by conducting surveillance, analyzing intelligence, and securing sensitive information within military and government installations. Counterterrorism specialists engage in proactive threat assessment, crisis response, and tactical operations to prevent and respond to terrorist activities in urban and high-risk environments. Both roles demand acute situational awareness, but counterintelligence prioritizes covert intelligence-gathering, while counterterrorism emphasizes immediate threat mitigation and rapid deployment.
Collaboration with Other Defense Agencies
Counterintelligence agents and counterterrorism specialists work closely with multiple defense agencies to enhance national security by sharing intelligence and coordinating strategic operations. Counterintelligence agents focus on detecting and neutralizing espionage threats through collaboration with military intelligence units and federal law enforcement. Counterterrorism specialists collaborate with defense agencies like the Department of Homeland Security and the FBI to prevent terrorist attacks by integrating tactical response efforts and intelligence analysis.
Tools, Technologies, and Analytical Methods
Counterintelligence agents utilize advanced surveillance systems, encryption-breaking software, and human intelligence platforms to detect and neutralize espionage threats. Counterterrorism specialists rely heavily on geospatial intelligence, biometric identification technologies, and predictive analytics to prevent and respond to terrorist activities. Both roles employ data mining and signal interception but apply these tools differently to address unique security challenges.
Career Advancement Pathways
Counterintelligence Agents advance through specialized training in espionage detection, insider threat analysis, and foreign intelligence operations, often progressing to senior analyst or supervisory roles within intelligence agencies. Counterterrorism Specialists develop expertise in threat assessment, crisis response, and interagency coordination, leading to career growth as tactical commanders, policy advisors, or coordinators in homeland security. Both career paths emphasize continuous skill development and certification to enhance operational effectiveness and promote leadership opportunities.
Impact on National Security
Counterintelligence agents play a critical role in safeguarding national security by identifying and neutralizing foreign intelligence threats, thereby preventing espionage and breaches of classified information. Counterterrorism specialists directly impact national security through the detection, prevention, and response to terrorist activities, minimizing casualties and infrastructure damage. Both roles are essential in creating a comprehensive security framework that addresses diverse threats to a nation's stability and defense.
Challenges and Future Trends in the Field
Counterintelligence agents face the challenge of detecting and neutralizing espionage activities while adapting to sophisticated cyber threats and insider risks, requiring advanced analytical tools and interagency collaboration. Counterterrorism specialists must anticipate and respond to evolving terror tactics, including the use of encrypted communications and autonomous weapons, necessitating real-time intelligence sharing and predictive analytics. Future trends emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data to enhance threat detection and decision-making efficiency across both disciplines.
Counterintelligence Agent vs Counterterrorism Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com