Unmanned Systems Operators oversee the control and management of a wide range of robotic platforms, including ground, sea, and aerial vehicles, ensuring mission success through advanced technical skills and real-time decision-making. Drone Pilots specialize exclusively in flying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), focusing on navigational precision, flight control, and data collection from the air. Both roles demand expertise in remote operation and situational awareness but differ in their operational environment and scope of responsibilities within defense applications.
Table of Comparison
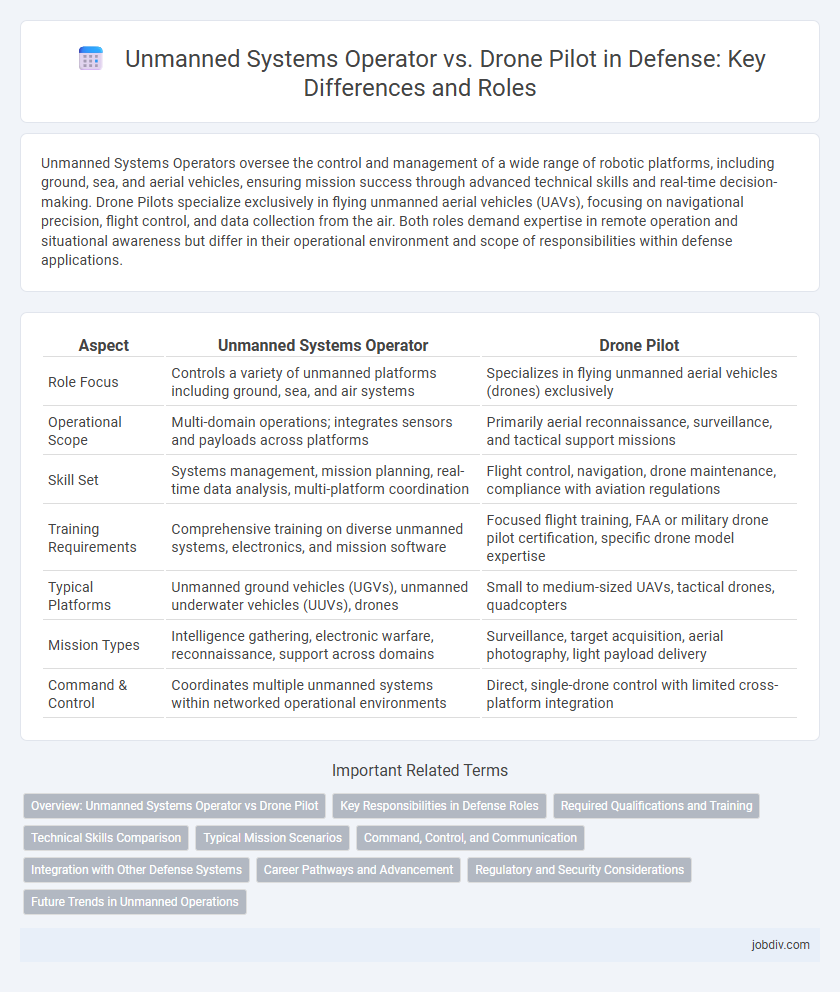
| Aspect | Unmanned Systems Operator | Drone Pilot |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Controls a variety of unmanned platforms including ground, sea, and air systems | Specializes in flying unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) exclusively |
| Operational Scope | Multi-domain operations; integrates sensors and payloads across platforms | Primarily aerial reconnaissance, surveillance, and tactical support missions |
| Skill Set | Systems management, mission planning, real-time data analysis, multi-platform coordination | Flight control, navigation, drone maintenance, compliance with aviation regulations |
| Training Requirements | Comprehensive training on diverse unmanned systems, electronics, and mission software | Focused flight training, FAA or military drone pilot certification, specific drone model expertise |
| Typical Platforms | Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs), unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs), drones | Small to medium-sized UAVs, tactical drones, quadcopters |
| Mission Types | Intelligence gathering, electronic warfare, reconnaissance, support across domains | Surveillance, target acquisition, aerial photography, light payload delivery |
| Command & Control | Coordinates multiple unmanned systems within networked operational environments | Direct, single-drone control with limited cross-platform integration |
Overview: Unmanned Systems Operator vs Drone Pilot
Unmanned Systems Operators are trained to manage a variety of autonomous and remotely controlled vehicles across multiple platforms, including aerial, ground, and underwater systems, focusing on mission execution and system integration. Drone Pilots primarily specialize in flying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for reconnaissance, surveillance, and tactical operations, emphasizing precise flight control and navigation. Both roles require expertise in remote operation technologies, but Unmanned Systems Operators possess broader multi-domain operational skills beyond piloting drones alone.
Key Responsibilities in Defense Roles
Unmanned Systems Operators manage and control a wide array of remotely operated vehicles, including aerial, ground, and maritime drones, executing complex missions such as intelligence gathering, surveillance, and target acquisition in defense operations. Drone Pilots specifically focus on flying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with precision, ensuring mission success through real-time navigation, monitoring flight systems, and adhering to strict operational protocols. Both roles demand expertise in advanced technologies, situational awareness, and coordination with command units to enhance battlefield effectiveness and minimize risks.
Required Qualifications and Training
Unmanned Systems Operators require comprehensive military or civilian training that emphasizes mission-specific tactics, system integration, and threat assessment, often involving certifications in defense protocols and cybersecurity. Drone Pilots typically undergo specialized flight training focused on remote aircraft operation, navigation, and compliance with aviation regulations, with certifications like the FAA Part 107 for commercial drones. Both roles demand proficiency in technology and real-time decision-making, but Unmanned Systems Operators generally possess broader operational and strategic expertise related to defense applications.
Technical Skills Comparison
Unmanned Systems Operators require expertise in integrated sensor systems, autonomous navigation algorithms, and secure communication protocols to manage complex multi-platform operations. Drone Pilots focus on hands-on flight control, real-time manual navigation, and compliance with airspace regulations, emphasizing precise maneuvering skills. Technical proficiency in data analysis, mission planning software, and radio frequency management differentiates Operators, while Pilots excel in aerodynamic understanding and in-field troubleshooting.
Typical Mission Scenarios
Unmanned Systems Operators typically manage complex, multi-domain missions involving surveillance, reconnaissance, and weapon system integration across air, land, and sea platforms. Drone Pilots primarily conduct aerial missions such as tactical reconnaissance, target acquisition, and real-time intelligence gathering using small to medium-sized UAVs. Both roles require mission-specific expertise, but Operators generally handle broader operational frameworks, whereas Pilots focus on precise aerial maneuvering and sensor operation.
Command, Control, and Communication
Unmanned Systems Operators manage complex command, control, and communication (C3) networks that integrate multiple unmanned platforms across diverse operational theaters. Drone Pilots primarily focus on the direct control and navigation of individual UAVs, ensuring real-time data transmission and secure communication link maintenance. The distinction in roles highlights the operator's broader responsibility for coordinating swarm tactics and situational awareness through advanced C3 systems.
Integration with Other Defense Systems
Unmanned systems operators coordinate complex missions by integrating drones with radar, communication networks, and ground control stations to enhance battlefield situational awareness and response capabilities. Drone pilots primarily focus on maneuvering UAVs during missions, while operators manage real-time data fusion across multiple platforms for strategic decision-making. This integration enables seamless interoperability between unmanned aerial systems and other defense assets, optimizing operational effectiveness.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Unmanned Systems Operators typically engage in the integrated control of various unmanned platforms, including ground and underwater vehicles, emphasizing versatile skill sets applicable to broader defense operations. Drone Pilots specialize in aerial vehicle navigation and remote piloting technology, often advancing through certifications and experience in surveillance, reconnaissance, and tactical deployment roles. Career progression for both paths involves continuous technical training, with operators advancing into leadership positions in mission planning, systems integration, and specialized combat or intelligence units.
Regulatory and Security Considerations
Unmanned systems operators navigate complex regulatory frameworks that govern both military and civilian drone use, ensuring compliance with national and international defense protocols. Drone pilots must maintain stringent security clearances and adhere to cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to critical defense operations. Regulatory bodies enforce standards on operator certification, flight permissions, and no-fly zones, emphasizing the strategic importance of secure unmanned system deployment.
Future Trends in Unmanned Operations
Unmanned Systems Operators and Drone Pilots will increasingly rely on advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance real-time decision-making and mission adaptability. Integration of autonomous swarm technology will redefine operational tactics, enabling coordinated actions among multiple unmanned vehicles for both surveillance and combat missions. Cybersecurity measures and secure communication networks will become paramount to protect unmanned operations from electronic warfare and hacking attempts in future defense scenarios.
Unmanned Systems Operator vs Drone Pilot Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com