A Signals Analyst specializes in intercepting and interpreting electronic communications, providing critical intelligence through technical means such as signal interception and cyber surveillance. A HUMINT Collector gathers intelligence from human sources, relying on interpersonal skills, fieldwork, and covert operations to obtain valuable information directly from people. Both roles are essential in defense operations, complementing each other by combining electronic data analysis with human-derived insights for comprehensive situational awareness.
Table of Comparison
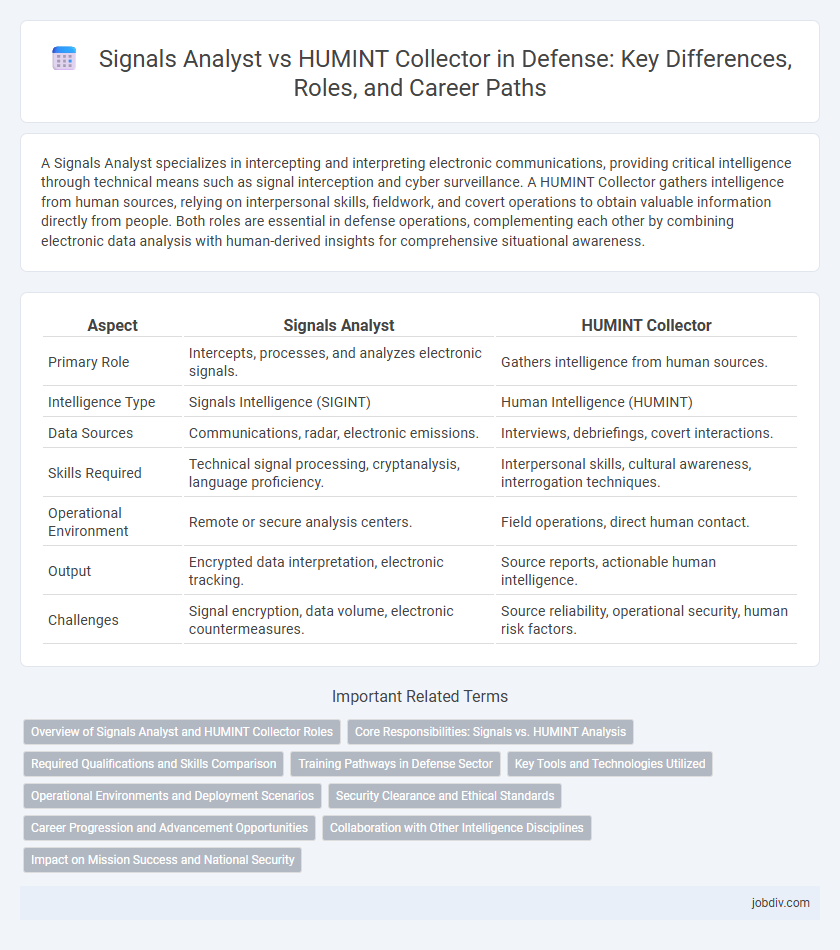
| Aspect | Signals Analyst | HUMINT Collector |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Intercepts, processes, and analyzes electronic signals. | Gathers intelligence from human sources. |
| Intelligence Type | Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) | Human Intelligence (HUMINT) |
| Data Sources | Communications, radar, electronic emissions. | Interviews, debriefings, covert interactions. |
| Skills Required | Technical signal processing, cryptanalysis, language proficiency. | Interpersonal skills, cultural awareness, interrogation techniques. |
| Operational Environment | Remote or secure analysis centers. | Field operations, direct human contact. |
| Output | Encrypted data interpretation, electronic tracking. | Source reports, actionable human intelligence. |
| Challenges | Signal encryption, data volume, electronic countermeasures. | Source reliability, operational security, human risk factors. |
Overview of Signals Analyst and HUMINT Collector Roles
Signals Analysts specialize in intercepting, analyzing, and interpreting electronic communications and signal transmissions to provide critical intelligence for military operations. HUMINT Collectors gather information through human sources, conducting interviews and debriefings to obtain strategic insights on enemy activities and intentions. Both roles are essential for comprehensive intelligence, combining technical signal data with human-derived information to support defense decision-making.
Core Responsibilities: Signals vs. HUMINT Analysis
Signals analysts specialize in intercepting, deciphering, and analyzing electronic communications and signals intelligence (SIGINT) to identify threats and gather actionable intelligence. HUMINT collectors focus on acquiring information through human sources, including interrogation, debriefing, and surveillance, to gain insights into enemy intentions and activities. Both roles require critical analysis skills, but signals analysis relies on technical data interception, while HUMINT emphasizes interpersonal communication and source development.
Required Qualifications and Skills Comparison
Signals Analysts require expertise in electronic surveillance, signal processing, and cryptography, along with proficiency in communication systems and data analysis software. HUMINT Collectors must possess strong interpersonal skills, cultural awareness, and language proficiency to gather intelligence through human sources effectively. Both roles demand security clearances, analytical thinking, and the ability to operate in high-pressure environments, but Signals Analysts focus more on technical and cyber capabilities while HUMINT Collectors emphasize human interaction and fieldwork.
Training Pathways in Defense Sector
Signals Analysts undergo rigorous technical training in electronic surveillance, signal processing, and cyber operations, often through specialized military communication schools and intelligence courses. HUMINT Collectors receive focused instruction in human interaction, interrogation techniques, cultural awareness, and covert operations, typically provided by intelligence agencies and specialized defense training centers. Both roles require continuous professional development, but Signals Analysts emphasize technical proficiency, while HUMINT Collectors develop advanced interpersonal and linguistic skills.
Key Tools and Technologies Utilized
Signals Analysts utilize advanced electronic interception technologies, signal processing software, and encryption-breaking tools to capture and analyze communication signals. HUMINT Collectors rely on human-based intelligence gathering techniques, employing secure communication devices, surveillance equipment, and digital databases to collect and verify information from human sources. Both roles integrate geospatial information systems and data analytics platforms to enhance intelligence accuracy and operational effectiveness.
Operational Environments and Deployment Scenarios
Signals Analysts operate primarily in technologically advanced operational environments where intercepted electronic communications and signal intelligence are critical for real-time battlefield awareness. HUMINT Collectors focus on human intelligence gathering in diverse deployment scenarios, often requiring close interaction with local populations to collect actionable information. Both roles adapt to dynamic threat landscapes, with Signals Analysts leveraging cyber and electronic warfare domains, while HUMINT Collectors excel in environments where cultural and interpersonal skills are paramount.
Security Clearance and Ethical Standards
Signals Analysts require Top Secret or higher security clearance due to their access to sensitive electronic communications and intelligence systems. HUMINT Collectors, who gather intelligence through human interactions, also need stringent clearances, often including Sensitive Compartmented Information (SCI) access, reflecting the high risks of human-source operations. Both roles adhere to strict ethical standards, ensuring the protection of classified information and the responsible handling of intelligence to maintain operational integrity and national security.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Signals Analysts advance by gaining expertise in electronic intelligence, cryptography, and signal processing, leading to roles such as senior analyst, cybersecurity specialist, or intelligence operations manager. HUMINT Collectors progress through experience in human source recruitment, interrogation techniques, and cultural knowledge, enabling promotion to senior collector, case officer, or intelligence officer positions. Career advancement for both roles depends on continuous training, operational performance, and the ability to integrate intelligence insights into strategic decision-making.
Collaboration with Other Intelligence Disciplines
Signals Analysts and HUMINT Collectors collaboratively enhance intelligence outcomes by integrating electronic signal intercepts with human-sourced information, facilitating comprehensive threat assessments. Signals Analysts decode and interpret communications data, while HUMINT Collectors provide contextual human insights, enabling multi-dimensional analysis. This synergy improves situational awareness and supports decision-making in defense operations through cross-disciplinary intelligence fusion.
Impact on Mission Success and National Security
Signals Analysts enhance mission success by intercepting and interpreting electronic communications, providing real-time intelligence crucial for tactical decision-making and threat assessment. HUMINT Collectors gather human-derived intelligence through direct interaction, offering context-rich, actionable insights that fill critical gaps unreachable by electronic means. Together, their complementary roles fortify national security by ensuring a comprehensive intelligence picture, enabling proactive countermeasures and strategic dominance.
Signals Analyst vs HUMINT Collector Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com