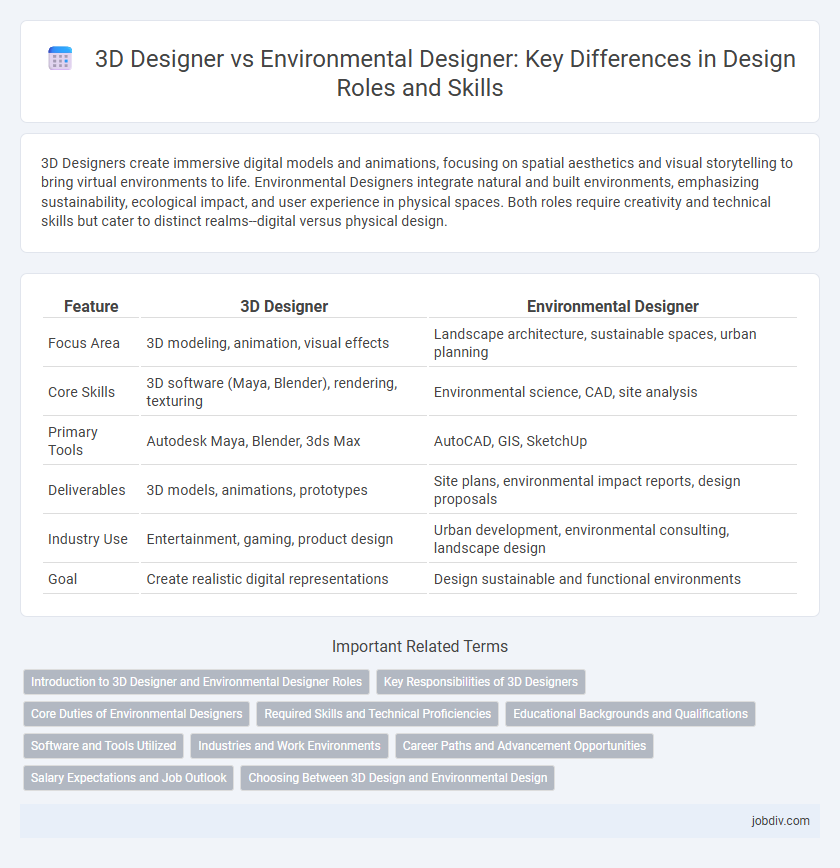
3D Designers create immersive digital models and animations, focusing on spatial aesthetics and visual storytelling to bring virtual environments to life. Environmental Designers integrate natural and built environments, emphasizing sustainability, ecological impact, and user experience in physical spaces. Both roles require creativity and technical skills but cater to distinct realms--digital versus physical design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Designer | Environmental Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | 3D modeling, animation, visual effects | Landscape architecture, sustainable spaces, urban planning |
| Core Skills | 3D software (Maya, Blender), rendering, texturing | Environmental science, CAD, site analysis |
| Primary Tools | Autodesk Maya, Blender, 3ds Max | AutoCAD, GIS, SketchUp |
| Deliverables | 3D models, animations, prototypes | Site plans, environmental impact reports, design proposals |
| Industry Use | Entertainment, gaming, product design | Urban development, environmental consulting, landscape design |
| Goal | Create realistic digital representations | Design sustainable and functional environments |
Introduction to 3D Designer and Environmental Designer Roles
A 3D designer specializes in creating three-dimensional digital models and animations for various industries, including gaming, film, and product design, utilizing software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max. An environmental designer focuses on planning and creating outdoor spaces, integrating natural and built elements to enhance ecological sustainability and user experience in urban planning, landscape architecture, and interior environments. Both roles require a strong understanding of spatial concepts, design principles, and technical skills, but they apply them in distinct contexts to shape physical or digital environments.
Key Responsibilities of 3D Designers
3D Designers specialize in creating three-dimensional models, animations, and visual effects for various media, focusing on rendering realistic textures, lighting, and virtual environments. Their key responsibilities include developing detailed design prototypes, collaborating with clients to refine concepts, and utilizing software such as Autodesk Maya, Blender, or 3ds Max to produce high-quality digital assets. They play a crucial role in product visualization, gaming, film production, and virtual reality applications, emphasizing precision and creativity in digital spatial representation.
Core Duties of Environmental Designers
Environmental designers focus on creating functional, sustainable spaces by integrating architecture, landscape, and urban planning to enhance user experience and ecological impact. They analyze site conditions, materials, and environmental factors to develop designs that balance aesthetics with environmental responsibility. Core duties include conducting site assessments, collaborating with engineers and stakeholders, and ensuring compliance with zoning and environmental regulations.
Required Skills and Technical Proficiencies
3D Designers require advanced proficiency in modeling software such as Blender, Maya, and 3ds Max, alongside skills in texturing, lighting, and animation to create realistic digital representations. Environmental Designers must excel in spatial planning, sustainability principles, and proficiency with tools like AutoCAD, Revit, and GIS software to develop functional, eco-friendly spaces. Both roles demand a strong understanding of design principles, but 3D Designers focus more on visual rendering, while Environmental Designers emphasize ecological impact and user experience.
Educational Backgrounds and Qualifications
3D Designers typically hold degrees in graphic design, computer graphics, or animation, with strong skills in software like Autodesk Maya, Blender, and Adobe Creative Suite. Environmental Designers often pursue education in architecture, landscape architecture, or urban planning, requiring knowledge of sustainable design, CAD software, and environmental regulations. Both fields value portfolios showcasing technical proficiency and creative problem-solving, but Environmental Designers must meet licensing requirements in many regions.
Software and Tools Utilized
3D Designers primarily utilize software such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, and Cinema 4D to create detailed three-dimensional models and animations, focusing on visualizing products, characters, and environments with precision. Environmental Designers rely heavily on tools like AutoCAD, SketchUp, and GIS software to plan and develop functional outdoor spaces, incorporating landscape architecture elements and urban planning data. Both disciplines often employ Adobe Creative Suite for presentation and visualization, but their core software selection reflects the distinct demands of virtual modeling versus spatial and ecological design.
Industries and Work Environments
3D designers primarily work in industries such as gaming, animation, film, and product design, creating detailed digital models and visualizations for virtual and physical environments. Environmental designers operate within urban planning, architecture, landscape design, and sustainable development sectors, focusing on enhancing real-world spaces through strategic planning and aesthetic integration. Both roles demand specialized software proficiency, with 3D designers utilizing tools like Blender and Maya, while environmental designers rely on GIS and CAD applications for spatial analysis and design implementation.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
3D Designers often pursue career advancement by specializing in animation, modeling, or visual effects within industries like gaming, film, and advertising, where mastery of software such as Blender or Maya is highly valued. Environmental Designers focus on large-scale spatial planning, urban design, and sustainable development, frequently advancing into roles that influence public policy or large infrastructure projects. Both careers offer opportunities for growth through project leadership, technical expertise, and interdisciplinary collaboration, but Environmental Designers may find increased demand in sectors driven by climate resilience and smart city initiatives.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
3D designers typically earn an average salary ranging from $50,000 to $75,000 annually, reflecting demand in entertainment, gaming, and advertising industries, while environmental designers command salaries between $55,000 and $80,000, driven by urban planning, landscape architecture, and sustainable development sectors. Job outlook for 3D designers is projected to grow by 8% over the next decade due to expanding virtual reality and computer graphics markets. Environmental designers face a 10% growth rate fueled by increasing emphasis on eco-friendly construction and community planning initiatives.
Choosing Between 3D Design and Environmental Design
Choosing between 3D design and environmental design depends on your career goals and interests. 3D designers specialize in creating digital models and animations for industries like gaming, film, and product visualization, leveraging software such as Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max. Environmental designers focus on shaping physical spaces and urban environments, integrating architecture, landscape, and sustainability principles to improve human interaction with surroundings.
3D Designer vs Environmental Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com