Digital designers specialize in creating visuals optimized for screens, focusing on interactivity, responsive layouts, and multimedia integration. Print designers prioritize high-resolution images, color accuracy, and print production techniques to ensure designs translate effectively on physical materials. Understanding the distinct technical requirements and end-use environments is crucial for choosing the right approach in pet design projects.
Table of Comparison
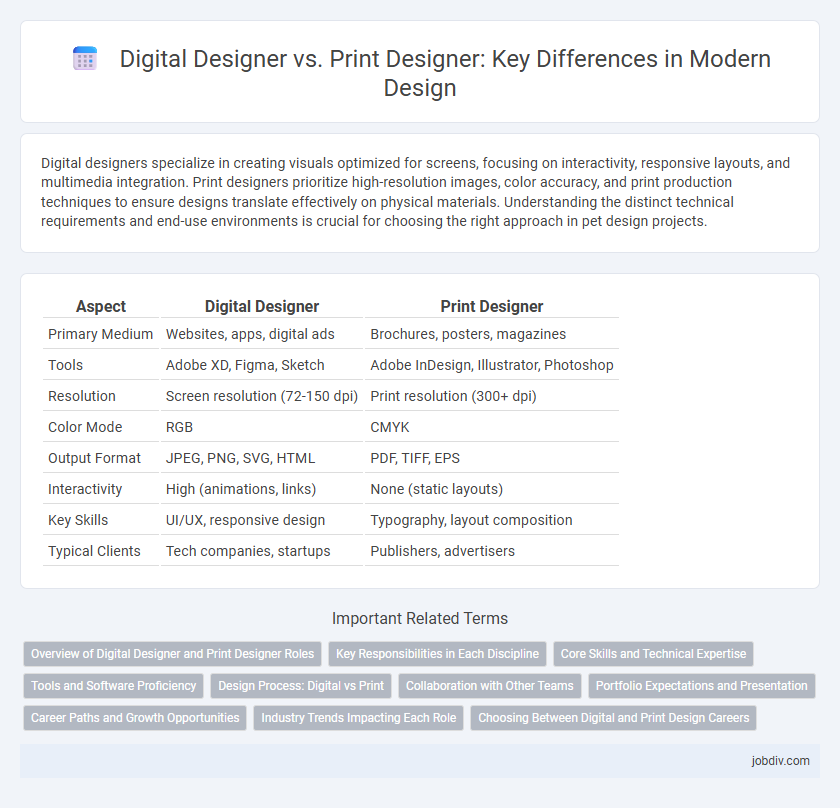
| Aspect | Digital Designer | Print Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Websites, apps, digital ads | Brochures, posters, magazines |
| Tools | Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch | Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop |
| Resolution | Screen resolution (72-150 dpi) | Print resolution (300+ dpi) |
| Color Mode | RGB | CMYK |
| Output Format | JPEG, PNG, SVG, HTML | PDF, TIFF, EPS |
| Interactivity | High (animations, links) | None (static layouts) |
| Key Skills | UI/UX, responsive design | Typography, layout composition |
| Typical Clients | Tech companies, startups | Publishers, advertisers |
Overview of Digital Designer and Print Designer Roles
Digital designers specialize in creating visual content for online platforms, utilizing tools like Adobe XD, Figma, and HTML/CSS to build interactive and responsive designs for websites, apps, and social media. Print designers focus on producing tangible materials such as brochures, posters, and packaging, emphasizing color accuracy, resolution, and print specifications using software like Adobe InDesign and Illustrator. Both roles require a strong understanding of typography, layout, and brand identity, yet digital designers prioritize screen-based user experience while print designers ensure physical product quality and print production processes.
Key Responsibilities in Each Discipline
Digital designers specialize in creating visually engaging content for websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms, focusing on user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design to enhance interactivity and accessibility. Print designers concentrate on producing physical media such as brochures, posters, and packaging, emphasizing color accuracy, typography, and layout suitable for various printing techniques. Both roles require proficiency in design software, but digital designers prioritize responsive design and animation skills, while print designers focus on material selection and prepress processes.
Core Skills and Technical Expertise
Digital designers master software like Adobe XD, Figma, and HTML/CSS, focusing on user interface, animation, and responsive design to optimize screens and interactive platforms. Print designers excel in Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, and Photoshop, emphasizing typesetting, color management, and print production techniques for physical media. Core skills in digital design revolve around UX/UI principles, wireframing, and prototyping, while print design prioritizes layout precision, material knowledge, and prepress workflows.
Tools and Software Proficiency
Digital designers primarily utilize software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and Sketch, with proficiency in UX/UI tools such as Figma and Adobe XD to create interactive and web-based designs. Print designers excel in tools specialized for layout and prepress processes, including Adobe InDesign, QuarkXPress, and CorelDRAW, ensuring color accuracy and print-ready formats. Mastery of these distinct toolsets is essential for each discipline, reflecting the differing demands of digital interfaces versus physical media production.
Design Process: Digital vs Print
Digital designers prioritize user experience, interactive elements, and responsive layouts during the design process, utilizing tools like Adobe XD and Figma to create adaptable graphics for various screens. Print designers focus on color accuracy, resolution, and material selection, working with software such as Adobe InDesign and Illustrator to ensure precise alignment and high-quality output on physical media. Both disciplines require distinct workflows and technical considerations tailored to their respective mediums to achieve optimal visual communication.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Digital designers collaborate closely with developers, marketers, and UX specialists to create interactive and user-focused content across multiple platforms. Print designers coordinate primarily with printers, copywriters, and brand managers to ensure color accuracy and material quality in physical outputs. Both roles require strong communication skills, but digital design demands agile teamwork to adapt quickly to evolving technologies and user feedback.
Portfolio Expectations and Presentation
A digital designer's portfolio emphasizes interactive elements, responsive layouts, and multimedia integration, showcasing expertise in UI/UX and web-based projects. Print designers highlight mastery in typography, color theory, and physical format constraints, presenting high-resolution images and mockups of brochures, posters, and packaging. Effective portfolio presentation for digital designers often includes clickable prototypes and animations, while print designers rely on crisp print samples and physical mockups to demonstrate their work quality.
Career Paths and Growth Opportunities
Digital designers specialize in creating interactive and multimedia content for websites, apps, and digital platforms, offering career growth through roles like UX/UI designer, motion graphics artist, or digital marketing specialist. Print designers focus on tangible media such as brochures, packaging, and branding materials, with career opportunities often leading to roles in brand identity, packaging design, or art direction within advertising agencies or publishing houses. Both paths demand strong design principles but differ in skill sets, tools, and industry trends, influencing long-term growth and specialization possibilities.
Industry Trends Impacting Each Role
Digital designers are increasingly adapting to trends such as interactive media, UX/UI advancements, and responsive design, driven by the growth of mobile and web platforms. Print designers continue to focus on tactile quality, color accuracy, and branding fundamentals, influenced by limited print media demand and sustainability concerns in materials. Both roles require evolving skill sets influenced by technological innovations and shifting consumer preferences within the graphic design industry.
Choosing Between Digital and Print Design Careers
Choosing between digital and print design careers depends on expertise with software such as Adobe XD and Figma for digital, versus proficiency in Adobe InDesign and color separation techniques for print. Digital designers prioritize responsive layouts, UX/UI principles, and multimedia integration, while print designers focus on typography, CMYK color accuracy, and physical material considerations. Understanding industry demands, salary trends, and job market growth in areas like web design and publishing helps guide career decisions effectively.
Digital Designer vs Print Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com