Print designers specialize in creating visually compelling materials for physical media such as brochures, posters, and packaging, prioritizing color accuracy and resolution for high-quality prints. Digital media designers focus on crafting interactive and dynamic content for websites, social media, and apps, emphasizing user experience and screen responsiveness. Both roles require a strong grasp of design principles but apply them differently based on the medium's technical requirements and audience engagement.
Table of Comparison
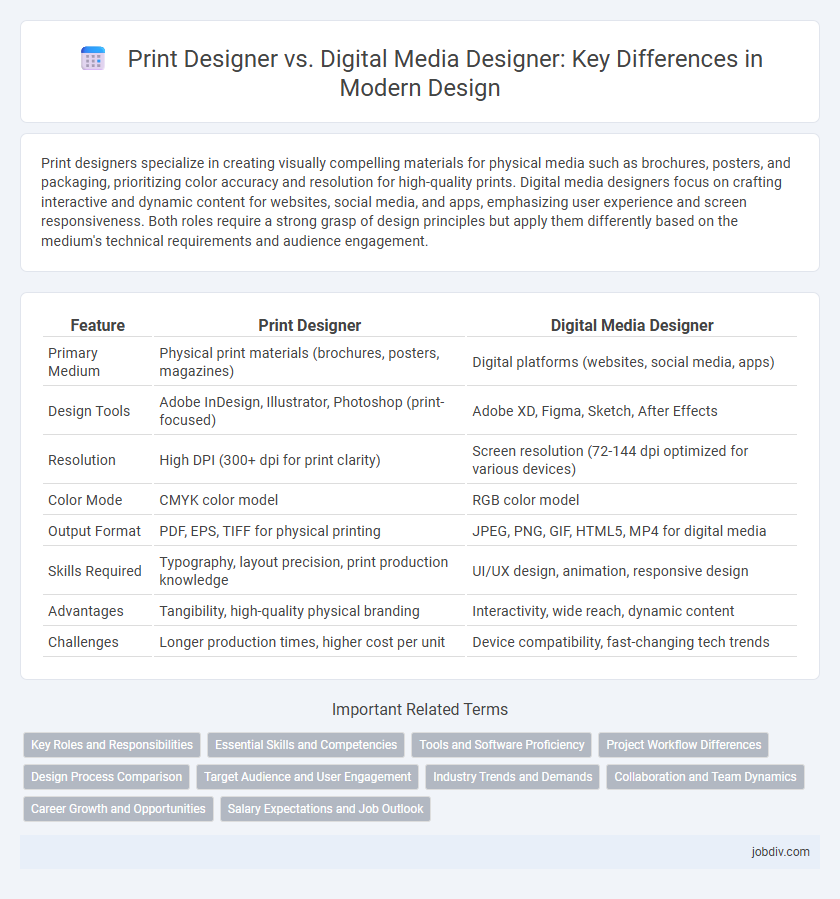
| Feature | Print Designer | Digital Media Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Physical print materials (brochures, posters, magazines) | Digital platforms (websites, social media, apps) |
| Design Tools | Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, Photoshop (print-focused) | Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch, After Effects |
| Resolution | High DPI (300+ dpi for print clarity) | Screen resolution (72-144 dpi optimized for various devices) |
| Color Mode | CMYK color model | RGB color model |
| Output Format | PDF, EPS, TIFF for physical printing | JPEG, PNG, GIF, HTML5, MP4 for digital media |
| Skills Required | Typography, layout precision, print production knowledge | UI/UX design, animation, responsive design |
| Advantages | Tangibility, high-quality physical branding | Interactivity, wide reach, dynamic content |
| Challenges | Longer production times, higher cost per unit | Device compatibility, fast-changing tech trends |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Print Designers specialize in creating visually compelling materials such as brochures, posters, and packaging, ensuring color accuracy, layout precision, and print-ready file preparation. Digital Media Designers focus on producing engaging content for online platforms, including websites, social media, and digital advertisements, emphasizing interactivity, responsiveness, and multimedia integration. Both roles require proficiency in design software, but Print Designers prioritize CMYK color models and print specifications, while Digital Media Designers optimize for RGB displays and user experience.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Print designers excel in typography, color theory, and layout skills tailored for physical media, mastering tools like Adobe InDesign and Illustrator to create high-resolution, print-ready files. Digital media designers focus on interactive design, user experience (UX), and motion graphics, utilizing software such as Adobe XD, After Effects, and web development basics to craft engaging digital content. Both roles demand strong creativity and attention to detail, but print designers prioritize print production knowledge while digital media designers require skills in responsive design and multimedia integration.
Tools and Software Proficiency
Print designers excel in tools like Adobe InDesign, Illustrator, and Photoshop, optimizing layouts for physical media such as flyers, brochures, and packaging. Digital media designers prioritize software proficiency in Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch, and After Effects, enabling responsive and interactive content creation for websites, apps, and digital platforms. Mastery of print-specific color management and resolution standards distinguishes print designers, while digital media designers leverage skills in coding basics and animation to enhance user experience.
Project Workflow Differences
Print designers follow a linear project workflow involving stages like concept development, layout design, proofing, and final printing, emphasizing color accuracy and resolution. Digital media designers adopt an iterative process prioritizing user interaction, responsive layouts, and multiple platform adaptability, often integrating real-time feedback and rapid prototyping. Collaboration in digital media projects typically involves cross-functional teams and version control tools, contrasting with the more segmented, production-focused print design workflow.
Design Process Comparison
Print designers emphasize tactile, color-accurate outputs optimized for physical materials, relying heavily on CMYK color models and resolution suited for print media. Digital media designers prioritize screen-based visuals with RGB color schemes, responsive layouts, and interactive elements that adapt across multiple devices and platforms. The design process for print involves strict prepress preparations, while digital media demands iterative prototyping, user experience testing, and continuous content updates.
Target Audience and User Engagement
Print Designers primarily target audiences who engage with tactile and visually rich materials, such as brochures, posters, and magazines, optimizing layouts for physical interaction and lasting impressions. Digital Media Designers focus on interactive content for online platforms, tailoring designs to enhance user engagement through responsive interfaces, animations, and multimedia elements. Understanding audience preferences and behavior in each medium is crucial for creating effective designs that maximize impact and user interaction.
Industry Trends and Demands
Print designers remain essential for industries valuing tactile branding experiences, with continued demand in packaging, print advertising, and publishing sectors. Digital media designers dominate markets driven by social media, web development, and app interfaces, reflecting the rise of dynamic and interactive content. Emerging trends emphasize cross-disciplinary skills, with employers seeking professionals proficient in both print and digital platforms to navigate evolving multimedia landscapes.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Print designers specialize in creating tangible materials such as brochures and posters, requiring close collaboration with printers and production teams to ensure color accuracy and material quality. Digital media designers work within dynamic teams involving developers, marketers, and UX specialists to produce interactive content optimized for various platforms. Effective collaboration in both roles depends on clear communication and an understanding of each discipline's technical constraints and creative goals.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Print designers specialize in creating visually compelling layouts for physical materials like brochures, posters, and packaging, with career growth often tied to expertise in traditional printing techniques and emerging eco-friendly materials. Digital media designers focus on interactive and dynamic content for websites, social media, and apps, benefiting from rapid expansion due to advancements in digital technology and increasing demand for UX/UI skills. Career opportunities for digital media designers tend to be broader, spanning industries such as advertising, entertainment, and tech, whereas print designers often find steady roles within publishing, branding agencies, and marketing firms.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Print designers typically earn between $45,000 and $65,000 annually, with demand gradually declining due to the shift towards digital platforms. Digital media designers command higher average salaries ranging from $55,000 to $85,000, driven by the growing need for web and social media content. Job outlook favors digital media designers, projecting a 15% growth rate over the next decade compared to a 3% decline for print design roles.
Print Designer vs Digital Media Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com