Textile designers specialize in creating fabric patterns, textures, and materials that serve as the foundation for various products, including clothing, upholstery, and home decor. Fashion designers focus on the overall garment design, combining fabrics, colors, and silhouettes to create wearable art that reflects current trends and personal style. While textile designers innovate with fabric construction and surface design, fashion designers bring those textiles to life through garment creation and styling.
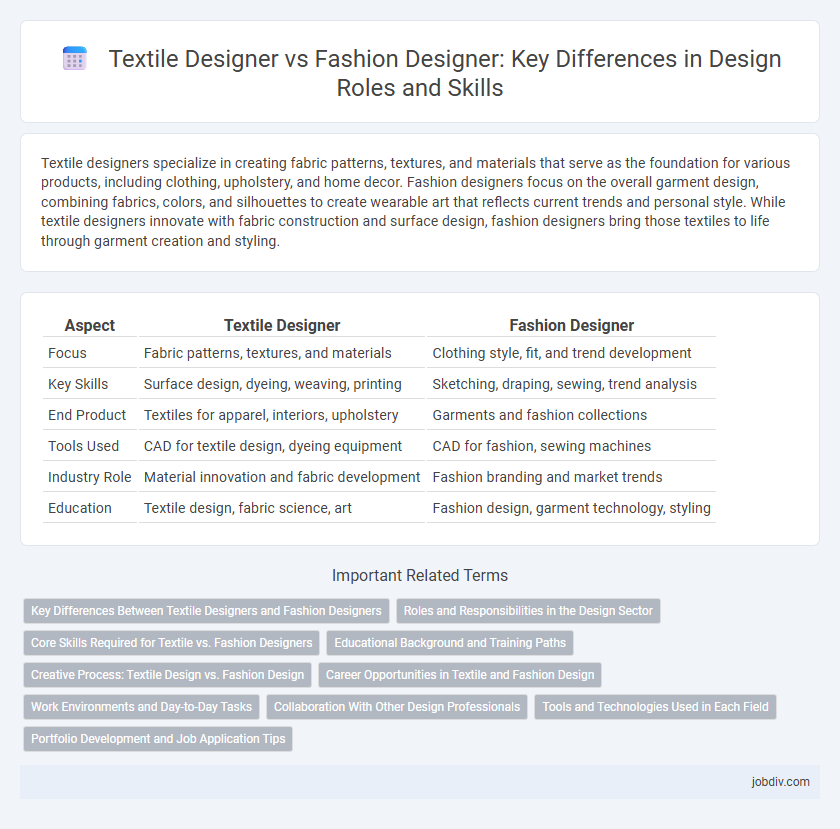
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Textile Designer | Fashion Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Fabric patterns, textures, and materials | Clothing style, fit, and trend development |
| Key Skills | Surface design, dyeing, weaving, printing | Sketching, draping, sewing, trend analysis |
| End Product | Textiles for apparel, interiors, upholstery | Garments and fashion collections |
| Tools Used | CAD for textile design, dyeing equipment | CAD for fashion, sewing machines |
| Industry Role | Material innovation and fabric development | Fashion branding and market trends |
| Education | Textile design, fabric science, art | Fashion design, garment technology, styling |
Key Differences Between Textile Designers and Fashion Designers
Textile designers create patterns, textures, and prints for fabrics used in various products, focusing on material properties and production techniques. Fashion designers use these textiles to conceptualize and construct garments, emphasizing garment aesthetics, fit, and trends. The key difference lies in textile designers working primarily with fabric development, while fashion designers focus on final clothing design and styling.
Roles and Responsibilities in the Design Sector
Textile designers specialize in creating patterns, textures, and fabric constructions, focusing on the material's aesthetics and functionality, which are crucial for manufacturing processes and product innovation. Fashion designers develop clothing and accessory concepts, emphasizing garment construction, style trends, and consumer preferences to create cohesive collections for retail markets. Both roles collaborate closely to ensure textile choices enhance the overall design vision while meeting production and market demands.
Core Skills Required for Textile vs. Fashion Designers
Textile designers require expertise in fabric construction, color theory, and pattern making, emphasizing material technology and surface design techniques to create innovative textiles. Fashion designers focus on garment construction, trend forecasting, and styling, combining creativity with technical skills in sewing, draping, and fitting to develop wearable clothing. Both roles demand strong artistic ability, knowledge of market trends, and proficiency in design software, but textile designers concentrate more on fabric development while fashion designers prioritize apparel design and consumer appeal.
Educational Background and Training Paths
Textile designers often pursue degrees in textile design, surface design, or material science, focusing on fabric creation, pattern development, and textile technology through specialized courses and technical training. Fashion designers typically earn degrees in fashion design, apparel design, or fashion merchandising, emphasizing garment construction, fashion illustration, and trend forecasting via internships and hands-on studio work. Both fields require mastery of design software, but textile designers prioritize knowledge in fiber properties and production processes, while fashion designers concentrate on garment fitting and fashion market analysis.
Creative Process: Textile Design vs. Fashion Design
Textile designers focus on creating patterns, textures, and fabric compositions that serve as foundational materials for various applications, emphasizing color theory and material innovation. Fashion designers interpret these textiles into wearable art, considering garment structure, silhouette, and consumer trends during the creative process. Both disciplines rely on iterative sketching and prototyping, but textile design prioritizes surface aesthetics while fashion design integrates these elements into finished apparel.
Career Opportunities in Textile and Fashion Design
Textile designers specialize in creating fabric patterns and textures, offering career opportunities in fabric manufacturing, interior design, and technical textiles, often collaborating with fashion brands and home furnishing companies. Fashion designers develop clothing, footwear, and accessories, leading to roles in apparel brands, fashion houses, retail merchandising, and trend forecasting. Both fields require creativity and technical skills, but textile design careers often emphasize material innovation, while fashion design careers focus more on garment construction and consumer trends.
Work Environments and Day-to-Day Tasks
Textile designers primarily create fabric patterns and textures, working in studios or manufacturing settings where they develop materials for fashion, interiors, or industrial use. Fashion designers focus on designing clothing and accessories, often collaborating in design houses, studios, or fashion brands to conceptualize collections and oversee garment production. Both roles require creativity and technical skills, but textile designers emphasize material innovation while fashion designers concentrate on garment aesthetics and market trends.
Collaboration With Other Design Professionals
Textile designers collaborate closely with fashion designers to develop innovative fabrics that complement garment construction and aesthetics. Their partnership extends to surface pattern designers and color specialists, ensuring cohesive design themes and functional materials. Coordination with textile engineers and production managers also enhances the feasibility and scalability of textile applications within fashion collections.
Tools and Technologies Used in Each Field
Textile designers primarily utilize CAD software like Textronic and Pointcarre for fabric pattern creation, alongside digital weaving and printing technologies to develop innovative textiles. Fashion designers rely on design software such as Adobe Illustrator and CLO 3D to visualize garments and streamline the prototyping process, integrating 3D modeling and virtual fitting tools. Both fields increasingly embrace sustainable technologies and smart textiles to enhance creativity and reduce environmental impact.
Portfolio Development and Job Application Tips
Textile designers should showcase fabric samples, pattern creations, and technical sketches in their portfolios to highlight expertise in material innovation and surface design. Fashion designers need to include garment construction, styling versatility, and collection concepts demonstrating their ability to translate trends into wearable art. Tailoring job applications with industry-specific keywords and emphasizing collaborative projects or internships can significantly improve hiring prospects in both fields.
Textile Designer vs Fashion Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com