Communication designers focus on creating visually engaging content that conveys a clear message to a target audience, often emphasizing branding, marketing, and user experience. Information designers specialize in organizing and presenting complex data or information in a way that is easily understandable, prioritizing clarity, structure, and usability. Both roles require a strong sense of visual hierarchy and audience awareness, but communication designers lean towards persuasive storytelling while information designers emphasize logical presentation.
Table of Comparison
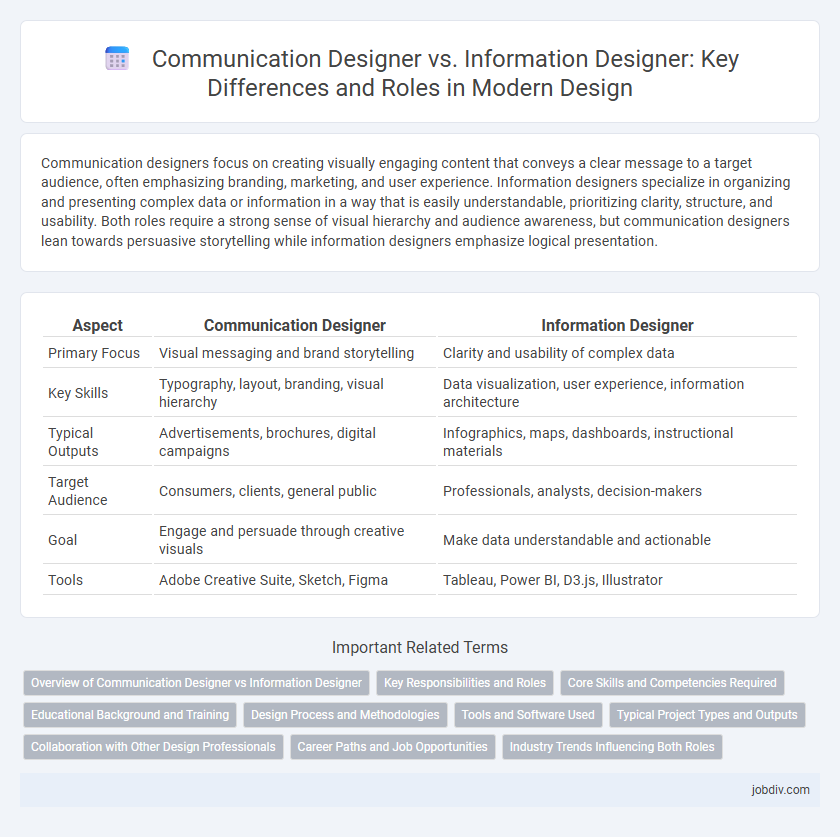
| Aspect | Communication Designer | Information Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Visual messaging and brand storytelling | Clarity and usability of complex data |
| Key Skills | Typography, layout, branding, visual hierarchy | Data visualization, user experience, information architecture |
| Typical Outputs | Advertisements, brochures, digital campaigns | Infographics, maps, dashboards, instructional materials |
| Target Audience | Consumers, clients, general public | Professionals, analysts, decision-makers |
| Goal | Engage and persuade through creative visuals | Make data understandable and actionable |
| Tools | Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch, Figma | Tableau, Power BI, D3.js, Illustrator |
Overview of Communication Designer vs Information Designer
Communication Designers specialize in crafting visual and verbal messages to engage audiences across various media, emphasizing brand identity, marketing, and user interaction. Information Designers focus on organizing and presenting complex data and information clearly and effectively, prioritizing clarity, usability, and accessibility through infographics, data visualization, and wayfinding systems. Both roles require strong design skills, but Communication Designers lean towards persuasive storytelling while Information Designers prioritize data clarity and structure.
Key Responsibilities and Roles
Communication Designers craft visual content to effectively convey messages through branding, advertising, and multimedia platforms, emphasizing aesthetics and emotional impact. Information Designers focus on organizing complex data into clear, user-friendly formats such as infographics, maps, and dashboards, prioritizing clarity and usability. Both roles require strong visual communication skills but differ in their primary objectives: persuasion and engagement versus data interpretation and accessibility.
Core Skills and Competencies Required
Communication designers excel in visual storytelling, mastering tools like Adobe Creative Suite and typography to effectively convey brand messages and marketing content. Information designers specialize in data visualization, user experience (UX) principles, and clarity in presenting complex information through infographics, dashboards, and interactive formats. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, creativity, and an understanding of audience behavior, but communication designers focus on emotional engagement while information designers prioritize clarity and usability.
Educational Background and Training
Communication designers typically hold degrees in graphic design, visual communication, or advertising, emphasizing creative skills in branding, marketing, and multimedia. Information designers often pursue education in information architecture, data visualization, or human-computer interaction, focusing on usability, user experience, and data clarity. Training for communication designers involves mastering visual storytelling and digital tools, while information designers receive specialized instruction in data analysis, cognitive psychology, and interactive design techniques.
Design Process and Methodologies
Communication designers prioritize visual storytelling by integrating graphic design, typography, and multimedia to convey messages effectively, often employing iterative prototyping and user-centered design methodologies. Information designers specialize in structuring and presenting data through clear, accessible formats such as infographics, charts, and wayfinding systems, using analytical frameworks and usability testing to enhance comprehension. Both disciplines emphasize research, audience analysis, and iterative feedback but differ in their primary focus on narrative engagement versus data clarity within the design process.
Tools and Software Used
Communication designers primarily use tools like Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign) to create visually engaging marketing materials, branding, and multimedia content, emphasizing aesthetics and message clarity. Information designers focus on data visualization software such as Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, and Adobe XD to translate complex data into clear, understandable graphics and user interfaces, prioritizing usability and data accuracy. Both disciplines increasingly integrate prototyping tools like Figma and Sketch to enhance collaboration and streamline the design process.
Typical Project Types and Outputs
Communication designers typically work on branding campaigns, advertising materials, and digital content to create visually compelling messages that engage target audiences effectively. Information designers concentrate on data visualization, wayfinding systems, and user interfaces, aiming to present complex information clearly and intuitively. Both roles produce distinct outputs: communication designers deliver logos, posters, and multimedia presentations, while information designers create infographics, diagrams, and interactive dashboards.
Collaboration with Other Design Professionals
Communication designers and information designers collaborate closely with graphic designers, user experience (UX) specialists, and content strategists to create cohesive visual narratives. Communication designers focus on visual storytelling and branding elements, while information designers prioritize clarity and usability in data presentation. This interdisciplinary teamwork ensures that design solutions are both engaging and functional across multiple platforms.
Career Paths and Job Opportunities
Communication designers focus on creating visual content to convey messages through branding, advertising, and multimedia platforms, often working in marketing agencies or corporate settings. Information designers specialize in organizing, structuring, and presenting complex data and information clearly, commonly found in sectors like government, healthcare, and data analytics firms. Career paths for communication designers tend to emphasize creativity and storytelling, while information designers require strong analytical skills and expertise in data visualization.
Industry Trends Influencing Both Roles
Communication designers increasingly integrate digital media and user experience strategies to meet evolving consumer expectations, driven by the rise of interactive platforms and social media. Information designers focus on data visualization and clarity in complex datasets, propelled by big data analytics and the demand for intuitive, actionable insights. Both roles adapt to AI-powered tools and cross-disciplinary collaboration, reshaping traditional design workflows and enhancing content delivery across industries.
Communication Designer vs Information Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com