Packaging designers concentrate on the visual and branding aspects of a product's packaging, ensuring it appeals to consumers and communicates the brand message effectively. Structural designers specialize in the engineering and functional design of the packaging, creating durable, cost-effective, and efficient structures that protect the product during shipping and handling. Collaboration between packaging and structural designers results in innovative packaging solutions that balance aesthetic appeal with practical functionality.
Table of Comparison
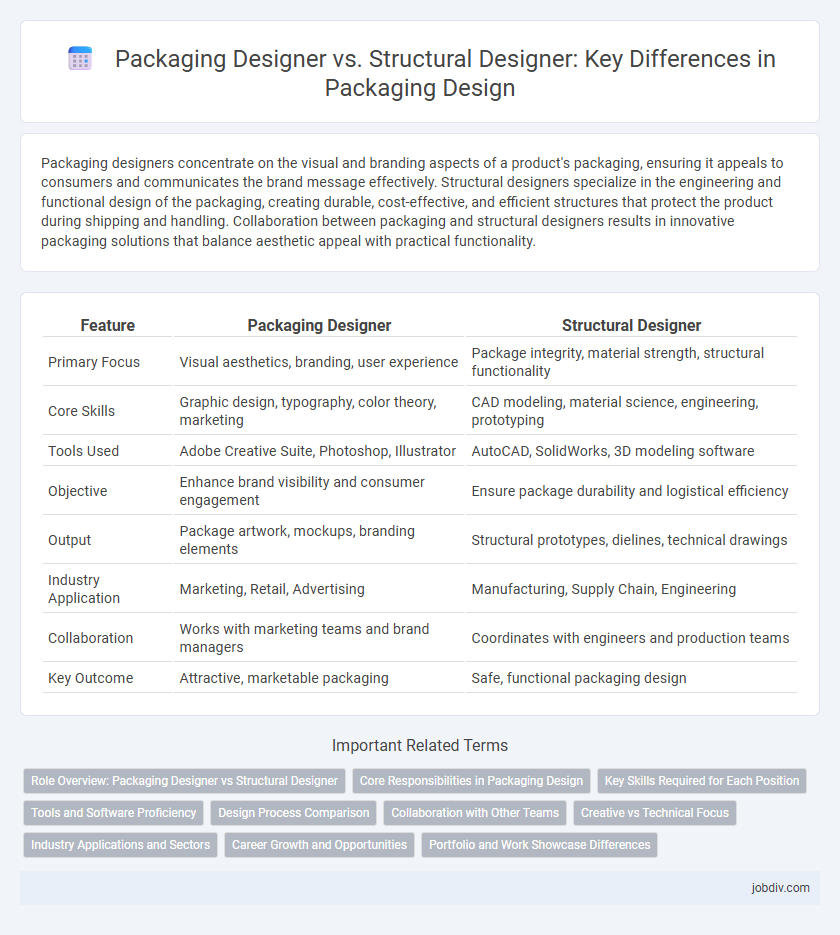
| Feature | Packaging Designer | Structural Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Visual aesthetics, branding, user experience | Package integrity, material strength, structural functionality |
| Core Skills | Graphic design, typography, color theory, marketing | CAD modeling, material science, engineering, prototyping |
| Tools Used | Adobe Creative Suite, Photoshop, Illustrator | AutoCAD, SolidWorks, 3D modeling software |
| Objective | Enhance brand visibility and consumer engagement | Ensure package durability and logistical efficiency |
| Output | Package artwork, mockups, branding elements | Structural prototypes, dielines, technical drawings |
| Industry Application | Marketing, Retail, Advertising | Manufacturing, Supply Chain, Engineering |
| Collaboration | Works with marketing teams and brand managers | Coordinates with engineers and production teams |
| Key Outcome | Attractive, marketable packaging | Safe, functional packaging design |
Role Overview: Packaging Designer vs Structural Designer
Packaging Designers concentrate on the visual aesthetics, graphic elements, and user experience of product packaging, ensuring brand consistency and consumer appeal. Structural Designers specialize in the engineering and physical construction of packaging, focusing on materials, durability, and functionality to protect the product. Both roles collaborate closely to deliver packaging that is both attractive and practical, balancing creative design with structural integrity.
Core Responsibilities in Packaging Design
Packaging Designers focus on creating visually appealing and brand-aligned graphics, typography, and overall aesthetics to enhance consumer engagement and product recognition. Structural Designers specialize in developing the physical form, ensuring the functionality, durability, and manufacturability of packaging through material selection, dielines, and folding techniques. Both roles collaborate to produce packaging solutions that are visually striking and structurally sound, optimizing protection and user experience.
Key Skills Required for Each Position
Packaging designers excel in creativity, graphic design, and brand communication, using tools like Adobe Illustrator and Photoshop to develop visually appealing packaging concepts. Structural designers focus on engineering principles, material science, and CAD software proficiency, such as AutoCAD and SolidWorks, to create functional, durable packaging structures. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities and collaboration skills, but packaging designers prioritize aesthetic innovation while structural designers emphasize technical feasibility.
Tools and Software Proficiency
Packaging designers excel in Adobe Creative Suite, focusing on Illustrator and Photoshop for visual aesthetics and brand communication, while structural designers prioritize CAD software such as AutoCAD and SolidWorks to engineer functional packaging layouts. Proficiency in 3D modeling tools like Esko ArtiosCAD is essential for structural designers to create precise dielines and prototypes, enabling efficient material usage and manufacturing feasibility. Packaging designers also leverage software for digital mock-ups and print production, ensuring a seamless transition from concept to shelf-ready product.
Design Process Comparison
Packaging designers concentrate on aesthetics, brand messaging, and consumer interaction, shaping the visual appeal and user experience. Structural designers prioritize material selection, durability, and functionality, ensuring packaging meets production requirements and protects contents effectively. The design process of packaging designers involves creative concept development and graphical layout, while structural designers focus on engineering prototypes, testing, and compliance with manufacturing standards.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Packaging designers collaborate closely with marketing and branding teams to ensure visual appeal aligns with product identity, while structural designers work with engineers and production teams to create functional, manufacturable packaging solutions. Effective communication between packaging and structural designers fosters innovation, balancing aesthetics with durability and cost-efficiency. Cross-team collaboration streamlines the development process, reducing errors and accelerating time-to-market.
Creative vs Technical Focus
Packaging designers prioritize creative elements such as visual aesthetics, branding, and user experience to ensure the packaging appeals to consumers and stands out on shelves. Structural designers focus on technical aspects including material strength, functionality, and manufacturability to create packaging that protects products and complies with industry standards. Both roles collaborate to balance innovation and practicality, optimizing packaging for market success and operational efficiency.
Industry Applications and Sectors
Packaging designers specialize in visual and brand aesthetics tailored for consumer appeal in industries like food and beverage, cosmetics, and retail, ensuring the packaging communicates product identity effectively. Structural designers focus on the engineering and physical integrity of packaging, optimizing materials and construction for sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial goods to enhance protection and functionality. Both roles intersect in sectors requiring sustainable solutions, where designers collaborate to create eco-friendly packaging that balances form and durability.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Packaging designers specialize in the visual and user experience elements of product packaging, boosting brand appeal and consumer engagement, which opens pathways into branding and marketing design roles. Structural designers focus on the engineering and physical integrity of packaging, ensuring durability and cost-effectiveness, leading to careers in materials engineering, product development, and manufacturing optimization. Both paths offer expanding opportunities due to increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions, but structural design often provides higher growth potential in industries prioritizing innovation and supply chain efficiency.
Portfolio and Work Showcase Differences
A Packaging Designer's portfolio emphasizes aesthetic appeal, branding integration, and user experience through visual mockups, dielines, and print-ready files showcasing material textures and colors. In contrast, a Structural Designer's work showcase highlights technical drawings, CAD models, prototyping details, and structural integrity analysis to demonstrate functionality, durability, and manufacturing feasibility. The Packaging Designer portfolio prioritizes creativity and market impact, while the Structural Designer portfolio focuses on engineering precision and production efficiency.
Packaging Designer vs Structural Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com