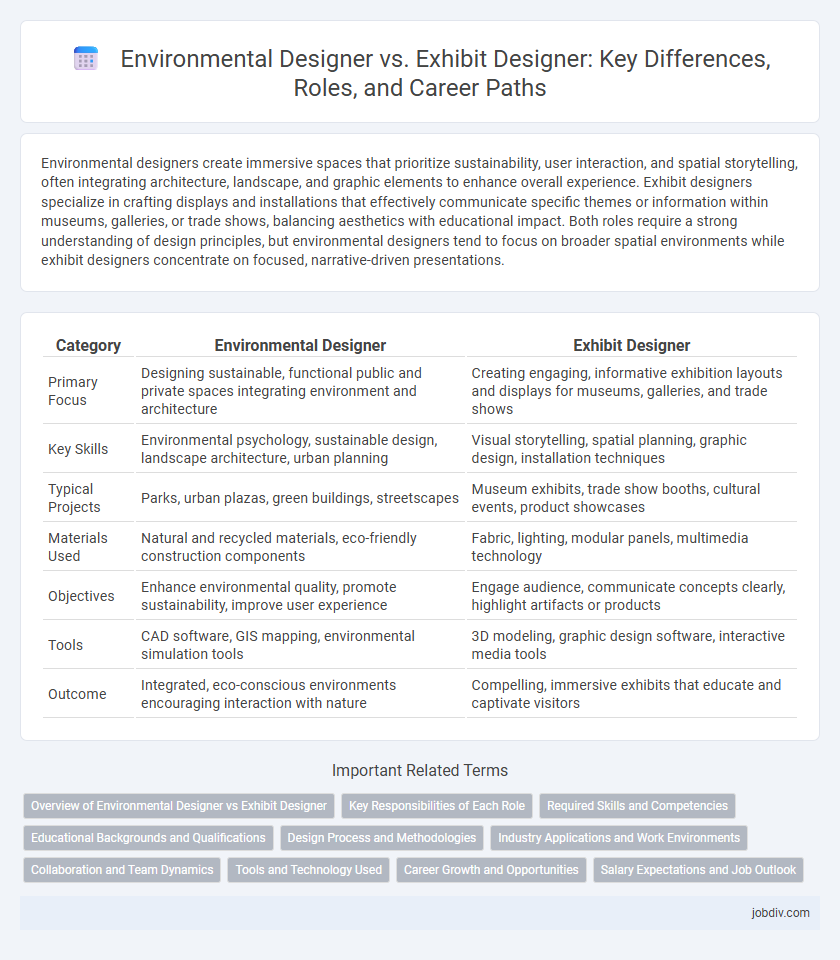
Environmental designers create immersive spaces that prioritize sustainability, user interaction, and spatial storytelling, often integrating architecture, landscape, and graphic elements to enhance overall experience. Exhibit designers specialize in crafting displays and installations that effectively communicate specific themes or information within museums, galleries, or trade shows, balancing aesthetics with educational impact. Both roles require a strong understanding of design principles, but environmental designers tend to focus on broader spatial environments while exhibit designers concentrate on focused, narrative-driven presentations.
Table of Comparison
| Category | Environmental Designer | Exhibit Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Designing sustainable, functional public and private spaces integrating environment and architecture | Creating engaging, informative exhibition layouts and displays for museums, galleries, and trade shows |
| Key Skills | Environmental psychology, sustainable design, landscape architecture, urban planning | Visual storytelling, spatial planning, graphic design, installation techniques |
| Typical Projects | Parks, urban plazas, green buildings, streetscapes | Museum exhibits, trade show booths, cultural events, product showcases |
| Materials Used | Natural and recycled materials, eco-friendly construction components | Fabric, lighting, modular panels, multimedia technology |
| Objectives | Enhance environmental quality, promote sustainability, improve user experience | Engage audience, communicate concepts clearly, highlight artifacts or products |
| Tools | CAD software, GIS mapping, environmental simulation tools | 3D modeling, graphic design software, interactive media tools |
| Outcome | Integrated, eco-conscious environments encouraging interaction with nature | Compelling, immersive exhibits that educate and captivate visitors |
Overview of Environmental Designer vs Exhibit Designer
Environmental designers specialize in creating sustainable, functional spaces that integrate natural and built environments, emphasizing environmental impact and user experience. Exhibit designers focus on crafting engaging, informative displays within museums, trade shows, and galleries, prioritizing visual storytelling and visitor interaction. Both roles require creativity and spatial awareness but differ in context, goals, and design constraints.
Key Responsibilities of Each Role
Environmental designers focus on creating functional and aesthetic spatial experiences that enhance human interaction with outdoor and indoor environments, emphasizing sustainability, ergonomics, and cultural context. Exhibit designers specialize in developing engaging and informative displays for museums, trade shows, and galleries, integrating graphic design, lighting, and interactive technology to effectively communicate themes and narratives. Both roles require collaboration with architects, engineers, and clients to ensure cohesive design solutions that meet user needs and project goals.
Required Skills and Competencies
Environmental designers require strong spatial awareness, proficiency in sustainable design principles, and expertise in materials and ecological impact assessment. Exhibit designers focus on storytelling through visual communication, mastery of graphic design tools, and skills in interactive technology integration to engage visitors. Both roles demand project management abilities and a keen understanding of user experience to create functional and impactful spaces.
Educational Backgrounds and Qualifications
Environmental designers typically possess degrees in environmental design, architecture, or urban planning, emphasizing sustainability, spatial dynamics, and ecological impact. Exhibit designers often hold qualifications in graphic design, industrial design, or museum studies, with a focus on storytelling, visitor engagement, and interactive displays. Both fields value proficiency in CAD software and 3D modeling, but their educational backgrounds highlight distinct aspects of design principles and technical expertise.
Design Process and Methodologies
Environmental designers prioritize holistic spatial planning, integrating architecture, landscape, and interior elements to create sustainable and user-centered environments. Exhibit designers focus on curating engaging, educational displays, employing storytelling techniques and visitor flow analysis to maximize interaction and comprehension. Both utilize iterative prototyping and stakeholder feedback, but environmental designers emphasize ecological impact, while exhibit designers concentrate on narrative and visual communication.
Industry Applications and Work Environments
Environmental designers focus on creating sustainable and functional spaces that enhance user interaction within natural and built environments, often working in urban planning, landscape architecture, and green building projects. Exhibit designers specialize in crafting engaging displays and interactive installations for museums, trade shows, and galleries, prioritizing visitor experience and storytelling through spatial design. Both roles require collaboration with clients and stakeholders but differ in their primary industry applications and targeted work environments--environmental designers operate in outdoor and public planning contexts, while exhibit designers work primarily within indoor settings focused on temporary or permanent displays.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Environmental designers collaborate closely with architects, engineers, and urban planners to integrate sustainable and human-centered elements into spaces, emphasizing ecological impact and user experience. Exhibit designers work alongside curators, graphic designers, and fabricators to create immersive displays that communicate narratives effectively within physical or digital environments. Both roles require strong teamwork skills, but environmental designers focus on long-term spatial functionality while exhibit designers prioritize visual storytelling and audience engagement.
Tools and Technology Used
Environmental designers use CAD software, GIS mapping tools, and sustainable materials databases to create immersive spaces that integrate architecture and landscape. Exhibit designers rely heavily on 3D modeling programs, lighting control systems, and multimedia technology to craft engaging displays and interactive visitor experiences. Both professionals leverage advanced visualization tools like VR and AR to prototype and refine their designs efficiently.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Environmental designers specialize in creating sustainable, functional spaces that enhance user experience through integration of architecture, landscape, and interior elements, offering diverse opportunities in urban planning, green building projects, and public installations with strong career growth driven by increasing environmental awareness. Exhibit designers focus on crafting engaging displays for museums, trade shows, and galleries, leveraging skills in spatial layout, storytelling, and multimedia technology, with career advancement linked to expanding sectors like experiential marketing and cultural institutions. Both roles demand creativity and technical proficiency, but environmental design generally provides broader prospects due to its impact on larger-scale public and commercial projects.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Environmental designers typically earn an average salary ranging from $55,000 to $85,000 annually, with growth driven by increasing demand for sustainable and user-centered spaces. Exhibit designers often command salaries between $50,000 and $80,000, benefiting from opportunities in museums, trade shows, and corporate presentations. Job outlook for environmental designers is strong due to rising environmental awareness and urban development, whereas exhibit designers face moderate growth influenced by cultural institutions and event industries adapting to digital integration.
Environmental Designer vs Exhibit Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com