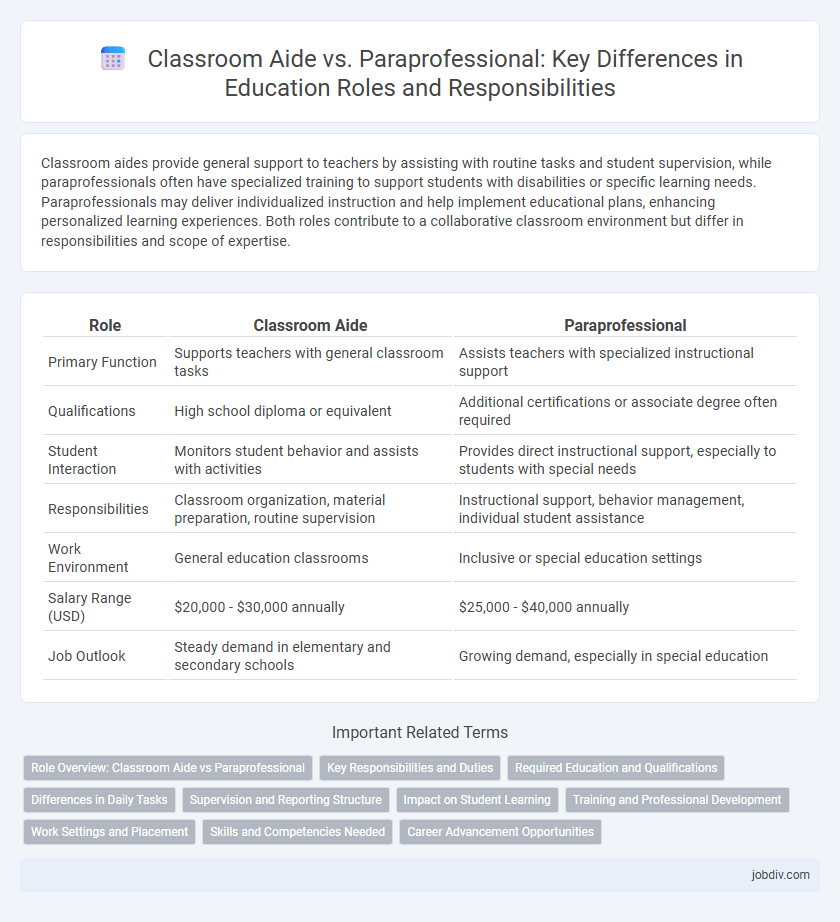
Classroom aides provide general support to teachers by assisting with routine tasks and student supervision, while paraprofessionals often have specialized training to support students with disabilities or specific learning needs. Paraprofessionals may deliver individualized instruction and help implement educational plans, enhancing personalized learning experiences. Both roles contribute to a collaborative classroom environment but differ in responsibilities and scope of expertise.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Classroom Aide | Paraprofessional |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Supports teachers with general classroom tasks | Assists teachers with specialized instructional support |
| Qualifications | High school diploma or equivalent | Additional certifications or associate degree often required |
| Student Interaction | Monitors student behavior and assists with activities | Provides direct instructional support, especially to students with special needs |
| Responsibilities | Classroom organization, material preparation, routine supervision | Instructional support, behavior management, individual student assistance |
| Work Environment | General education classrooms | Inclusive or special education settings |
| Salary Range (USD) | $20,000 - $30,000 annually | $25,000 - $40,000 annually |
| Job Outlook | Steady demand in elementary and secondary schools | Growing demand, especially in special education |
Role Overview: Classroom Aide vs Paraprofessional
Classroom aides provide direct support to lead teachers by assisting with student supervision, preparing instructional materials, and managing classroom behavior. Paraprofessionals perform more specialized instructional roles, including delivering tailored academic support, reinforcing learning concepts, and supporting students with disabilities. Both positions are essential for enhancing educational outcomes, with paraprofessionals typically requiring more formal training and certification.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Classroom aides primarily assist teachers by managing classroom activities, supporting individual students, and preparing teaching materials to enhance learning environments. Paraprofessionals perform more specialized duties such as implementing individualized education programs (IEPs), providing one-on-one support to students with disabilities, and facilitating communication between students and teachers. Both roles contribute to student success, with paraprofessionals often requiring specialized training or certification related to special education.
Required Education and Qualifications
Classroom aides typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, with some positions necessitating additional training or certification depending on state regulations. Paraprofessionals often need an associate degree or at least two years of college coursework, along with passing a state assessment or meeting federal requirements under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). Both roles demand skills in classroom management and student support, but paraprofessionals generally have more formal education and specialized qualifications.
Differences in Daily Tasks
Classroom aides primarily assist with general classroom management, such as organizing materials and helping students with routine tasks, while paraprofessionals perform more specialized instructional support, often working closely with students who have individualized education programs (IEPs). Paraprofessionals may take on responsibilities like adapting lesson plans, providing one-on-one academic assistance, and supporting behavior interventions under the supervision of certified teachers. The key difference in daily tasks lies in the level of instructional involvement and the focus on catering to diverse student needs.
Supervision and Reporting Structure
Classroom aides typically work under the direct supervision of a lead teacher, assisting with routine tasks and student support without independent decision-making authority. Paraprofessionals often have a more defined reporting structure, which may include school administrators or special education coordinators, allowing them to perform specialized instructional duties and provide targeted assistance. The supervision hierarchy distinguishes paraprofessionals as more integrated into educational planning and accountability compared to classroom aides.
Impact on Student Learning
Classroom aides provide essential support by assisting teachers with routine tasks, allowing for more individualized attention to students. Paraprofessionals often possess specialized training to deliver targeted instructional support, which directly enhances student comprehension and engagement. Their combined roles contribute significantly to creating an inclusive learning environment that addresses diverse student needs and improves academic outcomes.
Training and Professional Development
Classroom aides typically receive on-the-job training focused on basic instructional support and classroom management, while paraprofessionals undergo more formalized professional development programs, often including certifications aligned with special education or targeted intervention strategies. Paraprofessional training emphasizes skills in individualized student assistance, behavioral support, and collaboration with licensed teachers, enhancing their role in diverse learning environments. Continuous professional development opportunities for paraprofessionals contribute to improved educational outcomes and increased capacity to support students with specialized needs.
Work Settings and Placement
Classroom aides typically work under the supervision of certified teachers in general education classrooms, providing support with instructional tasks and student supervision across various grade levels. Paraprofessionals often have specialized roles in diverse educational settings, including special education classrooms, resource rooms, and inclusive environments, assisting students with disabilities and tailored learning needs. Both roles are essential for enhancing student engagement and ensuring individualized support within multiple school placement options.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Classroom aides and paraprofessionals both require strong communication, patience, and organizational skills to effectively support teachers and students. Paraprofessionals typically need more specialized competencies such as knowledge of individualized education programs (IEPs) and the ability to implement instructional strategies for students with disabilities. Proficiency in classroom management, adaptability, and collaboration with educators distinguishes the paraprofessional role from that of a general classroom aide.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Classroom aides often serve in entry-level support roles with limited responsibilities, while paraprofessionals typically have specialized training allowing for expanded duties in instructional support. Paraprofessionals have greater opportunities for career advancement, including pathways to become certified teachers or specialized educators. Investing in paraprofessional certification programs can significantly enhance career prospects in the education sector.
Classroom Aide vs Paraprofessional Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com