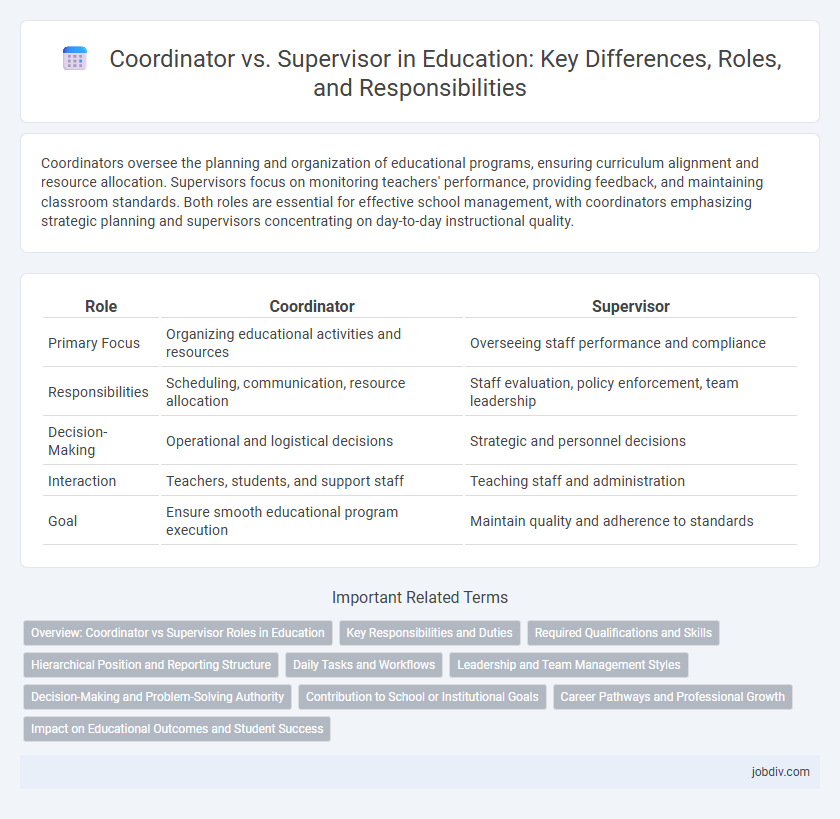
Coordinators oversee the planning and organization of educational programs, ensuring curriculum alignment and resource allocation. Supervisors focus on monitoring teachers' performance, providing feedback, and maintaining classroom standards. Both roles are essential for effective school management, with coordinators emphasizing strategic planning and supervisors concentrating on day-to-day instructional quality.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Coordinator | Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Organizing educational activities and resources | Overseeing staff performance and compliance |
| Responsibilities | Scheduling, communication, resource allocation | Staff evaluation, policy enforcement, team leadership |
| Decision-Making | Operational and logistical decisions | Strategic and personnel decisions |
| Interaction | Teachers, students, and support staff | Teaching staff and administration |
| Goal | Ensure smooth educational program execution | Maintain quality and adherence to standards |
Overview: Coordinator vs Supervisor Roles in Education
Coordinators in education focus on planning, organizing, and implementing specific academic programs or initiatives within schools or districts, ensuring curriculum alignment and resource allocation. Supervisors oversee teachers' performance, provide professional development, and evaluate instructional methods to maintain quality teaching standards. Both roles are essential for educational leadership, with coordinators emphasizing program management and supervisors concentrating on teacher support and evaluation.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Coordinators manage the organization and execution of educational programs, ensuring alignment with curriculum standards and facilitating communication between teachers, students, and administration. Supervisors oversee staff performance, conduct evaluations, and provide professional development to maintain instructional quality and adherence to school policies. Both roles require strong leadership skills but differ in scope, with coordinators focusing on program implementation and supervisors on personnel management.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Coordinators typically require strong organizational skills, proficiency in project management, and experience with curriculum development or administrative tasks, often holding a bachelor's degree in education or a related field. Supervisors need advanced leadership abilities, expertise in staff evaluation, conflict resolution, and often possess a master's degree or higher with extensive experience in educational settings. Both roles demand excellent communication skills, problem-solving capabilities, and a deep understanding of educational policies and compliance standards.
Hierarchical Position and Reporting Structure
A Coordinator typically operates at a mid-level position, managing specific projects or teams and reporting to a Supervisor or higher management. Supervisors hold a higher hierarchical role, overseeing multiple Coordinators or departments and directly reporting to senior leadership. This reporting structure ensures clear delegation of responsibilities and efficient workflow within educational institutions.
Daily Tasks and Workflows
Coordinators manage daily tasks by organizing schedules, facilitating communication between departments, and ensuring resource availability to maintain smooth educational operations. Supervisors oversee workflow by monitoring staff performance, evaluating compliance with educational standards, and providing guidance to improve teaching effectiveness. While coordinators focus on logistical support and event planning, supervisors emphasize oversight, quality control, and personnel development within educational programs.
Leadership and Team Management Styles
Coordinators often emphasize collaborative leadership, fostering teamwork by aligning individual strengths with project goals, whereas supervisors typically exercise authoritative leadership, focusing on task delegation and performance monitoring. Effective team management by coordinators involves facilitating communication and encouraging shared decision-making, while supervisors prioritize enforcing policies and maintaining workflow efficiency. Both roles require adaptive leadership styles, but coordinators lean toward inclusive strategies that enhance motivation and innovation within educational settings.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Authority
A Coordinator typically facilitates communication and organizes tasks within a team, with limited decision-making authority, primarily executing established protocols. Supervisors possess stronger decision-making and problem-solving authority, enabling them to make operational decisions, manage conflicts, and implement corrective actions to ensure team efficiency. The supervisor's role requires authoritative judgment in complex situations, while coordinators focus on logistical support and information flow.
Contribution to School or Institutional Goals
Coordinators streamline academic programs and facilitate communication between teachers and administration to enhance curriculum delivery and student performance. Supervisors oversee staff performance, ensuring compliance with school policies and maintaining educational standards to achieve institutional objectives. Both roles contribute to school goals by promoting effective teaching practices and fostering a collaborative learning environment.
Career Pathways and Professional Growth
Coordinators often focus on implementing educational programs and managing day-to-day operations, serving as a vital link between teachers and administration. Supervisors typically hold a higher level of responsibility, overseeing multiple programs or departments and making strategic decisions that shape educational outcomes. Career pathways in education usually progress from coordinator roles to supervisory positions, offering increased opportunities for leadership development and professional growth.
Impact on Educational Outcomes and Student Success
Coordinators streamline curriculum implementation and facilitate teacher collaboration, directly enhancing instructional quality and student engagement. Supervisors monitor teaching effectiveness and provide targeted feedback to improve classroom practices, which leads to higher academic performance and student success rates. Both roles contribute significantly to educational outcomes, with coordinators focusing on organizational support and supervisors emphasizing instructional leadership.
Coordinator vs Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com