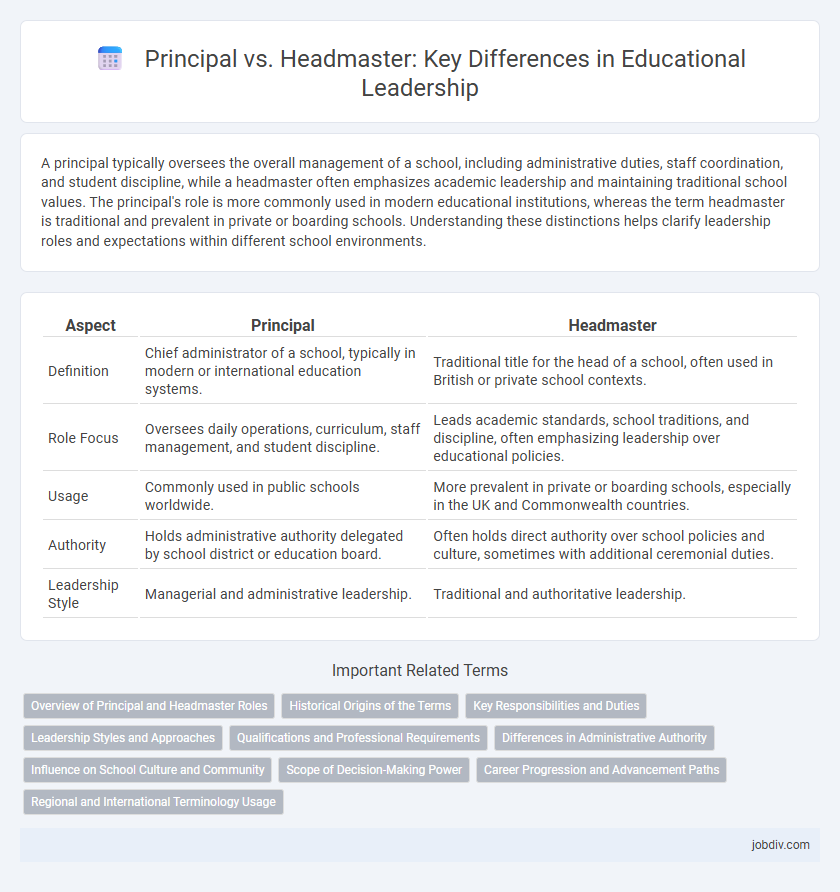
A principal typically oversees the overall management of a school, including administrative duties, staff coordination, and student discipline, while a headmaster often emphasizes academic leadership and maintaining traditional school values. The principal's role is more commonly used in modern educational institutions, whereas the term headmaster is traditional and prevalent in private or boarding schools. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify leadership roles and expectations within different school environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Principal | Headmaster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chief administrator of a school, typically in modern or international education systems. | Traditional title for the head of a school, often used in British or private school contexts. |
| Role Focus | Oversees daily operations, curriculum, staff management, and student discipline. | Leads academic standards, school traditions, and discipline, often emphasizing leadership over educational policies. |
| Usage | Commonly used in public schools worldwide. | More prevalent in private or boarding schools, especially in the UK and Commonwealth countries. |
| Authority | Holds administrative authority delegated by school district or education board. | Often holds direct authority over school policies and culture, sometimes with additional ceremonial duties. |
| Leadership Style | Managerial and administrative leadership. | Traditional and authoritative leadership. |
Overview of Principal and Headmaster Roles
The principal primarily oversees the overall administration of modern schools, focusing on instructional leadership, staff management, and policy implementation to enhance student achievement. The headmaster traditionally refers to the senior teacher or administrator in private or boarding schools, emphasizing discipline, curriculum oversight, and maintaining school traditions. Both roles involve leadership but differ in scope and institutional context, with principals often operating in public education systems and headmasters in private or specialized schools.
Historical Origins of the Terms
The term "headmaster" originated in the United Kingdom during the 16th century, traditionally referring to the male lead teacher of a school, particularly in private and grammar schools. "Principal" evolved from the Latin word "principalis," meaning chief or foremost, and became common in American English to denote the primary administrator of a school. While both titles signify leadership roles within educational institutions, "principal" increasingly reflects a modern, gender-neutral position, whereas "headmaster" retains its historical association with British schooling and often carries traditional connotations.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Principals oversee the overall management of schools, including budgeting, staff supervision, and curriculum implementation, ensuring compliance with educational standards and policies. Headmasters primarily focus on daily school operations, student discipline, and fostering a positive learning environment, often with a more hands-on approach to classroom activities. Both roles demand strong leadership, but principals typically engage more in strategic planning and community relations.
Leadership Styles and Approaches
Principals typically emphasize collaborative leadership, fostering a participative environment where teachers and staff contribute to decision-making processes, promoting innovation and community engagement. Headmasters often adopt a more authoritative leadership style, focusing on discipline, tradition, and maintaining established school policies to ensure order and academic rigor. Both roles require strong communication skills and a commitment to student success, but their leadership approaches reflect differing priorities in school management and culture.
Qualifications and Professional Requirements
Principals typically require a master's degree in education administration or leadership, along with state certification or licensure to meet professional standards. Headmasters often hold advanced degrees in education or related fields, with extensive experience in school management and sometimes additional qualifications specific to private or independent schools. Both roles demand strong leadership skills, but principals usually follow stricter regulatory frameworks tied to public education systems.
Differences in Administrative Authority
The principal holds broader administrative authority, overseeing daily school operations, managing staff, and implementing educational policies within public and private institutions. The headmaster traditionally leads private or boarding schools with a more focused role in enforcing discipline and maintaining academic standards. While principals often collaborate with district administrators, headmasters typically have more autonomous control over school governance.
Influence on School Culture and Community
Principals shape school culture through collaborative leadership and inclusive policies, fostering a positive and supportive learning environment. Headmasters often emphasize tradition and discipline, reinforcing established values that unify the school community. Both roles significantly impact student engagement and staff morale, shaping the overall identity and reputation of the institution.
Scope of Decision-Making Power
The principal holds broader decision-making authority, overseeing academic programs, staff management, budgeting, and policy implementation within modern schools. In contrast, the headmaster typically exercises more limited control, often focusing on disciplinary matters and day-to-day school operations, especially in traditional or private school settings. This distinction in scope reflects the evolving administrative roles tailored to contemporary educational demands.
Career Progression and Advancement Paths
Career progression for principals typically involves obtaining advanced degrees in educational leadership and accumulating years of teaching and administrative experience, leading to roles with broader responsibilities such as district administration or superintendent positions. Headmaster roles, often found in private or independent schools, prioritize extensive instructional leadership experience and may require deep involvement in school governance and community relations, with advancement paths including director of schools or executive roles within educational organizations. Both positions demand strong leadership skills, but principals generally follow a more standardized public education career ladder, whereas headmasters have varied advancement opportunities tied to private education networks.
Regional and International Terminology Usage
The term "Principal" is predominantly used in North America, Australia, and many international schools to describe the chief administrator of a school, while "Headmaster" or "Headmistress" remains common in the United Kingdom and some Commonwealth countries. Regional variations in terminology reflect differences in educational structures and cultural traditions, with "Headmaster" often signifying a more traditional or private school context. International schools may adopt either term depending on their cultural orientation and the educational system they follow, impacting perceptions of authority and leadership roles in education globally.
Principal vs Headmaster Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com